Abstract
Objective
Methods
Figures and Tables
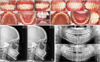 | Figure 1Case 1: Class I malocclusion with crowding. A, Pre-treatment intraoral photographs. B, Post-treatment intraoral photographs. C, Pre- (left) and post- (right) treatment lateral cephalograms. D, Pre- (upper) and post- (right) treatment panoramic radiographs. |
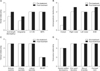 | Figure 2Changes in the scores for the dental, antero-posterior, vertical and transverse relationship criteria in Case 1.U1-SN, Upper incisor inclination to the anterior cranial base; IMPA, incisor-mandibular plane angle; ANB, Point A-nasion-Point B angle; SN-MP, mandibular plane angle to the anterior cranial base.
|
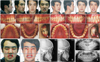 | Figure 3Case 2: skeletal Class III malocclusion. A, Pre-treatment facial and intraoral photographs. B, Post-treatment facial and intraoral photographs. C, Pre- (left) and post- (right) treatment occlusal plane cant. D, Pre- (left) and post- (right) treatment lateral cephalograms. E, Pre- (upper) and post- (lower) treatment panoramic radiographs. |
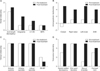 | Figure 4Changes in the scores for the dental, antero-posterior, vertical and transverse relationship criteria in Case 2.U1-SN, Upper incisor inclination to the anterior cranial base; IMPA, incisor-mandibular plane angle; ANB, Point A-nasion-Point B angle; SN-MP, mandibular plane angle to the anterior cranial base.
|
Table 2
Scoring system for the assessment of the dental relationship in the Improvement and Completion of Outcome index

ALD, Arch length discrepancy; IR, irregularity; U1-SN, upper incisor-inclination to the anterior cranial base; IMPA, incisor-mandibular plane angle.
*It is used to quantify the amount of crowding by measuring the mesio-distal width of each tooth, summing the widths of the individual teeth, and subtracting the sum from the amount of space available. A positive ALD suggests that spacing is present and is scored as −1.
†It is the sum of the number of teeth that do not follow on the line of occlusion.
‡If the inclination of the maxillary incisor is normal (Korean standard, 107.81° ± 5.94°), it indicates balance and harmony of the upper facial profile. A value > 2 standard deviation (SD) of the normal U1-SN was scored as "1"; a value between > 2 SD and > 1.5 SD of the normal U1-SN was scored as "2"; a value between < 1.5 SD and > 1 SD of the normal U1-SN was scored as "3"; a value between < 1 SD and > 0.5 SD of the normal U1-SN was scored as "4"; and a value normal U1-SN was scored as "5"
§If the position of the mandibular incisor is normal (Korean standard, 96.3° ± 6.5°), it indicates balance and harmony of the lower facial profile. A value of > 2 SD of the normal IMPA was scored as "1"; a value between < 2 SD and > 1.5 SD of the normal IMPA was scored as "2"; a value between < 1.5 SD and > 1 SD of the normal IMPA was scored as "3"; a value between < 1 SD and > 0.5 SD of the normal IMPA was scored as "4"; and a value of < 0.5 SD of the normal IMPA was scored as "5"
Table 3
Scoring system for the assessment of the antero-posterior relationship in the Improvement and Completion of Outcome index

Overjet, right molar and left molar position were assessed by using the dental model.
Point A-nasion-Point B angle (ANB) was assessed using cephalometric analysis. If its value is normal (Korean standard, 2.3° ± 1.8°), it indicates balance and harmony between the 2 jaws. A value of > 2 standard deviation (SD) of the normal ANB was scored as "1"; a value between < 2 SD and > 1.5 SD of the normal ANB was scored as "2"; a value between < 1.5 SD and > 1 SD of the normal ANB was scored as "3"; a value between < 1 SD and > 0.5 SD of the normal ANB was scored as '2'; and a value of < 0.5 SD of the normal ANB was scored as "5".
Table 4
Scoring system for the assessment of the vertical relationship in the Improvement and Completion of Outcome index

Anterior over-bite, anterior open-bite and lateral open-bite were assessed by using the dental model.
Mandibular plane angle to the anterior cranial base (SN-MP) was assessed using cephalometric analysis. Its normal value is 31.80° ± 5.53° (Korean standard). Excessively high or low SN-MP values suggest unfavorable growth patterns in individuals. A value of > 2 standard deviation (SD) of the normal SN-MP was scored as "1"; a value between < 2 SD and > 1.5 SD of the normal SN-MP was scored as "2"; a value between < 1.5 SD and > 1 SD of the normal SN-MP was scored as "3"; a value between < 1 SD and > 0.5 SD of the normal SN-MP was scored as "2"; a value of < 0.5 SD of the normal SN-MP was scored as "5".
Table 5
Scoring system for the assessment of the transverse relationship in the Improvement and Completion of Outcome index

Table 6
The Improvement and Completed of Outcome index assessment chart for evaluating the quality of orthodontic treatment outcome





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download