Abstract
Purpose
This study is reviewed of the available literature to identify the evidence of the value of Kegel exercise programs as an intervention to decrease urinary incontinence and the improvement of the quality of life following a radical prostatectomy in localized prostate cancer.
Methods
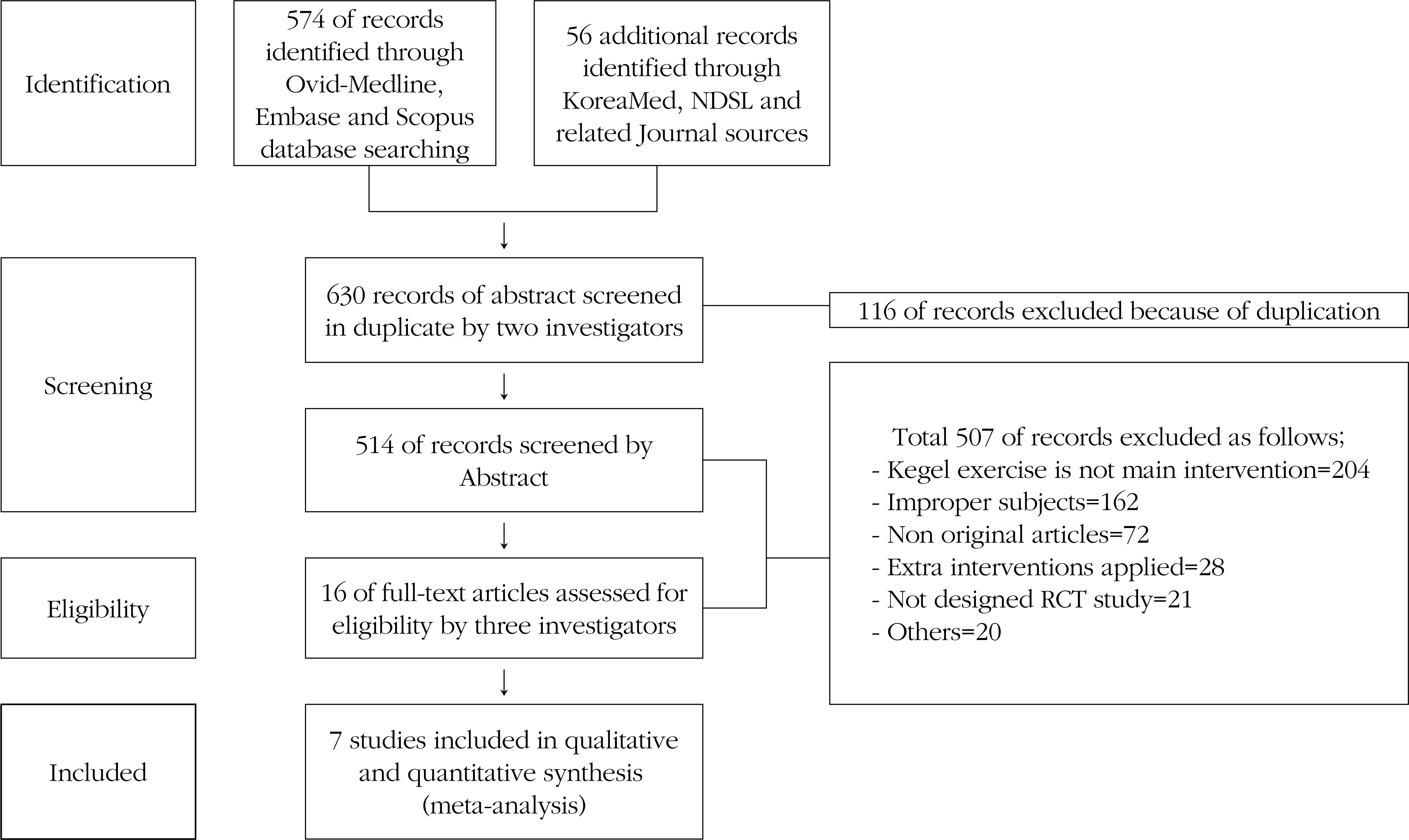
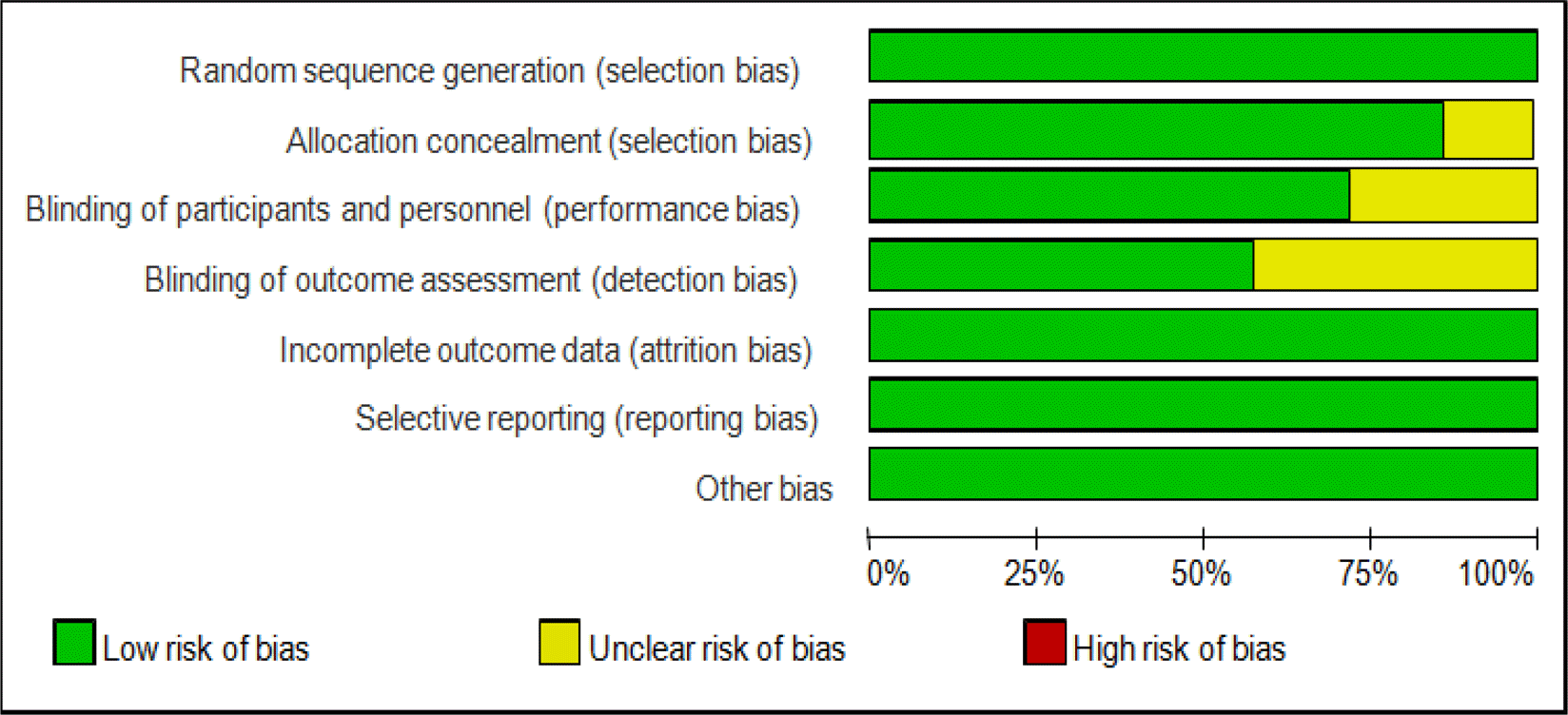
