Abstract
Objectives
This aim of this article is to provide current information on nucleoplasty as a therapeutic intervention for herniated disc or discogenic back pain in degenerative disc disease.
Summary of Literature Review
Nucleoplasty as a therapeutic intervention for discogenic pain is performed with increasing frequency, and has been reported to involve few complications and to have satisfactory clinical results.
Results
In nucleoplasty, the intervertebral disc is approached percutaneously. In this paradigm, a bipolar high frequency device in combination with ablation and coagulation is used to create a channel in the intervertebral disc in order to reduce intervertebral disc volume and to decrease intervertebral pressure and inflammatory markers. Standard indications for nucleoplasty have not been established, but it has been reported that the procedure had excellent outcomes regardless of the presence of radiculopathy or the results of discography. Many studies have reported their outcomes using various categories, because the procedure is comparatively new. Concomitantly, longterm follow-up studies remain to be performed, and each study reported a different follow-up period.
Conclusions
Nucleoplasty has been found to show an excellent prognosis for discogenic back pain and a low incidence of complications. Moreover, since it is a minimally invasive procedure, it offers improved possibilities for return to daily life and work. If degenerative changes have not progressed to a great extent or the intervertebral level remains intact, nucleoplasty may be considered prior to surgery. Due to the lack of reports on the subject, prospective analyses in the future are required.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Schmidt CO, Raspe H, Pfingsten M, et al. Back pain in the german adult population: prevalence, severity, and sociode-mographic correlates in a multiregional survey. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:2005–11.
2. Schwarzer AC, Aprill CN, Derby R, et al. The relative contributions of the disc and zygapophyseal joint in chronic low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19:801–6.

3. Mirza SK, Deyo RA. Systematic review of randomized trials comparing lumbar fusion surgery to nonoperative care for treatment of chronic back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007; 32:816–23.

4. Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, et al. Surgical versus nonoperative treatment for lumbar disc herniation: four-year results for the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008; 33:2789–800.
5. Wang X, Wanyan P, Tian JH, et al. Meta-analysis of randomized trials comparing fusion surgery to non-surgical treatment for discogenic chronic low back pain. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2015; 28:621–7.

7. Carragee EJ, Han MY, Suen PW, et al. Clinical outcomes after lumbar discectomy for sciatica: the effects of frag-ment type and anular competence. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85:102–8.
8. Choy DS, Case RB, Fielding W, et al. Percutaneous laser nucleolysis of lumbar disks. N Engl J Med. 1987; 317:771–2.

9. Sharps LS, Isaac Z. Percutaneous disc decompression using nucleoplasty. Pain Physician. 2002; 5:121–6.

10. Liliang PC, Lu K, Liang CL, et al. Nucleoplasty for treating lumbar disk degenerative low back pain: an outcome pre-diction analysis. J Pain Res. 2016; 9:893–8.

11. Zhu H, Zhou XZ, Cheng MH, et al. The efficacy of coblation nucleoplasty for protrusion of lumbar intervertebral disc at a two-year follow-up. Int Orthop. 2011; 35:1677–82.

12. Hoshide R, Feldman E, Taylor W. Cadaveric Analysis of the Kambin's Triangle. Cureus. 2016; 8:E475.

13. Karaman H, Tufek A, Olmez Kavak G, et al. Effectiveness of nucleoplasty applied for chronic radicular pain. Med Sci Monit. 2011; 17:461–6.

14. Kallas JL, Godoy BL, Andraus CF, et al. Nucleoplasty as a therapeutic option for lumbar disc degeneration related pain: a retrospective study of 396 cases. Arq Neurop-siquiatr. 2013; 71:46–50.
15. Gerges FJ, Lipsitz SR, Nedeljkovic SS. A systematic review on the effectiveness of the Nucleoplasty procedure for discogenic pain. Pain Physician. 2010; 13:117–32.
16. Chen YC, Lee SH, Chen D. Intradiscal pressure study of percutaneous disc decompression with nucleoplasty in human cadavers. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:661–5.

17. Kasch R, Mensel B, Schmidt F, et al. Disc volume reduction with percutaneous nucleoplasty in an animal model. PLoS One. 2012; 7:E50211.

18. O'Neill CW, Liu JJ, Leibenberg E, et al. Percutaneous plasma decompression alters cytokine expression in injured porcine intervertebral discs. Spine J. 2004; 4:88–98.
19. Ren D, Zhang Z, Sun T, et al. Effect of percutaneous nucleoplasty with coblation on phospholipase A2 activity in the intervertebral disks of an animal model of intervertebral disk degeneration: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015; 10:38.

20. Gerszten PC, Welch WC, King JT Jr. Quality of life assessment in patients undergoing nucleoplasty-based percutaneous discectomy. J Neurosurg Spine. 2006; 4:36–42.

21. Kumar NS, Shah SM, Tan BW, et al. Discogenic axial back pain: is there a role for nucleoplasty? Asian Spine J. 2013; 7:314–21.

22. Eichen PM, Achilles N, Konig V, et al. Nucleoplasty, a minimally invasive procedure for disc decompression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published clinical studies. Pain Physician. 2014; 17:E149–73.
23. Lemcke J, Al-Zain F, Mutze S, et al. Minimally invasive spinal surgery using nucleoplasty and the Dekompressor tool: a comparison of two methods in a one year follow-up. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2010; 53:236–42.

