Abstract
Purpose:
To investigate the effects of the intake of xylooligosaccharide-sugar mixture (XOS) on defecation frequency and symptoms in 56 young women (mean age of 22.1 years old) with constipation.
Methods:
Two experiments were conducted. In experiment 1, a randomized double-blind study was performed to evaluate the effect of 6 weeks' intake of 10 g sucrose containing 7% xylooligosaccharide or 10 g sucrose on constipation. In experiment 2, 24 g coffee mixture containing 12.8 g plant cream and 11.2 g xylooligosaccharide-sugar mixture was consumed by the subjects. During the study, the clinical efficacy was assessed by using a daily diary. The subjects indicated the number of frequencies they defecated in a day and the clinical symptom scores.
Results:
In experiment 1, the mean frequency of defecations was 2.07 in the pretreatment week and increased significantly to 4.05, 4.42, 4.84, 4.84, and 4.05 in weeks 2 to 6 of XOS intake, in comparison with the 3-3.67 with sucrose intake (sucrose, SUC). In experiment 2, the mean frequency of defecations significantly increased from 2.47 in the pretreatment week to 4.11-5.67 in weeks 1-6 of XOS intake. The occurrence of very loose or loose stools in the XOS group was significantly increased in weeks 5 and 6, compared with the pretreatment week and SUC group. XOS intake significantly alleviated the abdominal displeasure and feeling of residual stool leftness in weeks 2, 3, 5, and 6, while SUC did so in weeks 4 and 6 (p < 0.05). The coffee mixture containing xylooligosaccharide-sugar mixture reduced the abdominal displeasure and feeling of residual stool leftness from week 3 until the end of the experiment (p < 0.05).
REFERENCES
1.Johanson JF., Kralstein J. Chronic constipation: a survey of the patient perspective. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007. 25(5):599–608.

2.Kassinen A., Krogius-Kurikka L., Mäkivuokko H., Rinttilä T., Paulin L., Corander J., Malinen E., Apajalahti J., Palva A. The fecal microbiota of irritable bowel syndrome patients differs significantly from that of healthy subjects. Gastroenterology. 2007. 133(1):24–33.

3.Longstreth GF., Thompson WG., Chey WD., Houghton LA., Mearin F., Spiller RC. Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology. 2006. 130(5):1480–1491.

4.Suares NC., Ford AC. Prevalence of, and risk factors for, chronic idiopathic constipation in the community: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011. 106(9):1582–1591.

5.Sanchez MI., Bercik P. Epidemiology and burden of chronic constipation. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011. 25(Suppl B):11B–15B.

6.Nellesen D., Chawla A., Oh DL., Weissman T., Lavins BJ., Murray CW. Comorbidities in patients with irritable bowel syndrome with constipation or chronic idiopathic constipation: a review of the literature from the past decade. Postgrad Med. 2013. 125(2):40–50.

7.Gallegos-Orozco JF., Foxx-Orenstein AE., Sterler SM., Stoa JM. Chronic constipation in the elderly. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012. 107(1):18–25.

8.Nyberg C., Hendel J., Nielsen OH. The safety of osmotically acting cathartics in colonic cleansing. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. 7(10):557–564.

9.Olafsdottir LB., Gudjonsson H., Jonsdottir HH., Jonsson JS., Bjorns-son E., Thjodleifsson B. Irritable bowel syndrome: physicians' awareness and patients' experience. World J Gastroenterol. 2012. 18(28):3715–3720.

10.Hart AL., Stagg AJ., Kamm MA. Use of probiotics in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2003. 36(2):111–119.

11.Kinugasa A., Matsushita S. Effect of bifidobacterial material on abnormal evacuative symptoms. J New Rem Clin. 1993. 42:2181–2187.
12.Gibson GR., Beatty ER., Wang X., Cummings JH. Selective stimulation of bifidobacteria in the human colon by oligofructose and inulin. Gastroenterology. 1995. 108(4):975–982.

