Abstract
Objectives
To report a rare case of intractable psoas abscess due to delayed diagnosis of colon tuberculosis.
Summary of Literature Review
Most psoas abscesses occur primarily or secondarily due to infection of the vertebral body or discs; however, in rare cases, the etiology is not musculoskeletal in nature. In such cases, since diagnosis and treatment of the causal factor can be delayed, the psoas abscess may recur multiple times and eventually become difficult to treat.
Materials and Methods
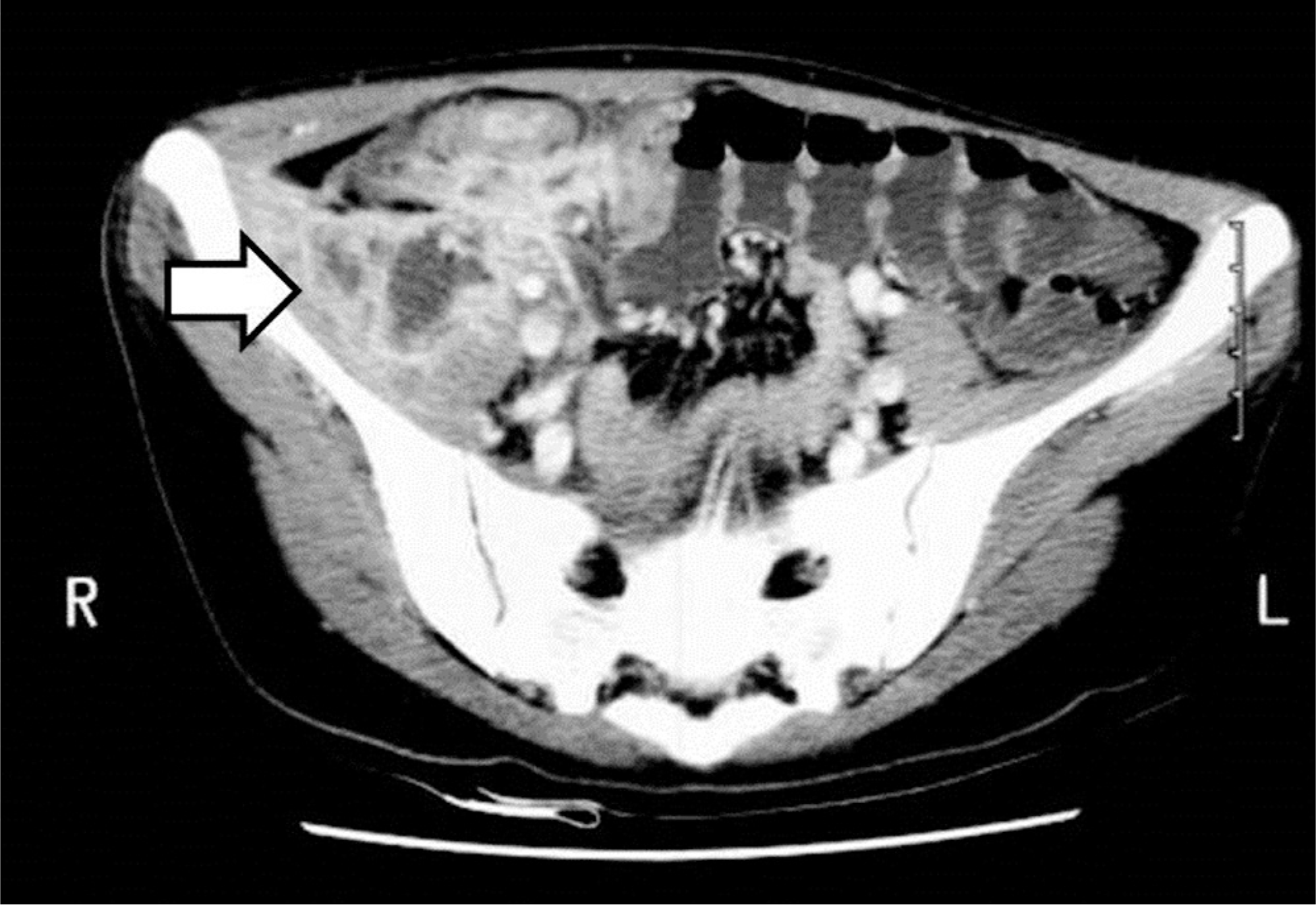
