Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to assess the usefulness of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in diagnosis, planning of treatment methods for suspected acute septic arthritis in children, and evaluation of the clinical results of the operations with the help of magnetic resonance imaging as a diagnostic modality.
Materials and Methods
Between March 2003 and May 2007, 20 patients suspected of having acute septic arthritis of the hip underwent MRI. The mean age of the patients was 3 years and 5 months (range: 10 days-14 years). The average follow-up was 2 years and 2 months (range: 1 year-3 years 6 months). Assessment of MRI findings and final results with recurrence of the infection and post-infectious radiographic sequelae was performed retrospectively.
Results
Among the 20 cases, 17 cases(85%) showed joint effusion. Among these 17 cases, accompanying signal changes were observed in the meta-epiphyseal region in seven cases, and accompanying signal changes were observed in surrounding soft tissue in three cases. Accompanying abscess formation was observed in one case. The remaining three cases(15%), which had no joint effusion, showed an intramuscular abscess pocket around the joint, which mimicked septic arthritis. At final follow up, two cases showed unsatisfactory results, with limited joint motion and radiographic sequelae.
Conclusion
In children who are suspected of having acute septic arthritis of the hip, MRI can provide useful information about the location and extent of infection and even the differential diagnosis of acute septic arthritis. MRI was considered to be a useful method for diagnosis of suspected acute septic arthritis in children.
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 19-year-old boy with acute septic arthritis in Rt hip joint. (A) Coronal T1-weighted spin-echo MR image Siemens (IR/TE,450/11), (B) T2-weighted spin-echo MR image (3000/99), (C) fat-suppressed gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighed spin-echo MR image (735/14), demonstrate effusion in Rt hip joint and diffuse enhancement in Rt hip joint synovium. |
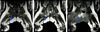 | Fig. 26-month-old girl with abscess in adductor muscle. (A) Coronal T1-weighted spin-echo MR image (TR/TE, 420/12), (B) T2-weighted spin-echo MR image (3000/99), (C) fat-suppressed gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image (616/12), demonstrate abscess pocket in adductor muscle and myositis involving adductor muscle and obturator muscle. |
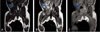 | Fig. 322-day-old girl with abscess in psoas muscle. (A) Low signal intensity mass-like lesion is seen in Coronal T1-weighted spin-echo MR image (TR/TE, 450/11), (B) T2-weighted spin-echo MR image (3000/99) shows high signal intensity fliud signal in the mass-like lesion, (C) that lesion have inhomogeneous enhancement in fat-suppressed gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image (735/14). |
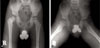 | Fig. 4(A) There was a residual deformity of right proximal femur and right acetabulum due to sequelae of septic arthritis in both hip antero-posterior, (B) frogleg lateral radiogragh. |
References
1. Betz RR, Cooperman DR, Wopperer JM, et al. Late sequelae of septic arthritis of the hip in infancy and childhood. J Pediatr Orthop. 1990. 10:365–372.

2. Kang SN, Sanghera T, Mangwani J, Paterson JM, Ramachandran M. The management of septic arthritis in children: systematic review of the English language literature. J Bone joint Surg Br. 2009. 91:1127–1133.
3. Shaw BA, Kasser JR. Acute septic arthritis in infancy and childhood. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990. (257):212–225.

4. Cooper C, Cawley MI. Bacterial arthritis in an English health district: a 10 year review. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986. 45:458–463.

5. Sultan J, Hughes PJ. Septic arthritis or transient synovitis of the hip in children: the value of clinical prediction algorithms. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010. 92:1289–1293.
6. Zawin JK, Hoffer FA, Rand FF, Teele RL. Joint effusion in children with an irritable hip: US diagnosis and aspiration. Radiology. 1993. 187:459–463.

7. Lopez M, Sauerbrei E. Septic arthritis of the hip joint: sonographic and CT findings. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1985. 36:322–324.
8. Mazur JM, Ross G, Cummings J, Hahn GA Jr, McCluskey WP. Usefulness of magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of acute musculoskeletal infections in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1995. 15:144–147.

9. Kwack KS, Cho JH, Lee JH, Oh KK, Kim SY. Septic arthritis versus transient synovitis of the hip: gadolinium-enhanced MRI finding of decreased perfusion at the femoral epiphysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007. 189:437–445.

10. Kim EY, Kwack KS, Cho JH, Lee DH, Yoon SH. Usefulness of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in differentiation between septic arthritis and transient synovitis in the hip joint. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012. 198:428–433.

11. Graif M, Schweitzer ME, Deely D, Matteucci T. The septic versus nonspecific inflamed joint: MRI characteristics. Skeletal Radiol. 1999. 28:616–620.
12. Learch TJ, Farooki S. Magnetic resonance imaging of septic arthritis. Clin Imaging. 2000. 24:236–242.

13. Modic MT, Pflanze W, Feiglin DH, Belhobek G. Magnetic resonance imaging of musculoskeletal infections. Radiol Clin North Am. 1986. 24:247–258.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download