Abstract
Objectives
To report a rare case of late pyogenic spondylitis around the cement mass in T12 that developed 4 years after vertebroplasty with L1-3 bodies already filled with cement due to previous vertebroplasty.
Summary of Literature Review
Pyogenic spondylitis after vertebroplasty is a rare complication, but very difficult to manage.
Materials and Methods
A 56-year old female visited us with pyogenic spondylitis around the T12 body. The bodies of L1-L3 had been filled with cement eight years previously, followed by another vertebroplasty for T12 four years previously in a local clinic. At first, conservative management with intravenous antibiotics was attempted for 8 weeks, without clinical improvement. Therefore, anterior surgery for T12 corpectomy, removal of the cement, and fusion was performed.
REFERENCES
1. Lin W-C, Lee C-H, Chen S-H, et a�. Unusua� presentation of infected vertebrop�ast� with de�a�ed cement dis�odgment in an immunocompromised patient: Case report and review of �iterature. Cardiovasc Intervent Radio�. 2008; 31:231–5. DOI: 10.1007/s00270-007-9234-z.
2. O�mos MA, Gonzá�ez AS, C�emente JD, et a�. Infected ver-tebrop�ast� due to uncommon bacteria so�ved surgica���: a rare and threatening �ife comp�ication of a common procedure: report of a case and a review of the �iterature. Spine. 2006; 31:E770–3.
3. Park JS, Kim DH, Kang BJ, et a�. Spina� epidura� abscess and psoas abscess combined with p�ogenic spond��odiscitis fo��owing vertebrop�ast�: A case report. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2014; 21:90. DOI: 10.4184/jkss.2014.21.2.90.
4. Wimmer C, G�uch H, Franzreb M, Ogon M. Predisposing factors for infection in spine surger�: A surve� of 850 spina� procedures. J Spina� Disorders. 1998; 11:124–8.
5. C�ark CE, Shuff�ebarger HL. Late-deve�oping infection in instrumented idiopathic sco�iosis. Spine. 1999; 15:1909–12.
6. Lee CB, Kim HS, Kim YJ. P�ogenic spond��itis after vertebrop�ast�-A report of two cases. Asian Spine J. 2007; 1:106–9.
7. Shin JH, Ha KY, Lee JS, Joo MW. Surgica� treatment for de�a�ed p�ogenic spond��itis after percutaneous vertebro-p�ast� and k�phop�ast�. Report of 4 cases. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008; 9:265–72.
8. Yu S-W, Chen W-J, Lin W-C, et a�. Serious p�ogenic spond��itis fo��owing vertebrop�ast�—a case report. Spine. 2004; 29:E209–11.
9. Schmid KE, Boszcz�k BM, Bierschneider M, et a�. Spon-d��itis fo��owing vertebrop�ast�: a case report. Eur Spine J. 2005; 14:895–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00586-005-0905-7.
10. Vats HS, McKiernan FE. Infected vertebrop�ast�: case report and review of �iterature. Spine. 2006; 31:E859–62.
11. Wa�ker DH, Mummaneni P, Rodts GE Jr. Report of two cases and review of the �iterature. Neurosurg Focus. 2004; 17:E6.
12. Vaudaux PE, Zu�ian G, Hugg�er E, et a�. Attachment of Staph��ococcus aureus to po��meth��methacr��ate increases its resistance to phagoc�tosis in foreign bod� infection. Infect Immun. 1985; 50:472–7.
13. Kim Y-M, Won C-H, Seo J-B, et a�. P�ogenic L4-5 spond��itis managed with percutaneous drainage fo�-�owed b� posterior �umbar interbod� fusion - A case report -. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2001; 8:513. DOI: 10.4184/jkss.2001.8.4.513.
Fig. 1.
A gross photograph of the patient shows a kyphotic back and ery-thematous swelling on the left flank.