13.Ford AC., Quigley EM., Lacy BE., Lembo AJ., Saito YA., Schiller LR., Soffer EE., Spiegel BM., Moayyedi P. Efficacy of prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics in irritable bowel syndrome and chronic idiopathic constipation: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014. 109(10):1547–1561.

14.Akpinar O., Erdogan K., Bostanci S. Enzymatic production of Xylooligosaccharide from selected agricultural wastes. Food Bio-prod Process. 2009. 87(2):145–151.

15.Gibson GR., Probert HM., Loo JV., Rastall RA., Roberfroid MB. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: updating the concept of prebiotics. Nutr Res Rev. 2004. 17(2):259–275.

16.Macfarlane S., Macfarlane GT., Cummings JH. Review article: prebiotics in the gastrointestinal tract. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006. 24(5):701–714.

17.Wong JM., de Souza R., Kendall CW., Emam A., Jenkins DJ. Colonic health: fermentation and short chain fatty acids. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006. 40(3):235–243.

18.Bray GA., Nielsen SJ., Popkin BM. Consumption of high-fructose corn syrup in beverages may play a role in the epidemic of obesity. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004. 79(4):537–543.

19.Korea Rural Economic Institute. Food balance sheet 2012. Seoul: Korea Rural Economic Institute;2013.
20.Shin HL. Customer attitude survey: beverage purchasing behaviors and preference [dissertation]. Seoul: Sejong University;2009.
21.Ministry of Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Korea Agro-Fisheries and Food Trade Corporation. 2012 Processed food segments status report: coffeemix. Seoul: Korea Agro-Fisheries and Food Trade Corporation;2012.
22.Ministry of Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Korea Agro-Fisheries and Food Trade Corporation. 2013 Processed food segments status report: coffee. Seoul: Korea Agro-Fisheries and Food Trade Corporation;2013.
23.Korea Consumer Agency. A report on the comparison of the component of coffee mixtures [Internet]. Eumseong: Korea Consumer Agency;2014. [cited 2014 Jul 9]. Available from:. http://www.kca.go.kr/brd/m_32/view.do?seq=1634.
24.Malik VS., Popkin BM., Bray GA., Després JP., Hu FB. Sugar-sweetened beverages, obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cardiovascular disease risk. Circulation. 2010. 121(11):1356–1364.

25.Alonso S., Setser C. Functional replacements for sugars in foods. Trends Food Sci Technol. 1994. 5(5):139–146.

27.Tateyama I., Hashii K., Johno I., Iino T., Hirai K., Suwa Y., Kiso Y. Effect of xylooligosaccharide intake on severe constipation in pregnant women. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2005. 51(6):445–448.

28.Preston DM., Lennard-Jones JE. Severe chronic constipation of young women: 'idiopathic slow transit constipation'. Gut. 1986. 27(1):41–48.

29.Chung YC., Hsu CK., Ko CY., Chan YC. Dietary intake of xylooli-gosaccharides improves the intestinal microbiota, fecal moisture, and pH value in the elderly. Nutr Res. 2007. 27(12):756–761.

30.Okazaki M., Fujikawa S., Matsumoto N. Effect of xylooligosaccharide on the growth of bifidobacteria. Bifidobact Microflora. 1990. 9(2):77–86.

31.Iino T., Nishijima Y., Sawada S., Sasaki H., Harada H., Suwa Y., Kiso Y. Improvement of constipation by a small amount of xylooligo-saccharides ingestion in adult women. J Jpn Assoc Diet Fiber Res. 1997. 1(1):19–24.
32.gosaccharides on feces of men. Nippon Nogeikagaku Kaishi. 1991. 65(11):1651–1653.
33.Faruqui AA., Joshi C. Lactitol: a review of its use in the treatment of constipation. Int J Recent Adv Pharm Res. 2012. 2(1):1–5.
34.Dukas L., Willett WC., Giovannucci EL. Association between physical activity, fiber intake, and other lifestyle variables and constipation in a study of women. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003. 98(8):1790–1796.