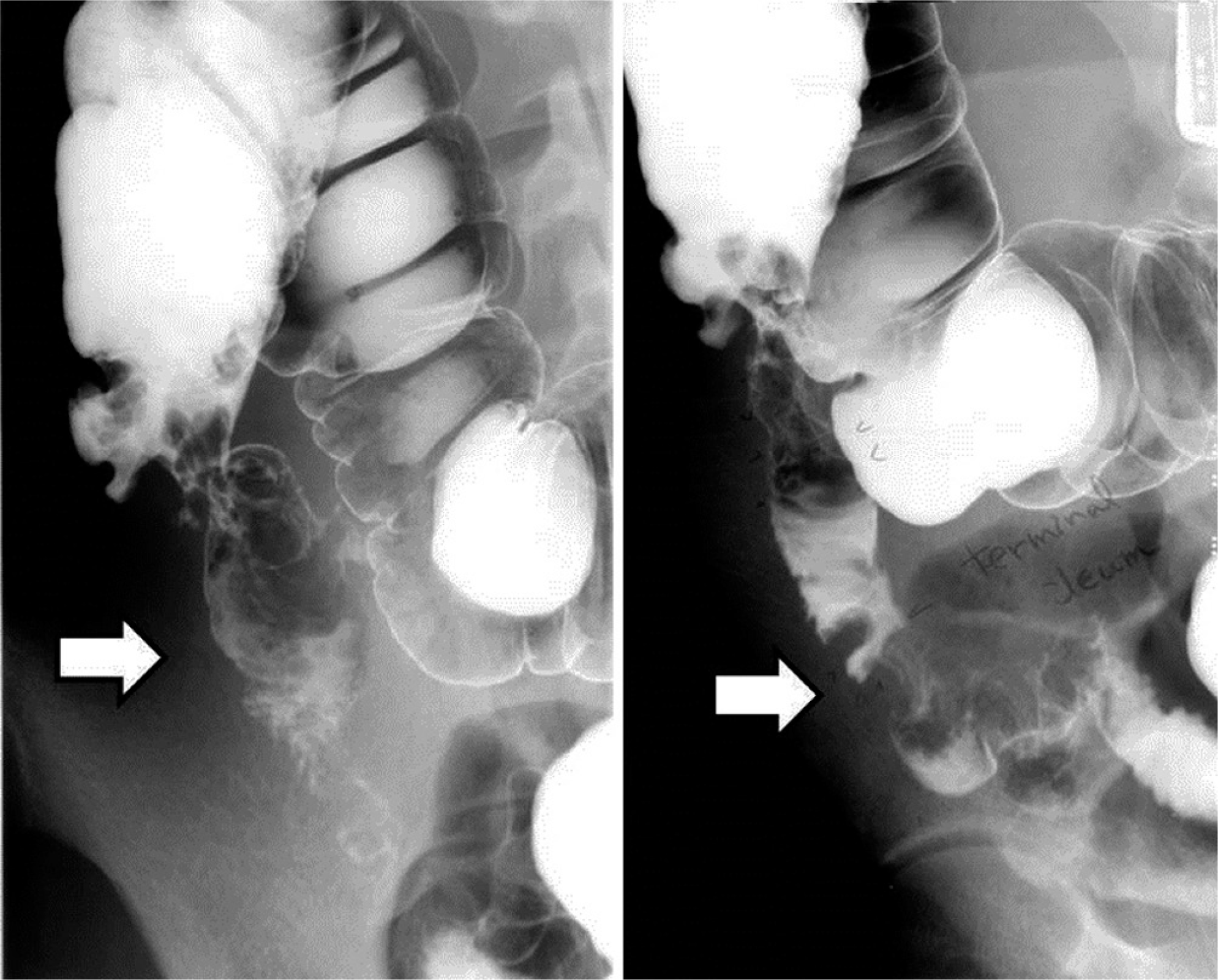
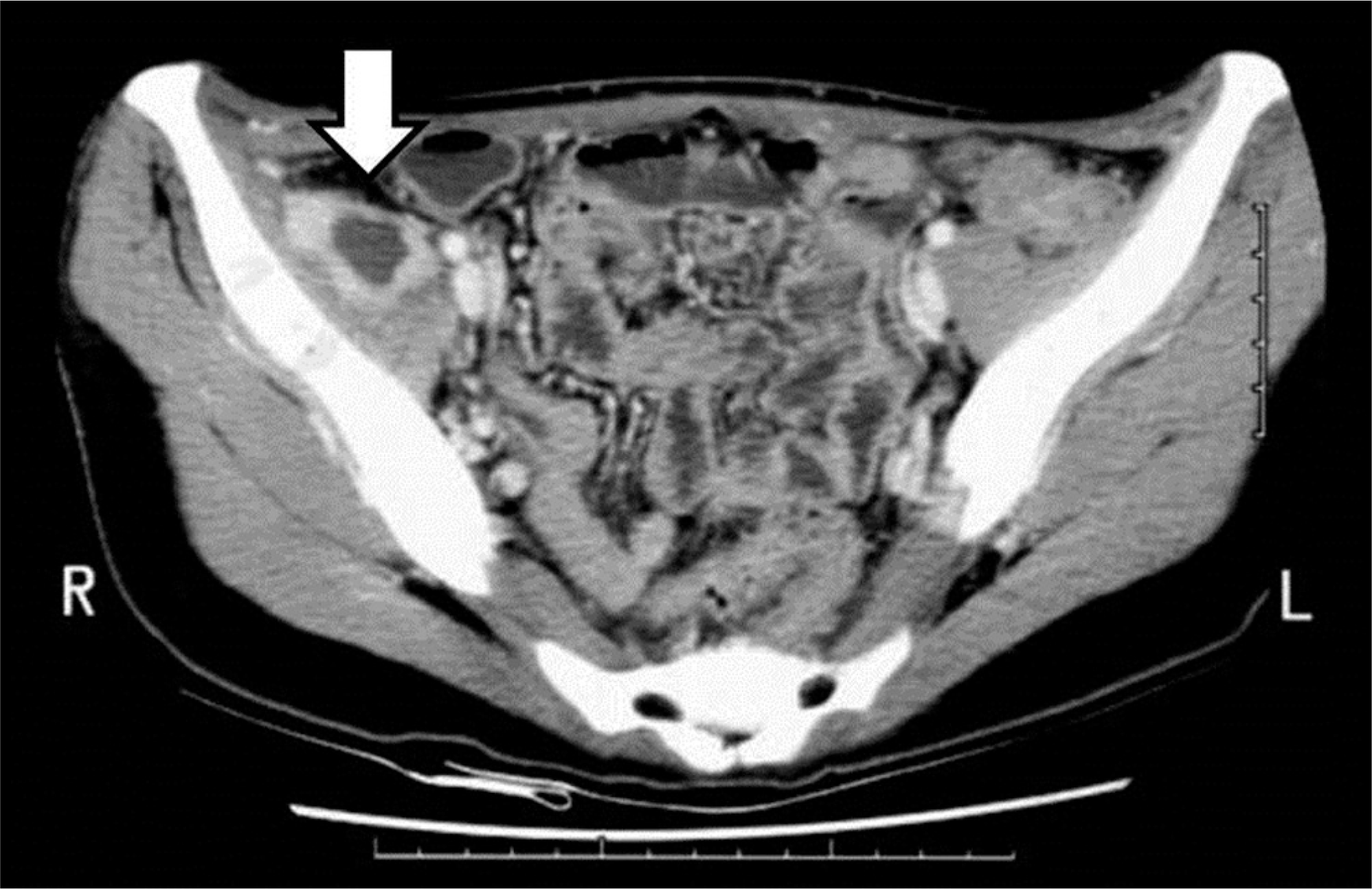
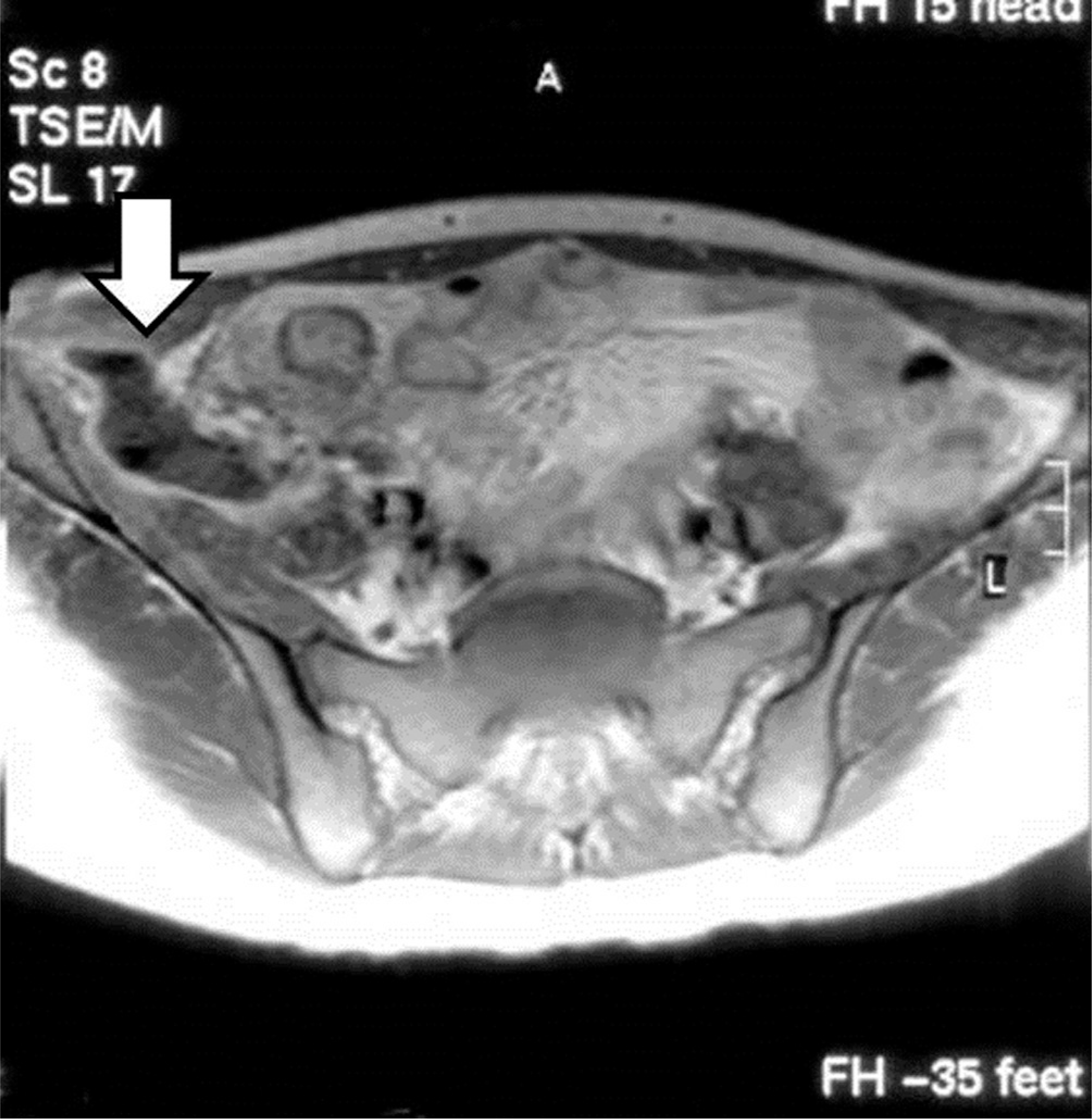
An 18-year-old female patient visited our institution complaining of right lower quadrant abdominal pain and right hip pain. On abdominal computed tomography (CT), a psoas abscess was observed and colon tuberculosis was suspected. She was treated with a ultrasonographically guided percutaneous drainage procedure. Considering the possibility of colon tuberculosis and related fistulae, a barium enema was performed; nonetheless, no fistula was found. After 2 months, the psoas abscess recurred, and thus incision and drainage were performed. Symptoms redeveloped 4 months after the incision and drainage; the patient was further evaluated with magnetic resonance imaging and recurrence of psoas abscess was again observed; incision and drainage were performed once again. A gross draining sinus developed on the right lower abdomen 11 months after the last procedure. On barium enema and abdominal CT scan, an enterocutaneous draining sinus was spotted at the right ascending colon, and right hemicolectomy was thus performed.
REFERENCES
1. Baier PK, Arampatzis G, Imdahl A, et al. The iliopsoas abscess: aetiology, therapy, and outcome. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2006; 391:411–7.

2. Demetriou GA, Nair MS, Navaratnam R. Right-sided co-lonic tuberculosis: a rare cause of iliopsoas abscess. BMJ Case Rep. 2013 April 23. [Epub ahead of print].

3. Leu SY, Leonard MB, Beart RW Jr, et al. Psoas abscess: changing patterns of diagnosis and etiology. Dis Colon Rectum. 1986; 29:694–8.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download