초록
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae is a Gram-positive bacillus that causes infections primarily in animals. In humans, the bacteria usually cause localized or generalized cuta-neous infections. A 75-year-old man with chronic alcohol-ism presented with abdominal pain. Abdominal computed tomography and laboratory findings suggested an intra-abdominal abscess in the periaortic soft tissue. While no definitive infectious source was identified, E. rhusiopathiae was identified by 16S rRNA-based gene sequencing from culture-negative, periaortic necrotic tissue, subsequent to empiric antibiotic treatment. It is suggested that E. rhusiopathiae has the potential to cause intra-abdominal abscesses. This case report highlights the usefulness of DNA sequencing to identify pathogens in patients pretreated with antibiotics.
REFERENCES
1. Reboli AC, Farrar WE. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: an occupational pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1989; 2:354–9.

3. Brooke CJ, Riley TV. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae: bacteriol-ogy, epidemiology and clinical manifestations of an occupational pathogen. J Med Microbiol. 1999; 48:789–99.

4. Reboli AC. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Mandell GL, Bennett JE, editors. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone;2010:p. 2733–5.
5. Hocqueloux L, Poisson DM, Sunder S, Guilbert S, Prazuck T. Septic arthritis caused by Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in a pros-thetic knee joint. J Clin Microbiol. 2010; 48:333–5.
6. Kim SR, Kwon MJ, Lee JH, Lee NY. Chronic meningitis caused by Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. J Med Microbiol. 2007; 56:1405–6.
7. Joo EJ, Kang CI, Kim WS, Lee NY, Chung DR, Peck KR, et al. Acute meningitis as an initial manifestation of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae endocarditis. J Infect Chemother. 2011; 17:703–5.
8. Meric M, Ozcan SK. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae pneumonia in an immunocompetent patient. J Med Microbiol. 2012; 61:450–1.

9. Feasi M, Bacigalupo L, Cappato S, Pontali E, Usiglio D, Rollandi GA, et al. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae intra-abdominal abscess. Int J Infect Dis. 2010; 14:e81–3.
10. Fredricks DN, Relman DA. Application of polymerase chain reaction to the diagnosis of infectious diseases. Clin Infect Dis. 1999; 29:475–86. quiz. 487–8.

11. Rantakokko-Jalava K, Nikkari S, Jalava J, Eerola E, Skurnik M, Meurman O, et al. Direct amplification of rRNA genes in diagnosis of bacterial infections. J Clin Microbiol. 2000; 38:32–9.

12. Fenollar F, Roux V, Stein A, Drancourt M, Raoult D. Analysis of 525 samples to determine the usefulness of PCR amplification and sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene for diagnosis of bone and joint infections. J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 44:1018–28.

13. Rampini SK, Bloemberg GV, Keller PM, Büchler AC, Dollenmaier G, Speck RF, et al. Broad-range 16S rRNA gene polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of culture-negative bacterial infections. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 53:1245–51.

14. Schuster MG, Brennan PJ, Edelstein P. Persistent bacteremia with Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in a hospitalized patient. Clin Infect Dis. 1993; 17:783–4.
15. Venditti M, Gelfusa V, Tarasi A, Brandimarte C, Serra P. Antimicrobial susceptibilities of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. An-timicrob Agents Chemother. 1990; 34:2038–40.
Fig. 1.
Abdominal computed tomography scan showing soft tissue infiltration and ischemic lesions around the aorta (arrow).
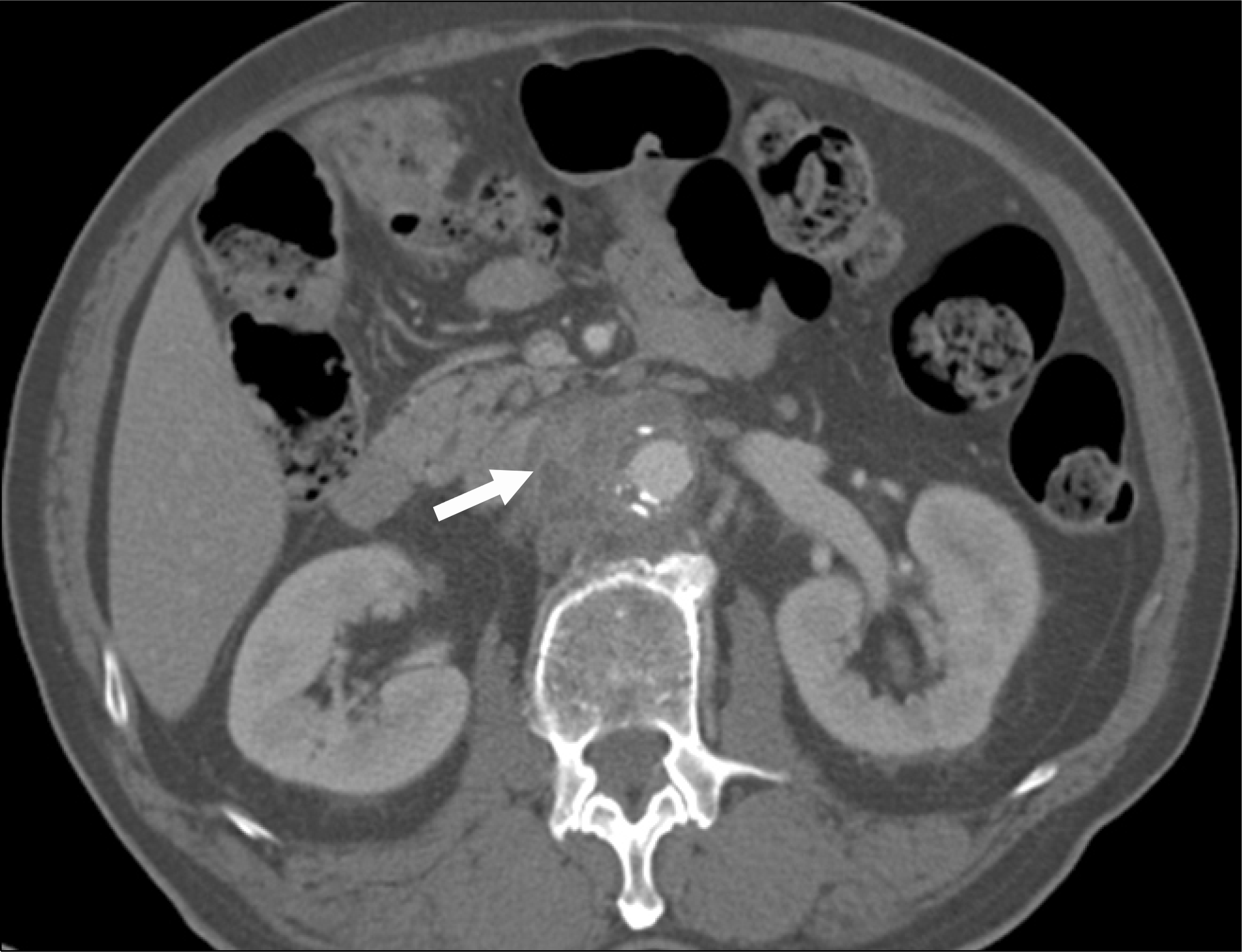
Table 1.
Primers used in this study for a semi-nested PCR for bacterial 16S rRNA gene




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download