Abstract
Background
Sequence type 131 (ST131) O25b serogroup Escherichia coli, producing CTX-M type ex-tended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL), is a major clone involved in worldwide pandemic spread in both community- and healthcare-associated infections. Recently, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) has become a routine tool for the identification of bacteria in many laboratories. This study aimed to assess the performance of MALDI-TOF MS for the screening of ESBL-producing E. coli ST131 in a rapid, inexpensive, and simple way.
Methods
A total 26 clinical E. coli, isolated from blood between 2013 and 2014, were used. The characteristics are ST131-O25b ESBL producers (n=6), ST131-O16 ESBL producers (n=4), non-ST131 ESBL producers (n=11), and non-ST131 non-ESBL producers (n=5). Specific biomarker peaks to distinguish the ST131 clonal group from others were investigated by MicroIDSys (ASTA, South Korea) and ASTA Tinker-bell 2.0 software.
Go to : 
References
1. Cantón R, González-Alba JM, Galán JC. CTX-M enzymes: origin and diffusion. Front Microbiol. 2012; 3:110.

2. Colpan A, Johnston B, Porter S, Clabots C, Anway R, Thao L, et al. Escherichia coli sequence type 131 (ST131) subclone H30 as an emergent multidrug-resistant pathogen among US veterans. Clin Infect Dis. 2013; 57:1256–65.

3. Johnson JR, Thuras P, Johnston BD, Weissman SJ, Limaye AP, Riddell K, et al. The pandemic H30 subclone of Escherichia coli sequence type 131 is associated with persistent infections and adverse outcomes independent from its multidrug resistance and associations with compromised hosts. Clin Infect Dis. 2016; 62:1529–36.
4. Institute Pasteur. Institute Pasteur MLST and whole genome MLST databases. http://bigsdb.web.pasteur.fr/[Online. ] (last visited on 11 May 2016).
5. The University of Warwick. Escherichia coli MLST database. http://mlst.ucc.ie/mlst/dbs/Ecoli. [Online] (last visited on 11 May 2016).
6. Clermont O, Bonacorsi S, Bingen E. Rapid and simple determination of the Escherichia coli phylogenetic group. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000; 66:4555–8.
7. Clermont O, Dhanji H, Upton M, Gibreel T, Fox A, Boyd D, et al. Rapid detection of the O25b-ST131 clone of Escherichia coli encompassing the CTX-M-15-producing strains. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2009; 64:274–7.

8. Johnson JR, Clermont O, Johnston B, Clabots C, Tchesnokova V, Sokurenko E, et al. Rapid and specific detection, molecular epidemiology, and experimental virulence of the O16 subgroup within Escherichia coli sequence type 131. J Clin Microbiol. 2014; 52:1358–65.

9. Price LB, Johnson JR, Aziz M, Clabots C, Johnston B, Tchesnokova V, et al. The epidemic of extended-spectrum-β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli ST131 is driven by a single highly pathogenic subclone, H30-Rx. MBio. 2013; 4:e00377–13.

10. CLSI. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; twenty-fifth informational supplement. CLSI document M100-S25. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2015.
11. Sidjabat HE, Paterson DL, Adams-Haduch JM, Ewan L, Pasculle AW, Muto CA, et al. Molecular epidemiology of CTX-M-producing Escherichia coli isolates at a tertiary medical center in western Pennsylvania. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009; 53:4733–9.
12. Tagg KA, Ginn AN, Partridge SR, Iredell JR. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry for multilocus sequence typing of Escherichia coli reveals diversity among isolates carrying bla CMY-2-like genes. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0143446.
13. Novais Â1, Sousa C, de Dios Caballero J, Fernandez-Olmos A, Lopes J, Ramos H, et al. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry as a tool for the discrimination of high-risk Escherichia coli clones from phylogenetic groups B2 (ST131) and D (ST69, ST405, ST393). Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014; 33:1391–9.

14. Nakamura A, Komatsu M, Kondo A, Ohno Y, Kohno H, Nakamura F, et al. Rapid detection of B2-ST131 clonal group of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry: discovery of a peculiar amino acid substitution in B2-ST131 clonal group. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015; 83.

