Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to identify the levels of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy (OXLIPN) and the quality of life (QOL) related to OXLIPN in patients with digestive system cancer.
Methods
A total of 83 patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN)-related symptoms participated in this study. Data were collected through self-reported questionnaire which were constructed to include general and clinical characteristics, EORTC QLQ-C30, Patient Neurotoxicity Questionnaire (PNQ), and EORTC QLQ-CIPN20.
Results
The average scores of OXLIPN upper and lower extremity scale were 30.01 and 29.16, respectively. The average scores of PNQ sensory and motor scale were 2.11 and 1.70, respectively. The mean score of the QLQ-C30 global health status was 54.85, and the range of mean score of the functional and symptom subdomains was 34.85~73.29 and 17.67~53.54, respectively. The CIPN-related symptoms positively correlated with the global health status scale and all subdomains of functional scale, respectively and negatively correlated with fatigue, pain, dyspnea, insomnia, and financial problem subdomains of the symptom scale, respectively.
Figures and Tables
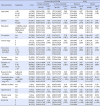
Table 2
Participants Reporting “quite a bit” or “very much” on 16-item QLQ-CIPN20 and Neurotoxic Events graded by PNQ (N=83)

References
1. Sasane M, Tencer T, French A, Maro T, Beusterien KM. Patient-reported outcomes in chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A review. J Support Oncol. 2010; 8(6):e15–e21. DOI: 10.1016/j.suponc.2010.09.029.

2. Kim HY, Kang JH, Song CE, Youn HJ. Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients. Asian Oncol Nurs. 2013; 13(4):222–230. DOI: 10.5388/aon.2013.13.4.222.

3. Woo IS. Recent updates on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Korean J Med. 2015; 88(1):35–37. DOI: 10.3904/kjm.2015.88.1.35.

4. Azhary H, Farooq MU, Bhanushali M, Majid A, Kassab MY. Peripheral neuropathy: differential diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. 2010; 81(7):887–892.
5. Tofthagen C. Patient perceptions associated with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2010; 14(3):E22–E28. DOI: 10.1188/10.CJON.E22-E28.

6. Dunlap B, Paice JA. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a need for standardization in measurement. J Support Oncol. 2006; 4:398–399.
7. Song CE, Kim HY, Lee ES. Relationship between chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy and quality of life in patients with hematological malignancies. Korean J Adult Nurs. 2015; 27(3):358–366. DOI: 10.7475/kjan.2015.27.3.358.
8. Jung SH, Kim SH, Kim JH. Clinical correlation between in vitro chemoresponse assay and first line chemotherapy for metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Korean J Clin Oncol. 2015; 11:51–58. DOI: 10.14216/kjco.15010.
9. Louvet C, Andre T, Tigaud JM, Gamelin E, Douillard JY, Brunet R, et al. Phase II study of oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and folinic acid in locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20(23):4543–4548.

11. Tofthagen C, McAllister R, McMillan SC. Peripheral neuropathy in patients with colorectal cancer receiving oxaliplatin. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2011; 15(2):182–188. DOI: 10.1188/11.CJON.182-188.

12. Kim JH, Choi KS, Kim TW, Hong YS. Quality of life in colorectal cancer patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Korean Oncol Nurs. 2011; 11(3):254–262. DOI: 10.5388/jkon.2011.11.3.254.

13. Barton DL, Wos EJ, Qin R, Mattar BI, Green NB, Lanier KS, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a topical treatment for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: NCCTG trial N06CA. Support Care Cancer. 2011; 19(6):833–841. DOI: 10.1007/s00520-010-0911-0.

14. Kwak MK, Kim EJ, Lee ER, Kwon IG, Hwang MS. Characteristics and quality of life in patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Korean Oncol Nurs. 2010; 10(2):231–239. DOI: 10.5388/jkon.2010.10.2.231.

15. Kato J, Nagahara A, Iijima K, Yoshimura M, Osada T, Yoshizawa T, Watanabe S. Evaluation of EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaire in patients undergoing in-hospital chemotherapy for gastrointestinal cancer in Japan. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 23:Suppl 2. S268–SS72. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2008.05414.x.

16. Kim HY, Kang JH, Youn HJ, So HS, Song CE, Chae SY, et al. Reliability and Validity of the Korean Version of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire to Assess Chemotherapy-induced Peripheral Neuropathy. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2014; 44(6):735–742. DOI: 10.4040/jkan.2014.44.6.735.

17. Faul F, Erdfelder E, Buchner A, Lang AG. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods. 2009; 41(4):1149–1160. DOI: 10.3758/BRM.41.4.1149.

18. Smith EM, Pang H, Cirrincione C, Fleishman S, Paskett ED, Ahles T, et al. Effect of duloxetine on pain, function, and quality of life among patients with chemotherapy-induced painful peripheral neuropathy: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2013; 309(13):1359–1367. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2013.2813.
19. Shimozuma K, Ohashi Y, Takeuchi A, Aranishi T, Morita S, Kuroi K, et al. Feasibility and validity of the Patient Neurotoxicity Questionnaire during taxane chemotherapy in a phase III randomized trial in patients with breast cancer: N-SAS BC 02. Support Care Cancer. 2009; 17(12):1483–1491. DOI: 10.1007/s00520-009-0613-7.

20. Postma TJ, Aaronson NK, Heimans JJ, Muller MJ, Hildebrand JG, Delattre JY, et al. The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: The QLQ-CIPN20. Eur J Cancer. 2005; 41(8):1135–1139.

21. Fayers PM, Aaronson NK, Bjordal K, Groenvold M, Curran D, Bottomley A. The EORTC QLQ-C30 Scoring Manual. 3rd ed. Brussels: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer;2001.
22. Yun YH, Park YS, Lee ES, Bang SM, Heo DS, Park SY, et al. Validation of the Korean version of the EORTC QLQ-C30. Qual Life Res. 2004; 13(4):863–868.

23. Wolf SL, Barton DL, Qin R, Wos EJ, Sloan JA, Liu H, et al. The relationship between numbness, tingling, and shooting/burning pain in patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) as measured by the EORTC QLQ-CIPN instrument, N06CA. Support Care Cancer. 2012; 20(3):625–632. DOI: 10.1007/s00520-011-1141-9.
24. Wickham R. chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a review and implications for oncology nursing practice. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2007; 11:361–376. DOI: 10.1188/07.CJON.361-376.

25. Yoon WK, Heo MJ, Lee OS, Lim SC. Evaluation of chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy by cisplatin, carboplatin and oxaliplatin. Korean J Clin Pharm. 2012; 22(4):356–366.
26. Armstrong T, Almadrones L, Gilbert MR. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2005; 32(2):305–311. DOI: 10.1188/05.ONF.305-311.

27. Bakitas MA. Background noise: the experience of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Nurs Res. 2007; 56(5):323–331. DOI: 10.1097/01.NNR.0000289503.22414.79.
28. Javier NS, Montagnini ML. Rehabilitation of the hospice and palliative care patient. J Palliat Med. 2011; 14(5):638–648. DOI: 10.1089/jpm.2010.0125.

29. Pachman DR, Barton DL, Swetz KM, Loprinzi CL. Troublesome symptoms in cancer survivors: fatigue, insomnia, neuropathy, and pain. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30(30):3687–3696. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2012.41.7238.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download