35.Jones MP., Talley NJ., Nuyts G., Dubois D. Lack of objective evidence of efficacy of laxatives in chronic constipation. Dig Dis Sci. 2002. 47(10):2222–2230.
36.Zoppi G., Cinquetti M., Luciano A., Benini A., Muner A., Bertazzoni Minelli E. The intestinal ecosystem in chronic functional constipation. Acta Paediatr. 1998. 87(8):836–841.

37.Qiang X., YongLie C., QianBing W. Health benefit application of functional oligosaccharides. Carbohydr Polym. 2009. 77(3):435–441.

38.Okazaki M., Koda H., Izumi R., Fujikawa S., Matsumoto N. In vitro digestibility and in vivo utilization of xylobiose. Nihon Eiyo Shokuryo Gakkai Shi. 1991. 44(1):41–44.

39.Wintola OA., Sunmonu TO., Afolayan AJ. The effect of Aloe ferox Mill. in the treatment of loperamide-induced constipation in Wistar rats. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010. 10:95.

40.Christensen J. Chapter 39 Possible effects of laxatives on the nerve plexuses of the colon. Kamm MA, Lennard-Jones JE, editors. editors.Constipation. Petersfield: Wrightson Biomedical Pub.;1994. p. 321–326.
Fig. 1.
The effect of xylooligosaccharide -sugar mixture intake on the bowl movement frequency of the subjects. A: Weekly transition of the mean frequency of stools of the subjects. B: Weekly transition of the number of days with defecation