Abstract
Purpose
To analyze, by radiograph, the difference in bone mineral density (BMD) and the proximal femoral morphology of females who are over 65 years old and have had either an intertrochanteric fracture or a femoral neck fracture.
Materials and Methods
One hundred twenty-five females over 65 years of age with femoral neck fractures or intertrochanteric fractures were examined for bone mineral density using computed tomography from April 2008 to March 2011. The bone mineral density was measured by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). The morphology of the proximal femur was also measured by computed tomography in the unaffected hip.
Results
In the femoral neck fracture group, the mean BMD value was 0.563 g/cm2 in the femoral neck region and 0.753 g/cm2 in the intertrochanteric region. In the intertrochanteric fracture group, the mean BMD value was 0.457 g/cm2 in the femoral neck region and 0.656 g/cm2 in the intertrochanteric region. There are statistically significant differences between the femoral neck fracture and intertrochanteric fracture groups (P=0.029, 0.030). The mean cortical index was 0.59 in the femoral neck fracture group and 0.51 in the intertrochanteric fracture group. There are statistical differences between the femoral neck fracture and intertrochanteric fracture groups (P=0.001).
Conclusion
The BMD of the proximal femoral neck and intertrochanteric regions of the intertrochanteric fracture group were significantly lower than that of the femoral neck fracture group. The cortical index was also significantly lower in the intertrochanteric fracture group than the femoral neck fracture group. BMD and computed tomography seem useful to check in women older than 65 who have fractures of the proximal femur.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Measurement made on computed tomography of morphologic features of the hip. Hip axis length defined as the length of head axis from the lateral aspect of the greater trochanter to the inner pelvic rim (AE), femoral neck axis length defined as the length of neck axis between the head center and the femoral medullary axis (BF), neck-shaft angle defined as the angle between femur shaft axis and femur neck axis (AFG), head offset defined as the length of head center from axis of femoral shaft. (BB').
Fig. 2
Cortical index defined as the ratio between the cortex diameter of the proximal femur and the total diameter of the proximal femur (Cortical index = (I-H)/I).
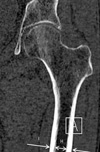
Table 1
Patient Distribution of Age, Height, Weight and BMI between Femoral Neck Fracture and Intertrochanteric Fracture Groups

Table 2
Predicting Variables and Multiple Regression Analysis Data on BMD* of Femoral Neck Fracture and Intertrochanteric Fracture Groups

References
1. Hwang KT, Yoo BW, Kim YS, Choi IY, Kim YH. Persistency and change of the bone mineral density with alendronate treatment after hip fracture. J Korean Hip Soc. 2010. 22:312–318.

2. Melton LJ 3rd, Wahner HW, Richelson LS, O'Fallon WM, Riggs BL. Osteoporosis and the risk of hip fracture. Am J Epidemiol. 1986. 124:254–261.

3. Riggs BL, Melton LJ 3rd. Evidence for two distinct syndromes of involutional osteoporosis. Am J Med. 1983. 75:899–901.

4. Cheng X, Li J, Lu Y, Keyak J, Lang T. Proximal femoral density and geometry measurements by quantitative computed tomography: association with hip fracture. Bone. 2007. 40:169–174.

5. Singh M, Nagrath AR, Maini PS. Changes in trabecular pattern of the upper end of the femur as index of osteoporosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970. 52:457–467.

6. Cameron JR, Sorenson J. Measurement of bone mineral in vivo: an improved method. Science. 1963. 142:230–232.

7. Carter DR, Hayes WC. Bone compressive strength: the influence of density and strain rate. Science. 1976. 194:1174–1176.

8. Naimark A, Kossoff J, Schepsis A. Intertrochanteric fracture: current concepts of an old subject. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979. 133:889–894.
9. Newton-John HF, Morgan DB. The loss of bone with age, osteoporosis, and fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1970. 71:229–252.
11. Johnston CC Jr, Epstein S. Clinical, biochemical, radiographic, epidemiologic, and economic features of osteoporosis. Orthop Clin North Am. 1981. 12:559–569.

13. Jang J, Kim WL, Kang SB, Lee JH, Yoon KS. The relationship of osteoporosis and hip fractures in elderly patients. J Korean Hip Soc. 2008. 20:299–304.

14. Dennison E, Mohamed MA, Cooper C. Epidemiology of osteoporosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2006. 32:617–629.

15. Cook PJ, Exton-Smith AN, Brocklehurst JC, Lempert-Barber SM. Fractured femurs, falls and bone disorders. J R Coll Physicians Lond. 1982. 16:45–49.
16. Jahng JS, Yoo JH, Sohn JS. The relationship between the fractures of the hip and the bone mineral density over fifty years. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1997. 32:46–52.

17. Suh KT, Lee SH, Cho BM. Radiological analysis of the proximal femoral morphology in normal Korean adults. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1999. 34:891–897.

18. Im GI, Lim MJ. Proximal hip geometry and hip fracture risk assessment in a Korean population. Osteoporos Int. 2011. 22:803–807.

19. Yang RS, Wang SS, Liu TK. Proximal femoral dimension in elderly Chinese women with hip fractures in Taiwan. Osteoporos Int. 1999. 10:109–113.

20. Michelotti J, Clark J. Femoral neck length and hip fracture risk. J Bone Miner Res. 1999. 14:1714–1720.

21. Glüer CC, Cummings SR, Pressman A, et al. The Study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. Prediction of hip fractures from pelvic radiographs: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 1994. 9:671–677.

22. Dretakis EK, Papakitsou E, Kontakis GM, Dretakis K, Psarakis S, Steriopoulos KA. Bone mineral density, body mass index, and hip axis length in postmenopausal cretan women with cervical and trochanteric fractures. Calcif Tissue Int. 1999. 64:257–258.

23. De Laet CE, Van Hout BA, Burger H, Weel AE, Hofman A, Pols HA. Hip fracture prediction in elderly men and women: validation in the Rotterdam study. J Bone Miner Res. 1998. 13:1587–1593.

24. Maeda Y, Sugano N, Saito M, Yonenobu K. Comparison of femoral morphology and bone mineral density between femoral neck fractures and trochanteric fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011. 469:884–889.

25. Crabtree N, Lunt M, Holt G, et al. Hip geometry, bone mineral distribution, and bone strength in European men and women: the EPOS study. Bone. 2000. 27:151–159.

26. Lotz JC, Hayes WC. The use of quantitative computed tomography to estimate risk of fracture of the hip from falls. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990. 72:689–700.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download