We searched studies of randomized controlled trials that utilized the Kegel exercise programs with patient with a radical prostatectomy. The review was conducted electronic bibliographic database of Ovid-Medline, Embase, Scopus, KoreaMed and NDSL, etc. Of 630 publications identified, seven studies that met the inclusion criteria, and all studies analyzed by meta-analysis. To ensure the quality of the studies, we used Cochrane's Risk of Bias.
Results
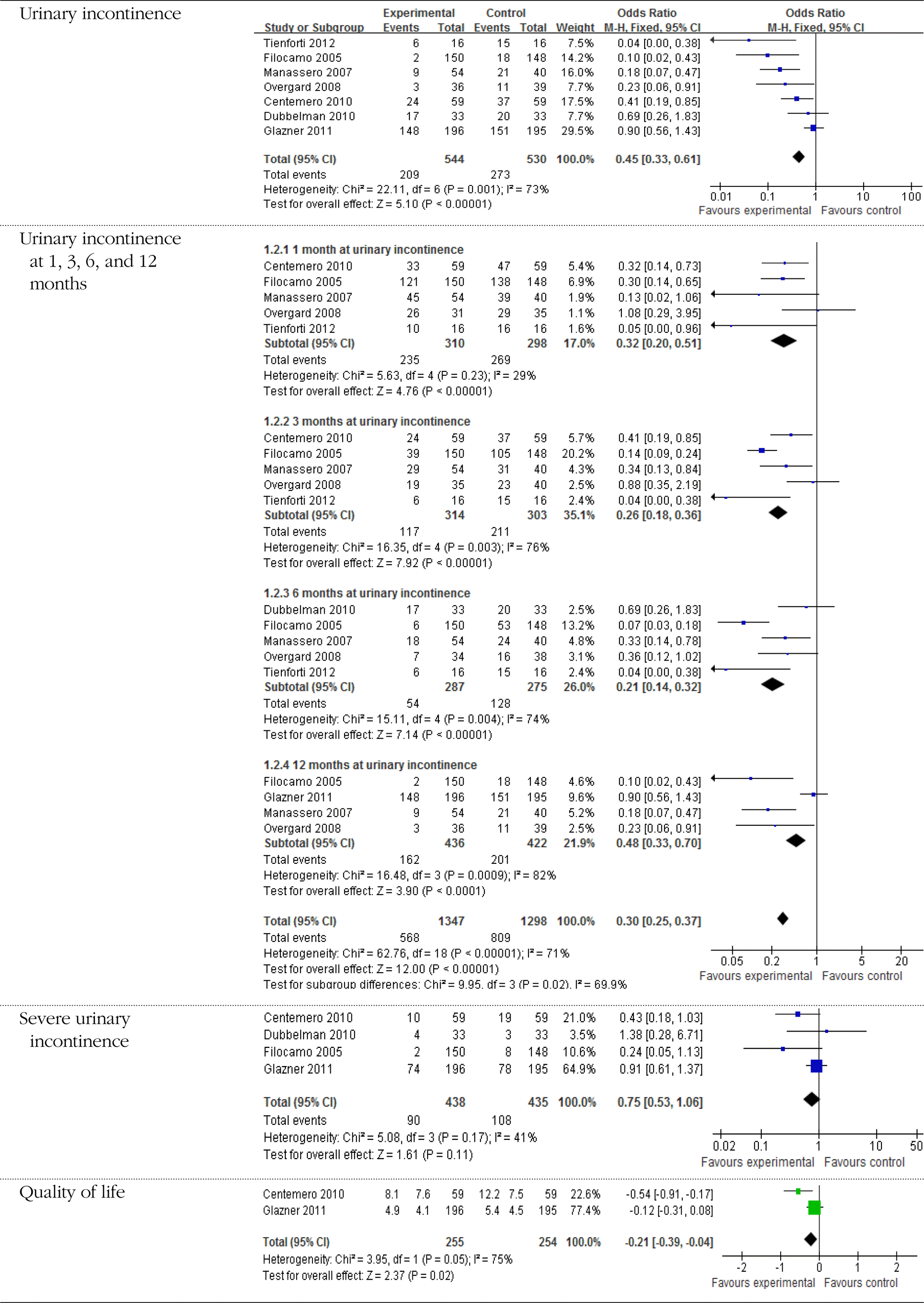
