초록
The efflux pump system has been suggested as an important mechanism in the drug resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB). In this study, molecular analysis of five genes in the efflux pump system of MTB isolates from Korean patients was performed in order to identify appropriate molecular targets. In this study, 35 culture-positive specimens were included. PCR was performed for five efflux genes, mmpL7, efpA, mmr, p55 and tap-like gene. In the 35 clinical isolates, molecular analysis of five kinds of efflux pump genes was performed. Only one clinical isolate showed negative PCR results for all five efflux pump genes. All the rest 34 isolates presented concurrent positive results for the five efflux pump genes. In the near future, gene expression study with quantitative PCR should be performed using these genes.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Soto SM. Role of efflux pumps in the antibiotic resistance of bacteria embedded in a biofilm. Virulence. 2013. 4:223–9.

2.Sarathy J., Dartois V., Dick T., Gengenbacher M. Reduced drug uptake in phenotypically resistant nutrient-starved nonreplicating Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013. 57:1648–53.
3.da Silva PE., Von Groll A., Martin A., Palomino JC. Efflux as a mechanism for drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2011. 63:1–9.
4.Balganesh M., Dinesh N., Sharma S., Kuruppath S., Nair AV., Sharma U. Efflux pumps of Mycobacterium tuberculosis play a significant role in antituberculosis activity of potential drug candidates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. 56:2643–51.
5.Escribano I., Rodríguez JC., Llorca B., García-Pachon E., Ruiz M., Royo G. Importance of the efflux pump systems in the resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to fluoroquinolones and linezolid. Chemotherapy. 2007. 53:397–401.
6.Schmalstieg AM., Srivastava S., Belkaya S., Deshpande D., Meek C., Leff R, et al. The antibiotic resistance arrow of time: efflux pump induction is a general first step in the evolution of mycobacterial drug resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. 56:4806–15.

8.Rodrigues L., Machado D., Couto I., Amaral L., Viveiros M. Contribution of efflux activity to isoniazid resistance in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Infect Genet Evol. 2012. 12:695–700.
9.Cho SY., Kim MJ., Suh JT., Lee HJ. Comparison of diagnostic performance of three real-time PCR kits for detecting Mycobacterium species. Yonsei Med J. 2011. 52:301–6.
Go to : 
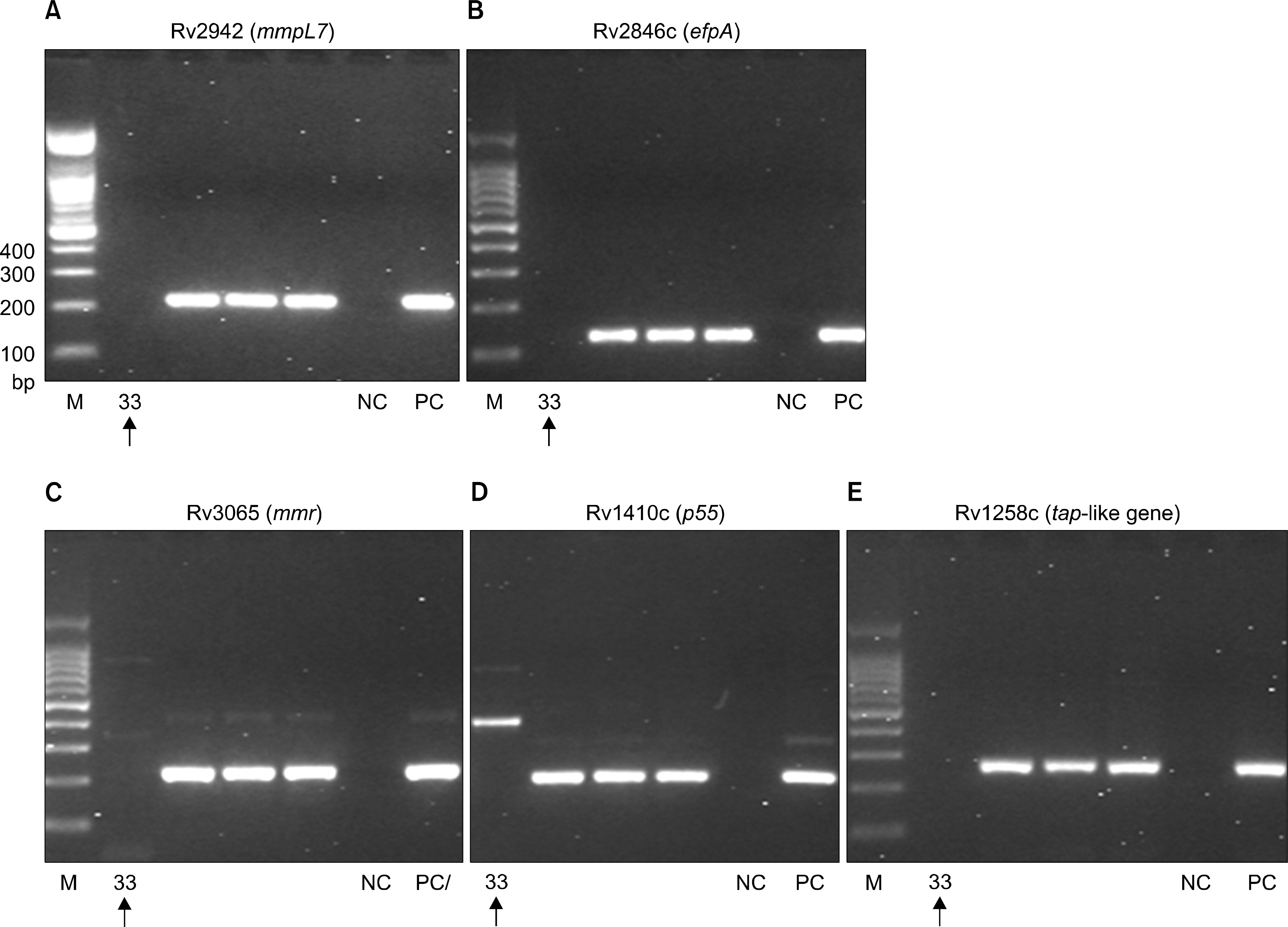 | Fig. 1.Molecular analysis of efflux pump genes in clinical specimens of Korean patients. In total 35 specimens showing the positivity for M. tuberculosis, only one clinical strain shows negative results in all of 5 kinds of efflux pump gene PCR (specimen serial number 33, arrows). The rest of strains present positive results in 5 efflux pump genes, simultaneously. M, size marker; NC, negative control; PC, positive control. |
Table 1.
Primers for molecular analysis in 5 efflux pump genes
Table 2.
Characteristics of 35 clinical isolates in this study




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download