Abstract
Background
The introduction of rotavirus vaccines has decreased the prevalence of rotavirus infections and might have changed the distribution of rotavirus genotypes. However, neonates are not eligible for vaccination and, therefore, are at risk for rotavirus infection while in the hospital nursery or neonatal intensive care unit. Our aim was to evaluate the shift of genotypes of group A rotavirus strains among neonates cared for in two geographically distant hospitals in Korea. between 2011 and 2013.
References
1. Leshem E, Lopman B, Glass R, Gentsch J, Bányai K, Parashar U, et al. Distribution of rotavirus strains and strain-specific effectiveness of the rotavirus vaccine after its introduction: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014; 14:847–56.

3. Choe YJ, Yang JJ, Park SK, Choi EH, Lee HJ. Comparative estimation of coverage between national immunization program vaccines and non-NIP vaccines in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2013; 28:1283–8.

4. Monk HM, Motsney AJ, Wade KC. Safety of rotavirus vaccine in the NICU. Pediatrics. 2014; 133:e1555–60.

5. Ladhani SN and Ramsay ME. Timely immunisation of premature infants against rotavirus in the neonatal intensive care unit. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014; 99:F445–7.

6. Kim JS, Kim HS, Hyun J, Kim HS, Song W, Lee KM, et al. Analysis of rotavirus genotypes in Korea during 2013: an increase in the G2P[4] genotype after the introduction of rotavirus vaccines. Vaccine. 2014; 32:6396–402.

7. World Health Organization. Manual of rotavirus detection and characterization methods. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2009.
8. Agócs MM, Serhan F, Yen C, Mwenda JM, de Oliveira LH, Teleb N, et al. WHO global rotavirus surveillance network: a strategic review of the first 5 years, 2008–2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014; 63:634–7.
9. Rotavirus vaccines WHO position paper: January 2013 – Recom10. Danchin M, Kirkwood CD, Lee KJ, Bishop RF, Watts E, Justice FA, et al. Phase I trial of RV3-BB rotavirus vaccine: a human neonatal rotavirus vaccine. Vaccine. 2013; 31:2610–6.

11. Bines JE, Danchin M, Jackson P, Handley A, Watts E, Lee KJ, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of RV3-BB human neonatal rotavirus vaccine administered at birth or in infancy: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015; 15:1389–97.

12. Cowley D, Boniface K, Bogdanovic-Sakran N, Kirkwood CD, Bines JE. Rotavirus shedding following administration of RV3-BB human neonatal rotavirus vaccine. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2017; 13:1908–15.

13. Kang JO, Kim CR, Kilgore PE, Choi TY. G and P genotyping of human rotavirus isolated in a university hospital in Korea: implications for nosocomial infections. J Korean Med Sci. 2006; 21:983–8.

15. Jang SJ, Kang JO, Moon DS, Lee SH, Yeol AG, Jeong OY, et al. Comparison of clinical characteristics of patients with rotavirus gastroenteritis relative to the infecting rotavirus g-p genotype. Korean J Lab Med. 2006; 26:86–92.
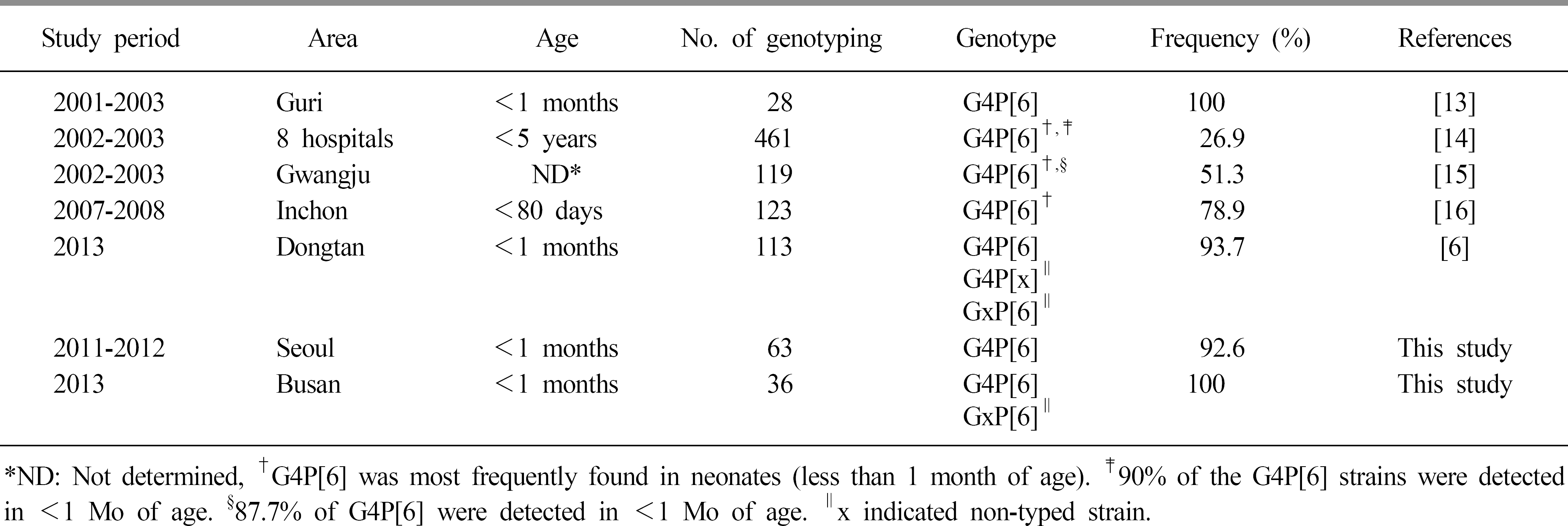
Table 1.
The genotypic distributions of rotaviruses isolated from neonates less than one month of age in this study




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download