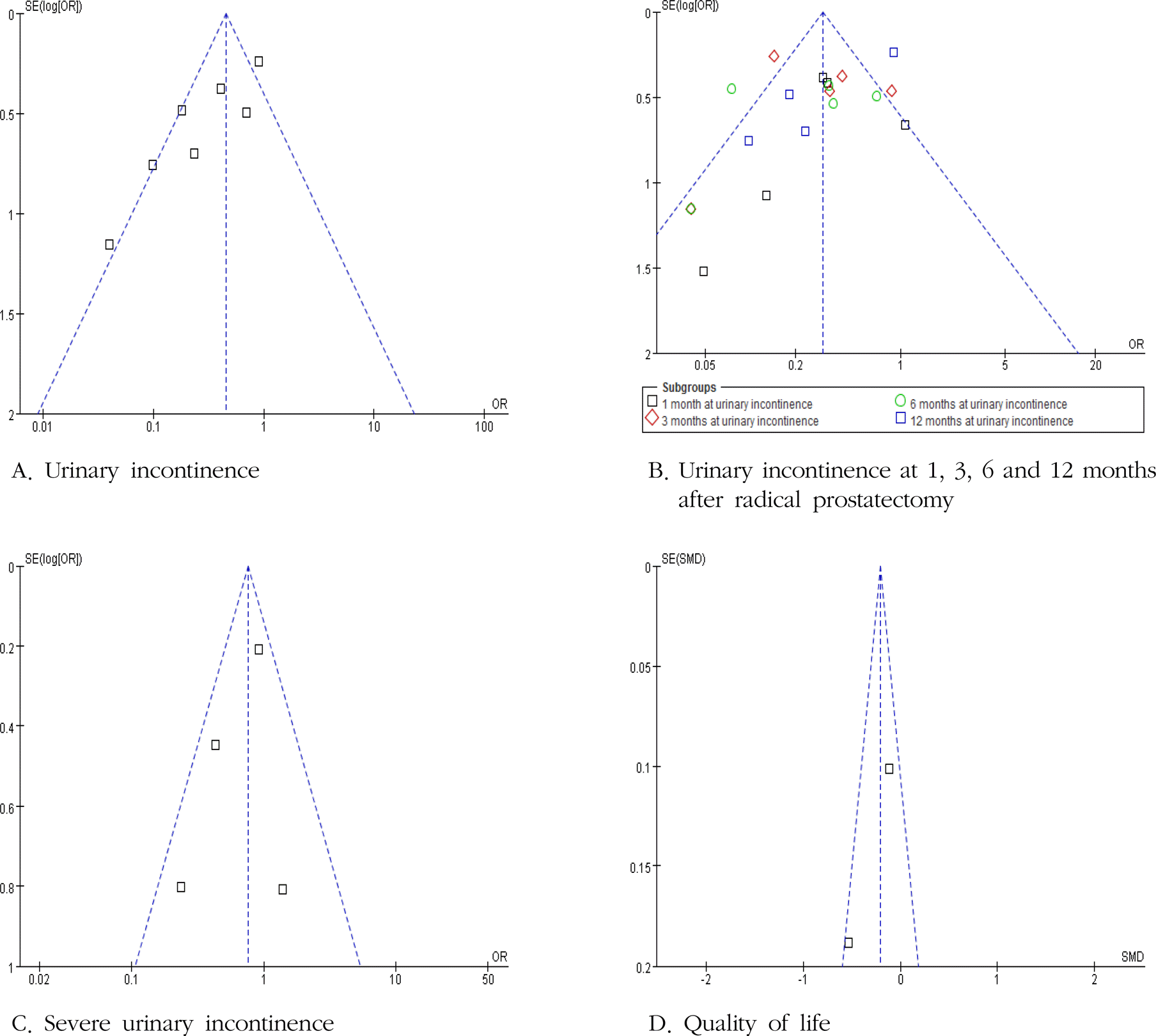
Kegel exercise helped patient to achieve continence more quickly (after 1, 3, 6, 12 months) than men not using Kegel exercises. Especially, Kegel exercise significantly reduced the development of urinary incontinence at one month after prostatectomy. The effectiveness of Kegel exercise after prostatectomy was found to improve the quality of life at a significant level.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
Bidwell S.., Jensen F. M.2000. Etext on Health Technology Assessment (HTA) Information Resources. United States National Library of Medicine. Retrieved October 26, 2012, from. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/archive/20060905/nichsr/ehta/chapter3.html#CORE.
Bridgeman B.., Roberts S. G.2010. The 4-3-2 method for Kegel exercises. American Journal of Mens Health. 4(1):75–76.