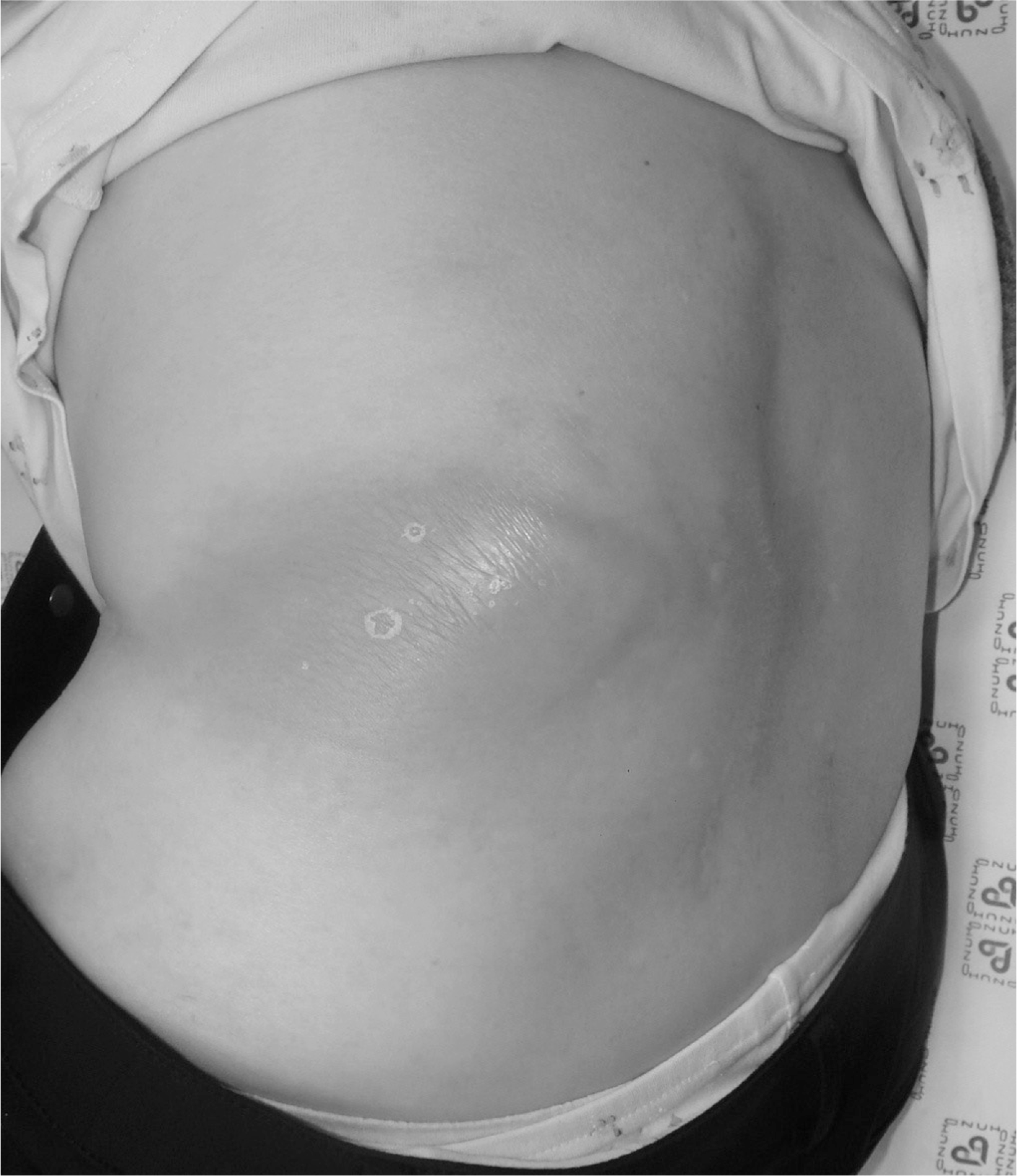
Fig. 2.
A simple X-ray shows cement-filled vertebral bodies from T12 to L3 (A) and acute kyphosis (B) at thoracolumbar junction due to collapse of the T12 body.
