초록
Background
The prestorage condition of blood culture bottles prior to entering the automated blood culture system may affect the time to detection (TTD) of microorganisms and the final report days.
Methods
We compared the TTD and final report days according to the preincubation conditions after laboratory operating hours: room temperature (RT) vs. a BacT/Alert unit (BioMerieux Inc.) for 3 months respectively. All bottles were inserted into the main BacT/Alert system the next morning.
Results
TTD was significantly reduced by preincubating bottles in a BacT/Alert unit (median, 8.4 h) compared to prestorage at RT (median, 12.4 h) (P< 0.001). The final report of bacterial identification and drug susceptibility within 2 days was available for 24.4% of bottles preincubated in a BacT/Alert unit compared to 14.9% of those incubated at RT. The false positive results were significantly higher for preincubation in a BacT/Alert unit (0.81%) than for that (0.29%) at RT (P<0.001).
Conclusion
If a clinical microbiology laboratory is not operational for 24 hours, an automated blood culture unit might be a good alternative to reduce TTD and allow the submission of a faster final report compared to prestorage at RT. However, false positive readings increased more than two-fold by preincubation in a BacT/Alert unit.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Seegmüller I., Eschenbach U., Kamereck K., Miethke T. Sensitivity of the BacT/ALERT FA-medium for detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in preincubated blood cultures and its temperature- dependence. J Med Microbiol. 2004. 53:869–74.
2.Koh EH., Lee DH., Kim S. Effects of preincubating blood culture bottles at 37°C during the night shift and of collected blood vol-ume on time to detection and days to final report. Ann Clin Microbiol. 2014. 17:14–9.
3.CLSI. Principles and procedures for blood cultures; approved guidline. CLSI document M47-A. Wayne, PA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2007.
4.van der Velden LB., Vos FJ., Mouton JW., Sturm PD. Clinical im-pact of preincubation of blood cultures at 37°C. J Clin Microbiol. 2011. 49:275–80.

5.Kerremans JJ., van der Bij AK., Goessens W., Verbrugh HA., Vos MC. Immediate incubation of blood cultures outside routine laboratory hours of operation accelerates antibiotic switching. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. 47:3520–3.

6.Saito T., Iinuma Y., Takakura S., Nagao M., Matsushima A., Shirano M, et al. Delayed insertion of blood culture bottles into automated continuously monitoring blood culture systems increases the time from blood sample collection to the detection of microorganisms in bacteremic patients. J Infect Chemother. 2009. 15:49–53.

7.Janapatla RP., Yan JJ., Chien ML., Chen HM., Wu HM., Wu JJ. Effect of overnight storage of blood culture bottles on bacterial detection time in the BACTEC 9240 blood culture system. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2010. 43:126–32.

8.Lee DH., Koh EH., Choi SR., Kim S. Growth dynamics of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a function of time to detection in BacT/alert 3D blood culture bottles with various preincubation conditions. Ann Lab Med. 2013. 33:406–9.
Go to : 
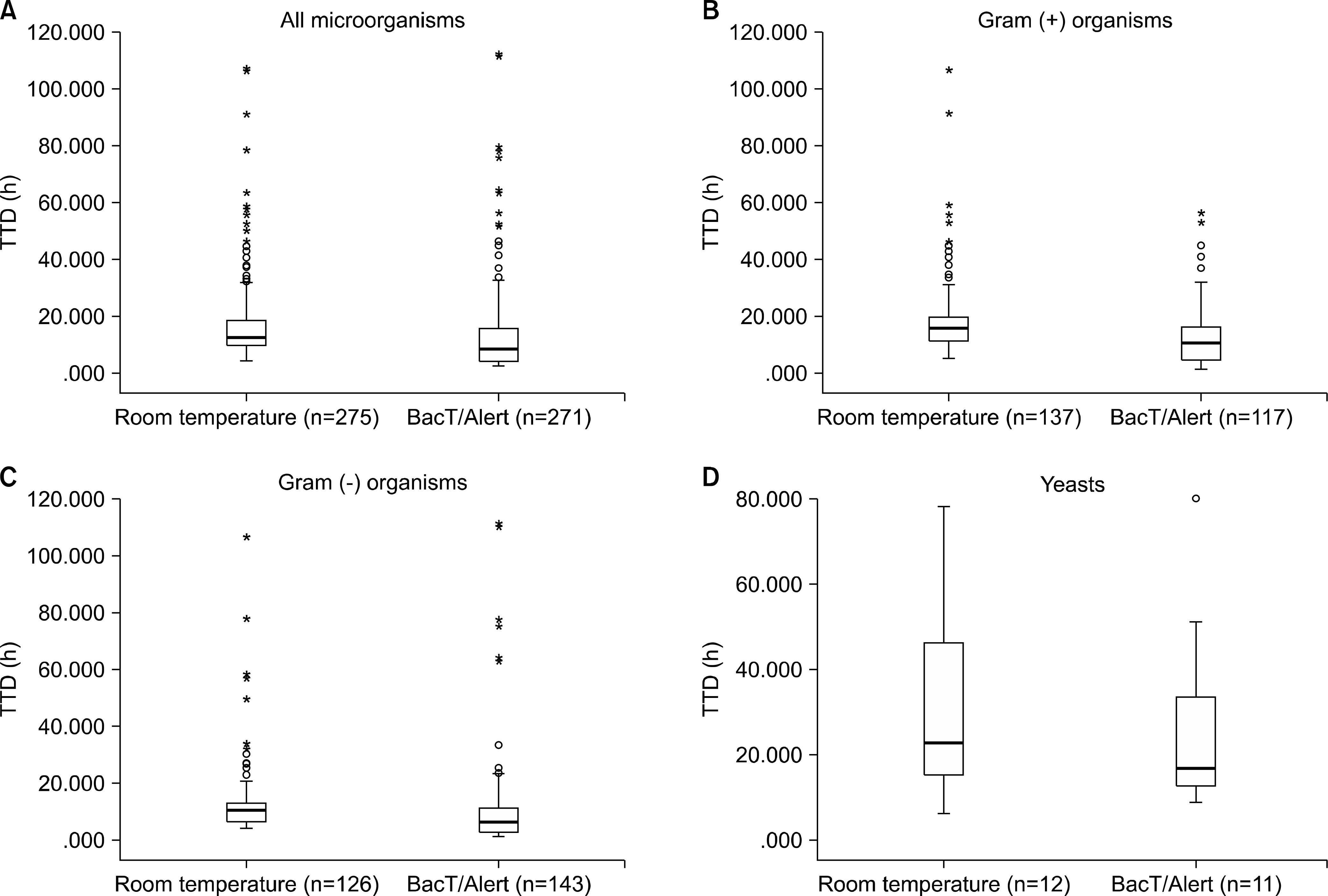 | Fig. 1.Comparison of time to detection (TTD) of (A) all microorganisms, (B) Gram (+) organisms, (C) Gram (-) organisms, and (D) yeasts according to prestorage of blood culture bottles at room temperature and in a BacT/Alert unit outside laboratory operating hours. P<0.001 in (A), (B), and (C) by Mann-Whitney U test. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download