Centemero A.., Rigatti L.., Giraudo D.., Lazzeri M.., Lughezzani G.., Zugna D., et al. 2010. Preoperative pelvic floor muscle exercise for early continence after radical prostatectomy: A randomised controlled study. European Urology. 57:1039–1044.

Choe J. H.., Choi Y. S.., Choi H. J.., Choi H. Y.., Lee S. W.2005. Quality of life and sexual outcomes: Radical prostatectomy and external beam radiation therapy for prostate cancer. The Korean Journal of Urology. 46(9):962–969.
Donovan J. L.., Peter T. J.., Abrams P.., Brookes S. T.., de aa Rosette J. J.., Schafer W.2000. Scoring the short form ICSmaleSF questionnaire. The Journal of Urology. 164:1948–1955.

Dorey G.., Speakman M.., Feneley R.., Swinkels A.., Dunn C.., Ewings P.2004. Randomised controlled trial of pelvic floor muscle exercises and manometric biofeedback for erectile dysfunction. British Journal of General Practice. 54(58):819–825.
Dubbelman Y.., Groen J.., Wildhagen M.., Rikken B.., Bosch R.2010. The recovery of urinary continence after radical retropubic prostatectomy: A randomized trial comparing the effect of physiotherapist-guided pelvic floor muscle exercises with guidance by an instruction folder only. British Journal of Urology International. 106:515–522.