24. Abrishamkar S, Kouchakzadeh M, Mirhosseini A, et al. Comparison of open surgical discectomy versus plasma-laser nucleoplasty in patients with single lumbar disc herniation. J Res Med Sci. 2015; 20:1133–7.

25. Nikoobakht M, Yekanineajd MS, Pakpour AH, et al. Plasma disc decompression compared to physiotherapy for symptomatic contained lumbar disc herniation: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2016; 50:24–30.

26. Gerszten PC, Smuck M, Rathmell JP, et al. Plasma disc decompression compared with fluoroscopy-guided transforaminal epidural steroid injections for symptomatic contained lumbar disc herniation: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. J Neurosurg Spine. 2010; 12:357–71.

27. Bhagia SM, Slipman CW, Nirschl M, et al. Side effects and complications after percutaneous disc decompression using coblation technology. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2006; 85:6–13.

28. Lee MS, Cooper G, Lutz GE, et al. Histologic characterization of coblation nucleoplasty performed on sheep intervertebral discs. Pain Physician. 2003; 6:439–42.
Go to : 
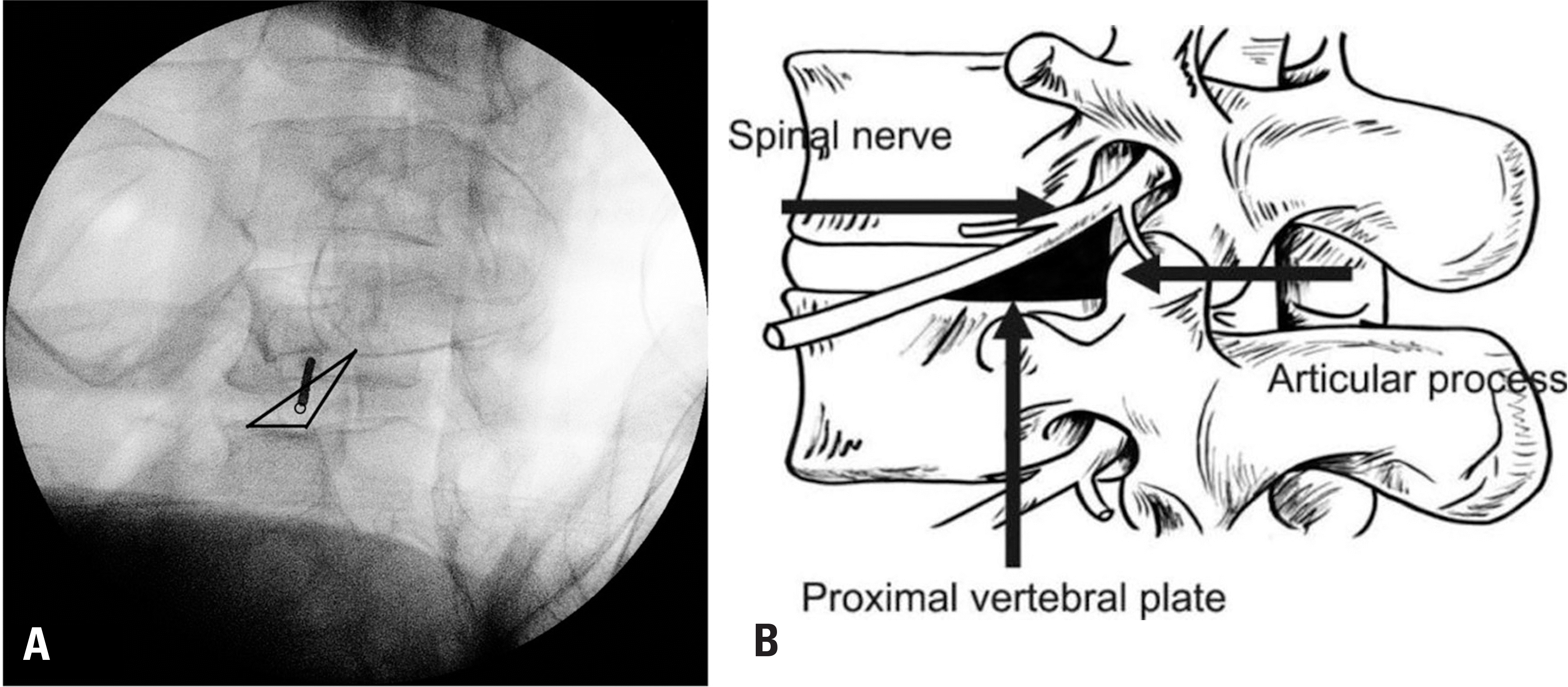 | Fig. 1.Kambin's triangle (triangle). (A) Kambin's triangle on a fluoroscopic image (the empty dot indicates the guide pin tip). (B) A schematic diagram of Kambin's triangle. The schematic diagram was adapted from the study of Hoshide et al.12)
|
 | Fig. 2.Fluoroscopic images, with the guide needle placed at the center of the intervertebral L4-L5 disc. (A) Anteroposterior view, (B) lateral view. |
Table 1.
Factors were associated with the outcomes after nucleoplasty




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download