of the subjects. ∗Significant difference between XOS and SUC groups at p < 0.05. XOS: Xylooligosaccharide containing sugar mixture group, SUC: sugar group.
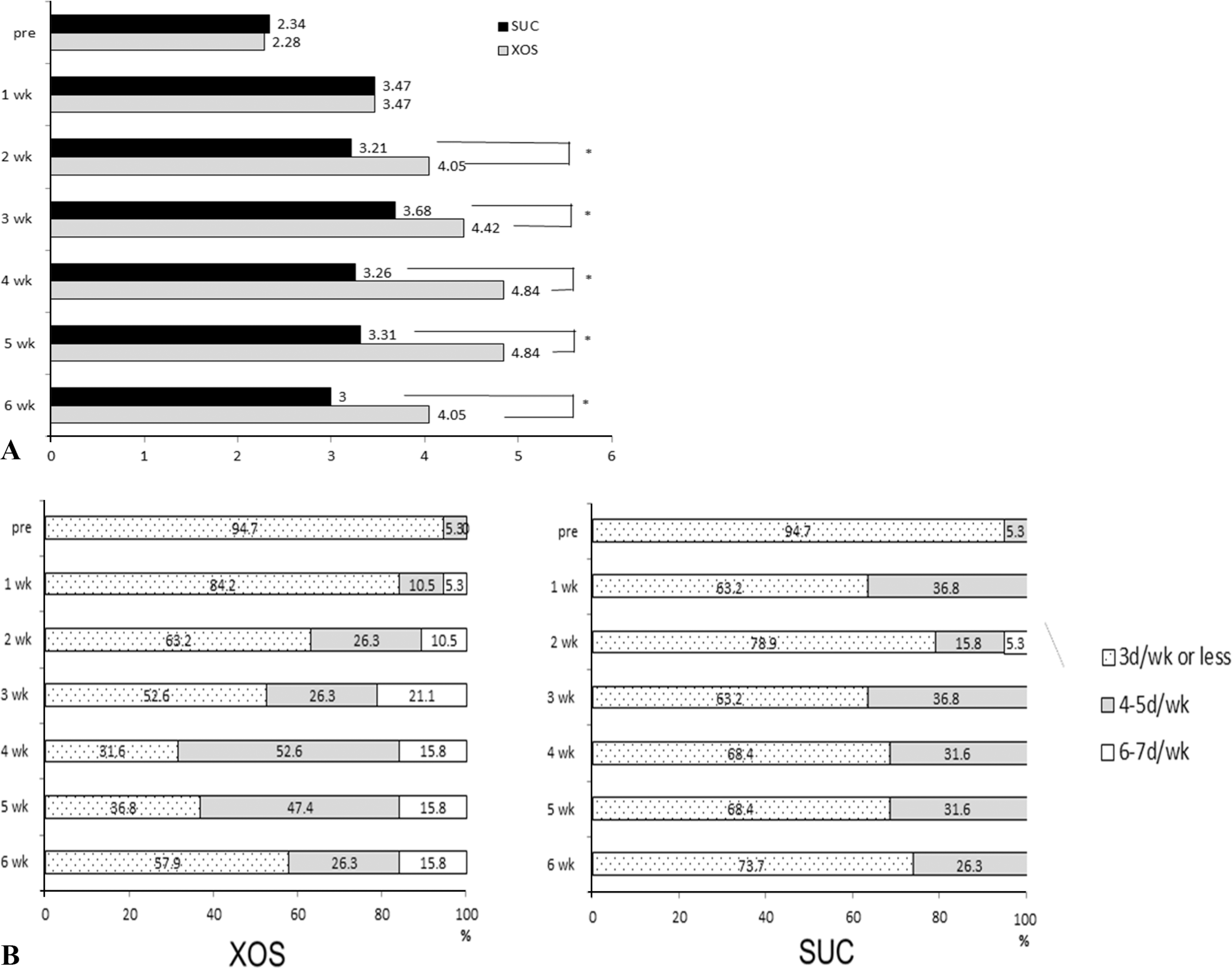
Fig. 2.
The effect of xylooligosaccharide-sugar mixture intake on the stool state of the subjects. A: Weekly transition of the subjective amount of stool. B: Weekly transition of the color of stool. C: Weekly transition of the stool consistency. †Significant difference from the pre treatment, p < 0.05. ∗Significant difference between XOS group and SUC group at the same week, p < 0.05. XOS: Xylooligosaccha-ride-sugar mixture group, SUC: sugar group.