Filocamo M. T.., Li M. V.., Del Popolo G.., Cecconi F.., Marzocco M.., Tosto A., et al. 2005. Effectiveness of early pelvic floor rehabilitation treatment for post-prostatectomy incontinence. European Urology. 48:734–738.

Floratos D. L.., Sonke G. S.., Rapidou C. A.., Alivizatos G. J.., Deli-veliotis C.., Constantinides C. A., et al. 2002. Biofeedback vs verbal feedback as learning tools for pelvic muscle exercises in the early management of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. British Journal of Urology International. 89:714–719.

Glazener C.., Boachie C.., Buckley B.., Cochran C.., Dorey G.., Grant A., et al. 2011. Urinary incontinence in men after formal one-to-one pelvic-floor muscle training following radical prostatectomy or transurethral resection of the prostate (MAPS): Two parallel randomised controlled trials. Lancet. 378:328–337.

Gormley E. A.2002. Biofeedback & behavioral therapy for the management of female urinary incontinence. Urologic Clinics of North America. 29(3):551–557.
Han D. Y.., Jeong H. J.2008. Initial 4 cases experience of male sling procedure for the treatment in patients with post-prostatectomy incontinence. Journal of Korean Continence Society. 12:81–87.

Higgins J., Green S., editors2011. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration. Retrieved March 30, 2011, from. http://www.cochrane-handbook.org.
Ju Y. H.2001. The effects of urinary incontinence management program on female urinaty incontinence. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Pusan National University, Busan.
Kim H. S.2007. The development & evaluation of self care agency promoting program for prostatectomy patient. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, Korea University, Seoul.
Kim J. C.., Cho K. J.2012. Current trends in management of post-prostatectomy incontinence. The Korean Journal of Urology. 53(8):511–518.
Kim K. S.., Choi E. S.2004. Relationship of urinary symptom, urinary discomfort and quality of life in bladder cancer and benign prostatic hypertrophy of male patients. Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing. 7(1):78–87.
Kim Y. T.2011, August. Incontinence post prostatic surgery. Retrieved October 26, 2012, from Medical Doctor Journal Web site:. http://mdjournal.net/bbs/md/list.asp?table=bbs_md_journal&category=&page=4&s_year=1999&s_month=9&e_year=2011&e_month=8&search=&keyword=&left_search.
Manassero F.., Traversi C.., Ales V.., Pistolesi D.., Panicucci E.., Valent F., et al. 2007. Contribution of early intensive prolonged pelvic floor exercises on urinary continence recovery after bladder neck-sparing radical prostatectomy: Results of a prospective controlled randomized trial. Neurourology and Urodynamics. 26:985–989.

Ministry of Health & Welfare. 2011, December. The 2009 National Cancer Registry statistics announced. Retrieved October 26, 2012, from Web site:. http://www.mw.go.kr/front/al/sal0301vw.jsp?CONT_SEQ=262115&MENU_ID=0403&PAR_MENU_ID=04&page=2.
Overgard M.., Angelsen A.., Lydersen S.., Mørkved S.2008. Does physiotherapist-guided pelvic floor muscle training reduce urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy? A randomised controlled trial. European Urology. 54:438–448.
Parekh A. R.., Feng M. I.., Kirages D.., Bremner H.., Kaswick J.., Aboseif S.2003. The role of pelvic floor exercises on post-prostatectomy incontinence. The Journal of Urology. 170:130–133.

Park H. J.2001. Development of educational video program on women's urinary incontinence: Pelvic floor muscle exercise. Unpublished master's thesis, Ewha Womans University, Seoul.
Peyromaure M.., Ravery V.., Boccon-Gibod L.2002. The management of stress urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. British Journal of Urology International. 90(2):155–161.

Ribeiro L. H.., Prota C.., Gomes C. M.., de Bessa J. Jr.., Boldarine M. P.., Dall'Oglio M. F., et al. 2010. Long-term effect of early postoperative pelvic floor biofeedback on continence in men undergoing radical prostatectomy: A prospective, randomized, controlled trial. The Journal of Urology. 184:1034–1039.

Sampselle C. M.2000. Behavioral intervention for urinary incontinence women: Evidence for practice. Journal of Midwifery & Women's Health. 45(2):94–103.
Statistic Korea. 2012. June. Population projections for provinces: 2010-2040. Retrieved October 26, 2012, from Web site:. http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/kor_nw/2/2/6/index.board?bmode=read&aSeq=258593.
Tibaek S.., Klaskov P.., Hansen B. L.., Thomsen H.., Andresen H.., Jensen C. S., et al. 2007. Pelvic floor muscle training before transurethral resection of the prostate: A randomized, controlled, blinded study. Scandinavian Journal of Urology and Nephrology. 41:329–334.

Tienforti D.., Sacco E.., Marangi F.., D'Addessi A.., Racioppi M.., Gulino G., et al. 2012. Efficacy of an assisted low-intensity programme of perioperative pelvic floor muscle training in improving the recovery of continence after radical prostatectomy: A randomized controlled trial. British Journal of Urology International. 110(7):1004–1010.

Go to : 
Table 1.
Characteristics of Selected Studies




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download