Abstract
In the RNA-based study, it is important to extract high-quality RNA. However, RNA extraction from Mycobacterium tuberculosis is problematic due to its thick, waxy cell wall rich in mycolic acid, which ren-ders the cells resistant to lysis. Using TRIzol reagent and several powerful bead-beating steps, a high qua-ntity of RNA was obtained.
References
1. World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2014. World Health Organization;2014.
2. Mangan JA, Sole KM, Mitchison DA, Butcher PD. An effective method of RNA extraction from bacteria refractory to disruption, including mycobacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997; 25:675–6.

3. Fleige S and Pfaffl MW. RNA integrity and the effect on the real-time qRT-PCR performance. Mol Aspects Med. 2006; 27:126–39.
4. Hia F, Chionh YH, Pang YL, DeMott MS, McBee ME, Dedon PC. Mycobacterial RNA isolation optimized for non-coding RNA: high fidelity isolation of 5S rRNA from Mycobacterium bovis BCG reveals novel post-transcriptional processing and a complete spectrum of modified ribonucleosides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015; 43:e32.

Fig. 1.
Ethidium bromide-stained 1% agarose gel of RNA extracted from clinical isolates of M. tuberculosis. All lanes showed 16S and 23S rRNA bands. Lanes 1 to 33: M. tuberculosis clinical isolates; lanes 25, 26 and 27 were identical isolates with lanes 19, 23 and 24 respectively.
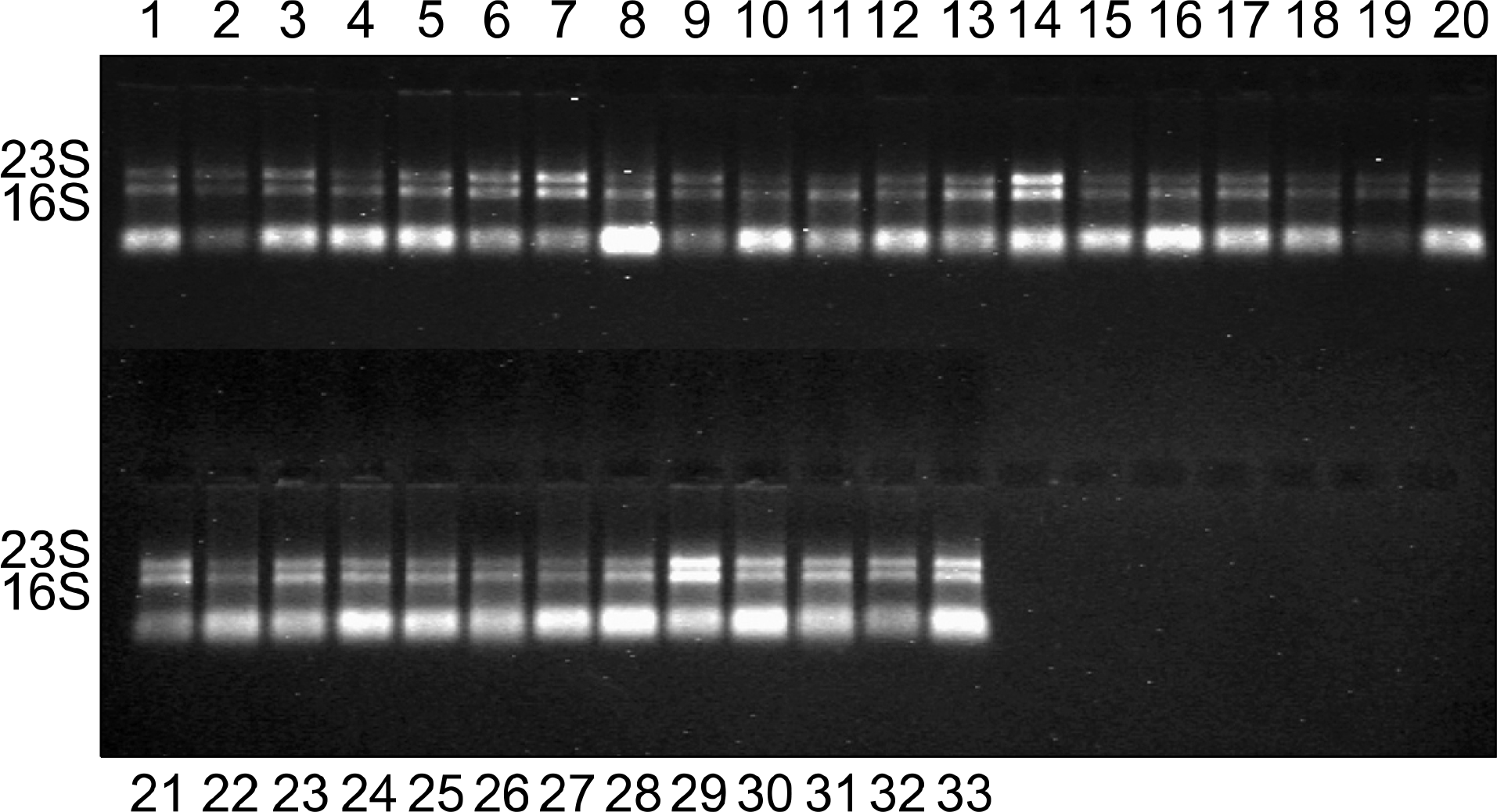
Fig. 2.
Ethidium bromide-stained 1% agarose gel of RNA extracted from M. tuberculosis clinical isolates and strain H37Rv. Lanes 2 to 5: 16S and 23S rRNA bands. Lane 1: M. tuberculosis clinical isolate grown in MGIT; Lane 2: M. tuberculosis H37Rv cultured in Enriched Middlebrook 7H9 Broth; Lanes 3 to 5: M. tuberculosis clinical isolates cultured in Enriched Middlebrook 7H9 Broth; Lanes 6 to 7: M. tuberculosis clinical isolates cultured in MGIT.
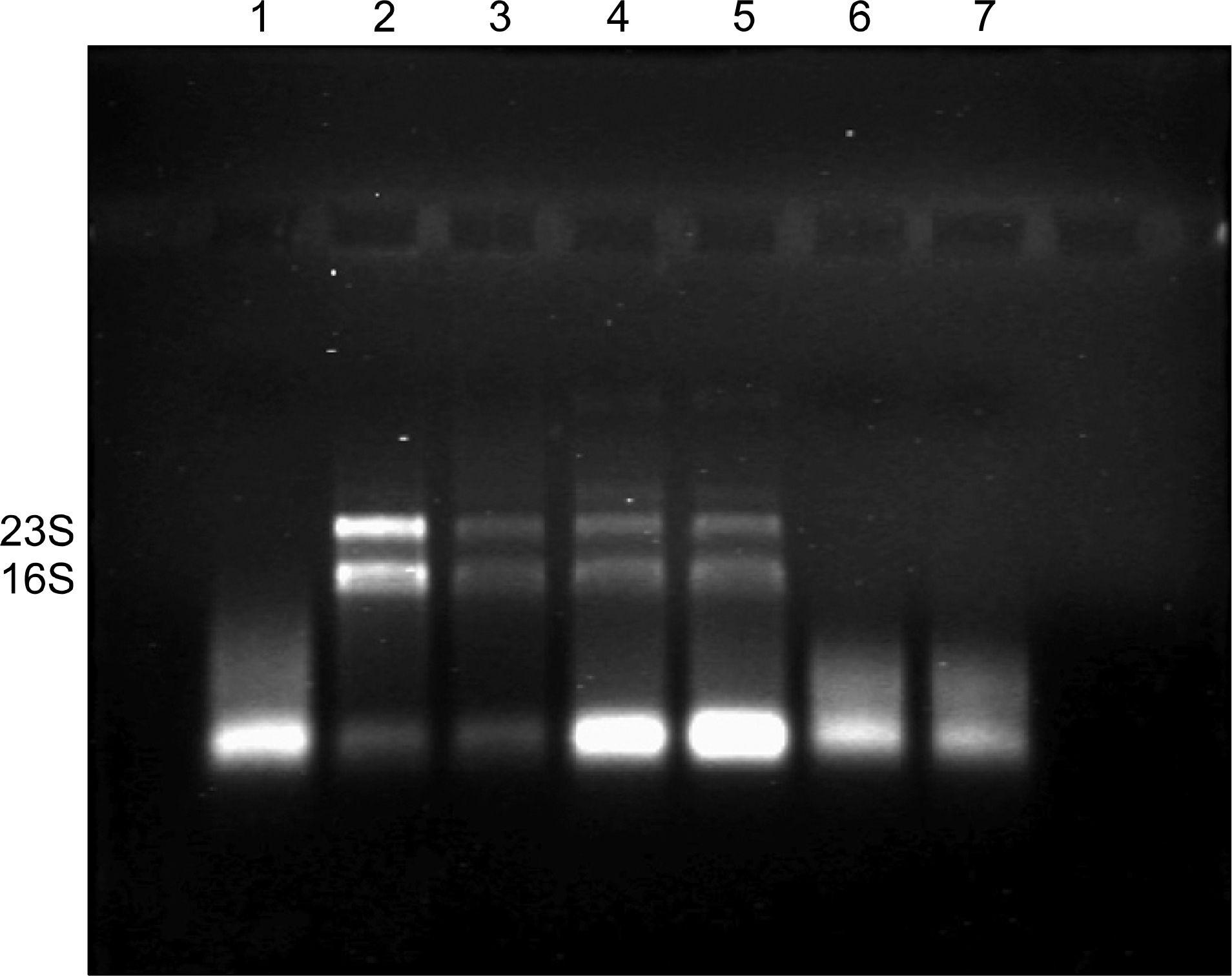
Table 1.
Flow of RNA extraction of M. tuberculosis




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download