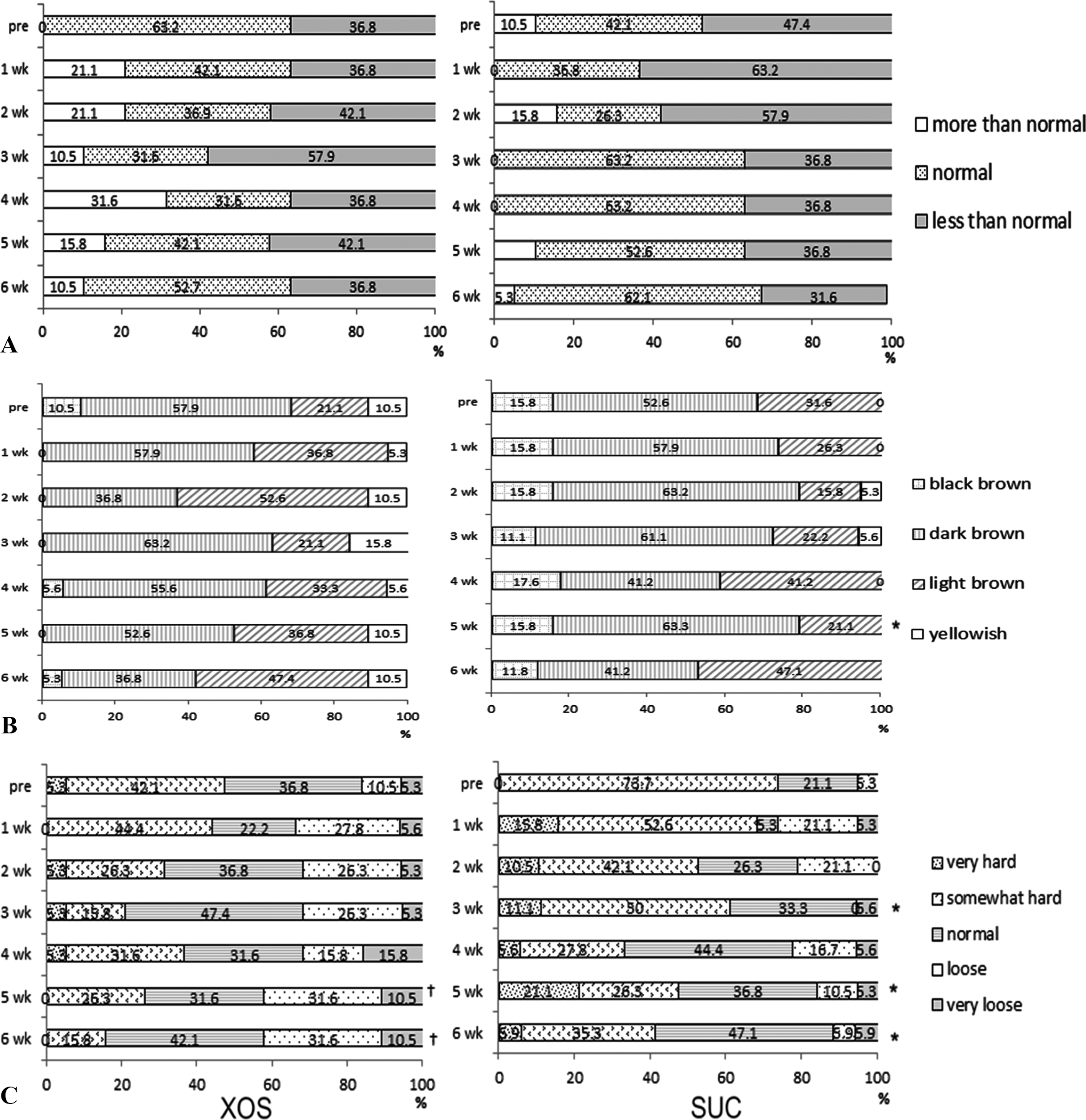
Fig. 3.
The effect of xylooligosaccharide- sugar mixture intake on abdominal state of the subjects. A: Weekly transition of the feeling of abdominal displeasure. B: Weekly transition of the feeling of residual stool leftness. †Significant difference from the pre treatment, p < 0.05. XOS: Xylooligosaccharide-sugar mixture group, SUC: sugar group.
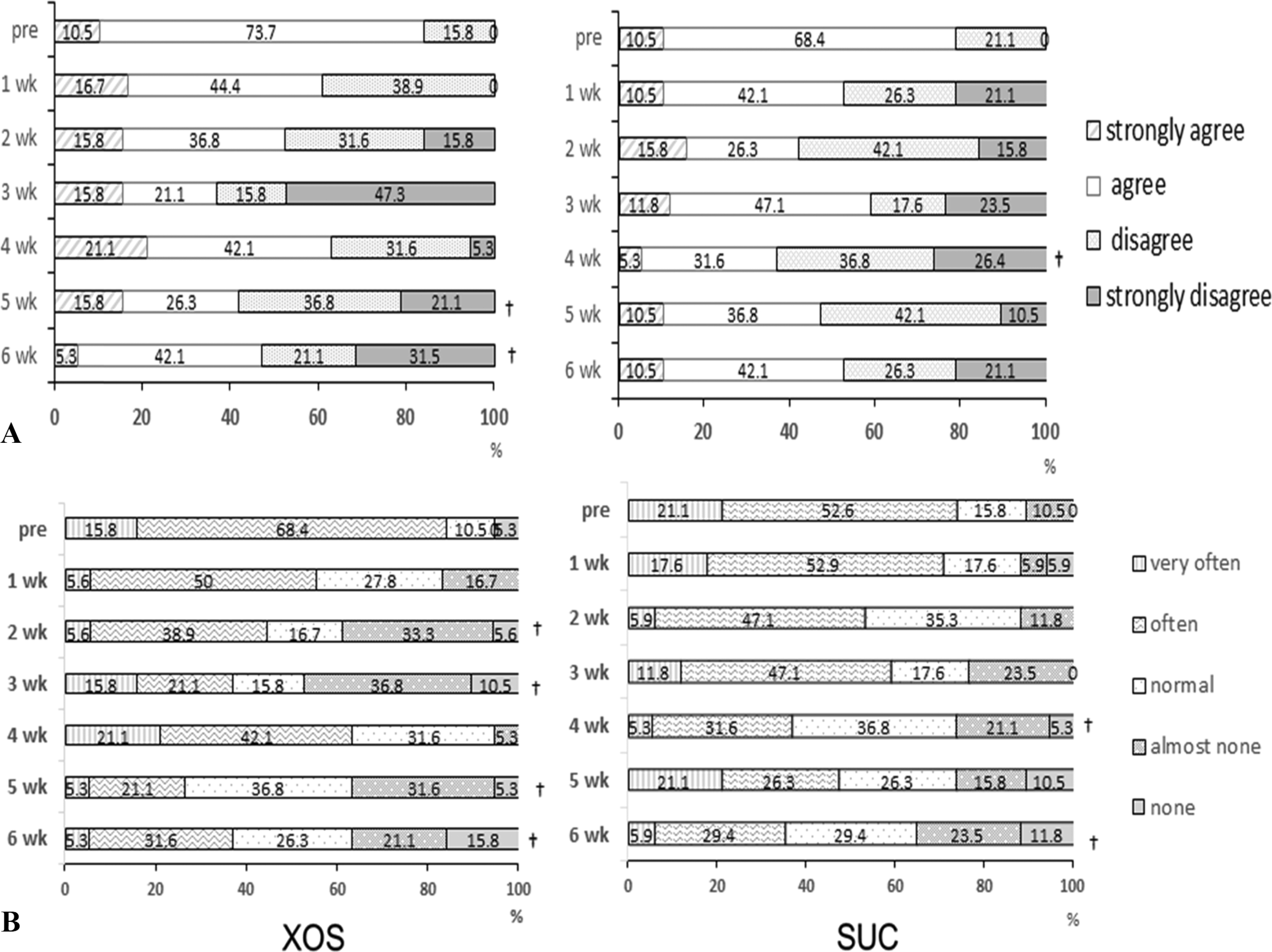
Fig. 4.
The effect of xylooligosaccharide- sugar mixture containing coffee mix intake on the bowel movement frequency of the subject. A: Weekly transition of the mean number of stools of the subjects. B: Weekly transition of