Go to : 
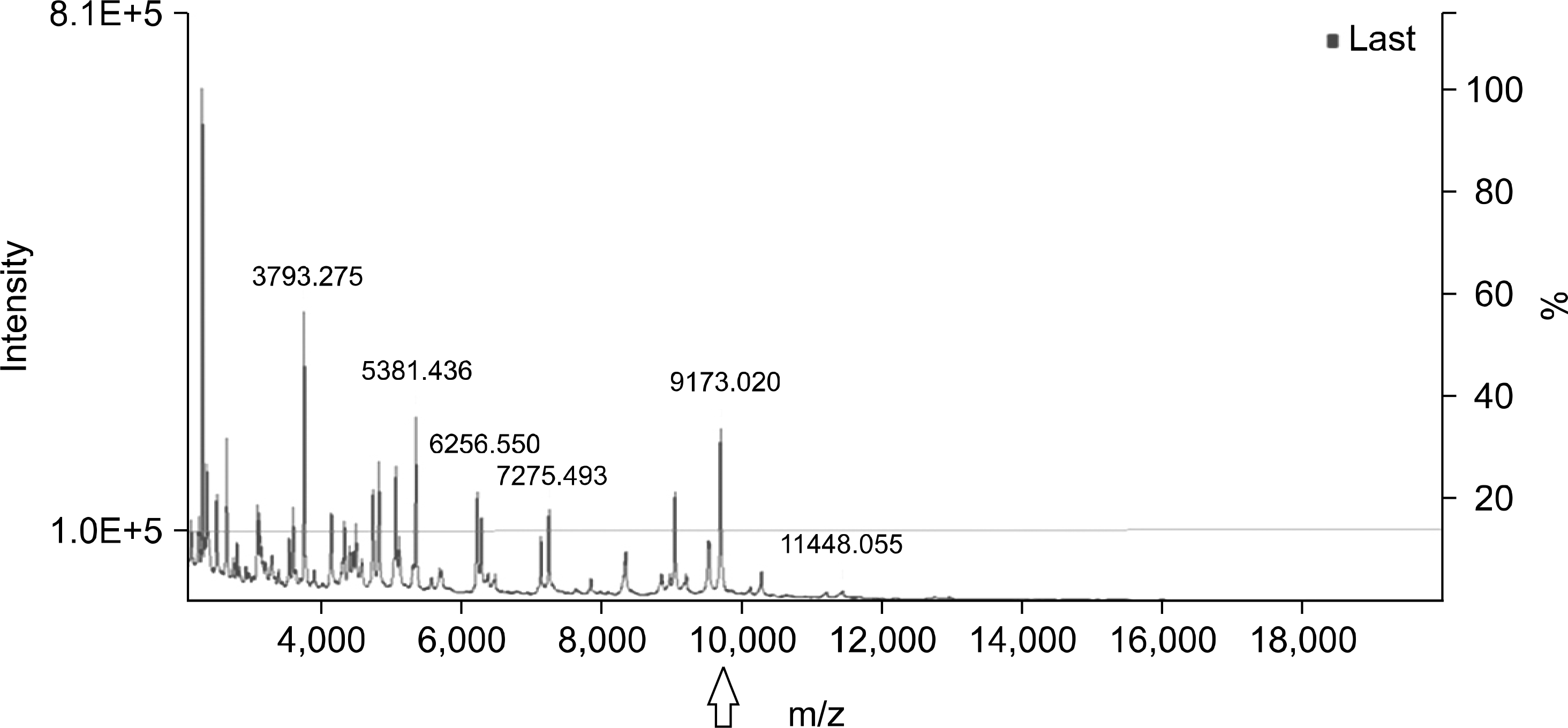 | Fig. 1.Visual inspection of 9,713 m/z for ST131 E. coli with relative intensity 15% (cutoff). Test performance: sensitivity 100%, specificity 56.2%, positive-predictive value 58.8%, and negative-predictive vale 100%. |
Table 1.
Characteristics of the 26 Escherichia coli isolates, included in this study
Table 2.
The peaks for the detection of ST131 Escherichia coli and their performances




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download