Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the symptoms and interference of activities of daily living (ADL) of chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) in patients receiving taxane and platinums.
Methods
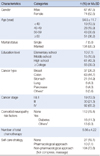
141 cancer patients were recruited in the cross-sectional survey design. The instruments used in the study was the Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy Assessment Tool (CIPNAT) developed by Tofthagen and colleagues.
Results
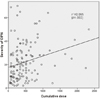
The patients experienced the symptom and interference of ADL of CIPN moderately. The most common symptom was nerve pain (70.2%) and the patients with high cumulative doses showed a significant of tingling sensation in the feet. Symptom severity increased substantially with cumulative dose of chemotherapeutic agents.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Wickham R. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a review and implications for oncology nursing practice. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2007; 11(3):361–376.

2. Armstrong T, Almadrones L, Gilbert MR. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2005; 32(2):305–311.

3. Kumar SP, Sisodia V. Chemotherapy-induced or chemotherapy-associated? Does physical therapy play a role in prevention and/or management of peripheral neurotoxicity and neuropathy? Indian J Palliat Care. 2013; 19(1):77–78.

4. Visovsky C, Collins M, Abbott L, Aschenbrenner J, Hart C. Putting evidence into practice: evidence-based interventions for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2007; 11(6):901–913.

5. Sweeney CW. Understanding peripheral neuropathy in patients with cancer: background and patient assessment. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2002; 6(3):163–166.

6. Kim IY. Review article: Management of peripheral neuropathy for cancer patients. Korean J Clin Oncol. 2011; 7(1):11–22.

7. Nurgalieva Z, Xia R, Liu CC, Burau K, Hardy D, Du XL. Risk of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in large population-based cohorts of elderly patients with breast, ovarian, and lung cancer. Am J Ther. 2010; 17(2):148–158.

8. Tanabe Y, Hashimoto K, Shimizu C, Hirakawa A, Harano K, Yunokawa M, et al. Paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2013; 18(1):132–138.

9. Kim JG, Ryu BR, Park YH, Kim BS, Choi SJ, Kim TY, et al. Cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2000; 36(5):614–621.
10. Park AR, Kim SJ, Bang JS, La HO. Oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer. Korean J Clin Pharm. 2009; 19(1):18–22.
11. Quasthoff S, Hartung HP. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Neurol. 2002; 249(1):9–17.

12. Aiello-Laws L, Reynolds J, Deizer N, Peterson M, Ameringer S, Bakitas M. Putting evidence into practice: what are the pharmacologic interventions for nociceptive and neuropathic cancer pain in adults? Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2009; 13(6):649–655.
13. Tofthagen C. Patient perceptions associated with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2010; 14(3):E22–E28.

14. Tofthagen C, Visovsky CM, Hopgood R. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: an algorithm to guide nursing management. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2013; 17(2):138–144.
15. Kwak MK, Kim EJ, Lee ER, Kwon IG, Hwang MS. Characteristics and quality of life in patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Korean Oncol Nurs. 2010; 10(2):231–239.

16. Postma T, Aaronson N, Heimans J, Muller M, Hildebrand J, Delattre J, et al. The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: The QLQCIPN20. Eur J Cancer. 2005; 41(8):1135–1139.

17. Kim JH, Choi KS, Kim TW, Hong YS. Quality of life in colorectal cancer patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Korean Oncol Nurs. 2011; 11(3):254–262.

18. Hwang WH. Assessment using CIPNAT for peripheral neuropathy in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy [dissertation]. Pusan: Kosin Univ.;2013.
19. Tofthagen C, McAllister RD, McMillan SC. Peripheral neuropathy in patients with colorectal cancer receiving oxaliplatin. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2011; 15(2):182–188.

20. Tofthagen CS, McMillan SC, Kip KE. Development and psychometric evaluation of the chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy assessment tool. Cancer Nurs. 2011; 34(4):E10–E20.

21. Lavoie Smith EM, Cohen JA, Pett MA, Beck SL. The validity of neuropathy and neuropathic pain measures in patients with cancer receiving taxanes and platinums. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2011; 38(2):133–142.

22. Kim HM. Symptoms and relief therapy related to chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with cancer [dissertation]. Daequ: Keimyung Univ.;2012.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download