the number of days with defecation of the subjects. †Significant difference from the pre treatment, p < 0.05.
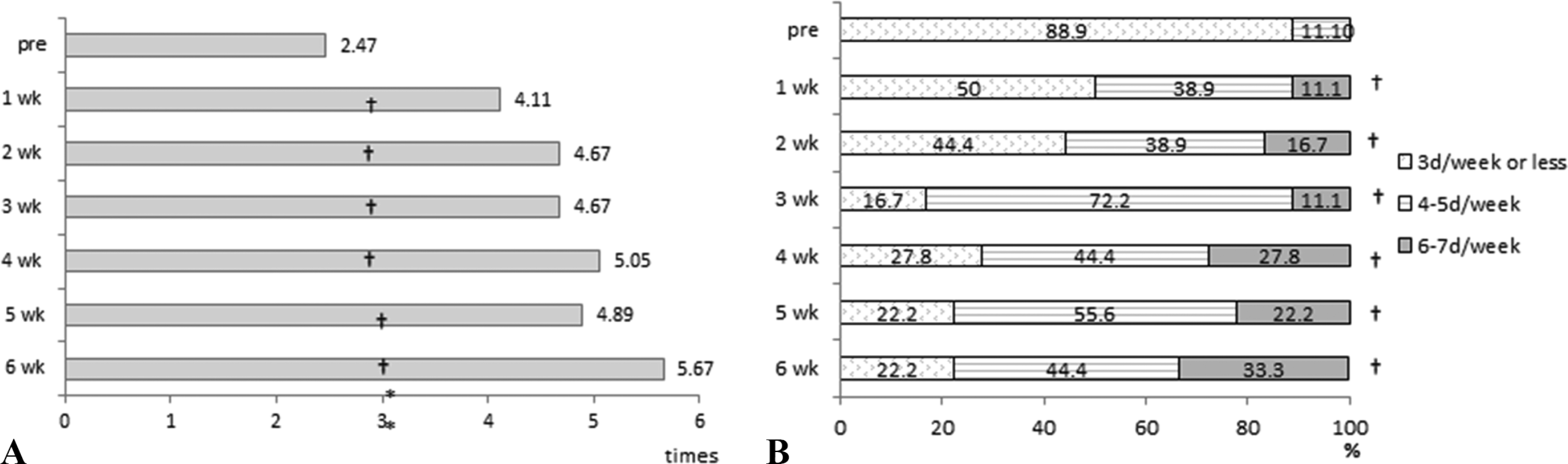
Fig. 5.
The effect of xylooligosaccharide- sugar mixture containing coffee mix intake on abdominal state of the subjects. A: Weekly transition of the feeling of abdominal displeasure. B: Weekly transition of the feeling of residual stool leftness. ∗Significant difference from the pre treatment, p < 0.05.
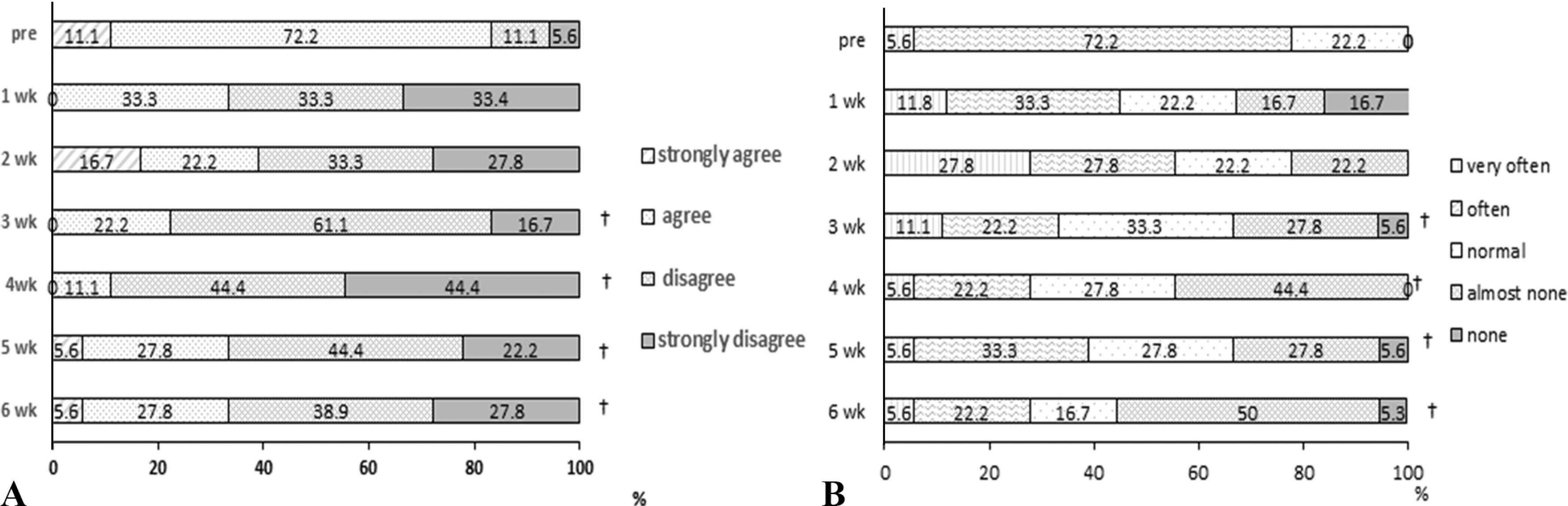
Table 1.
General characteristics and defecation state of pre treatment stage in subjects




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download