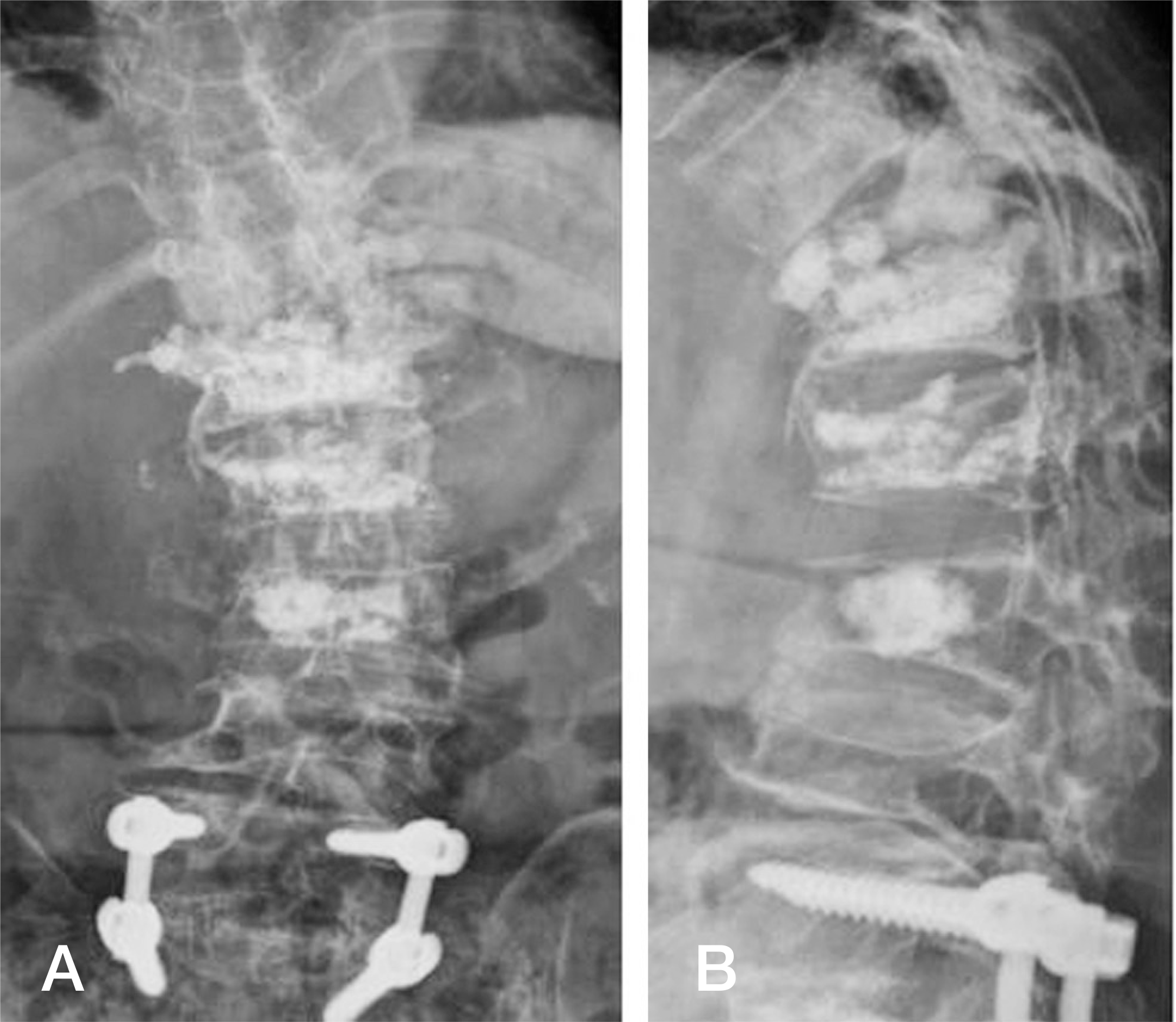
Fig. 3.
CT images reveal that most of the bone was dissolved and only the cement mass in the T12 body was remaining (A). The PMMA mass in the L1 body seemed to invade the upper end plate (B).
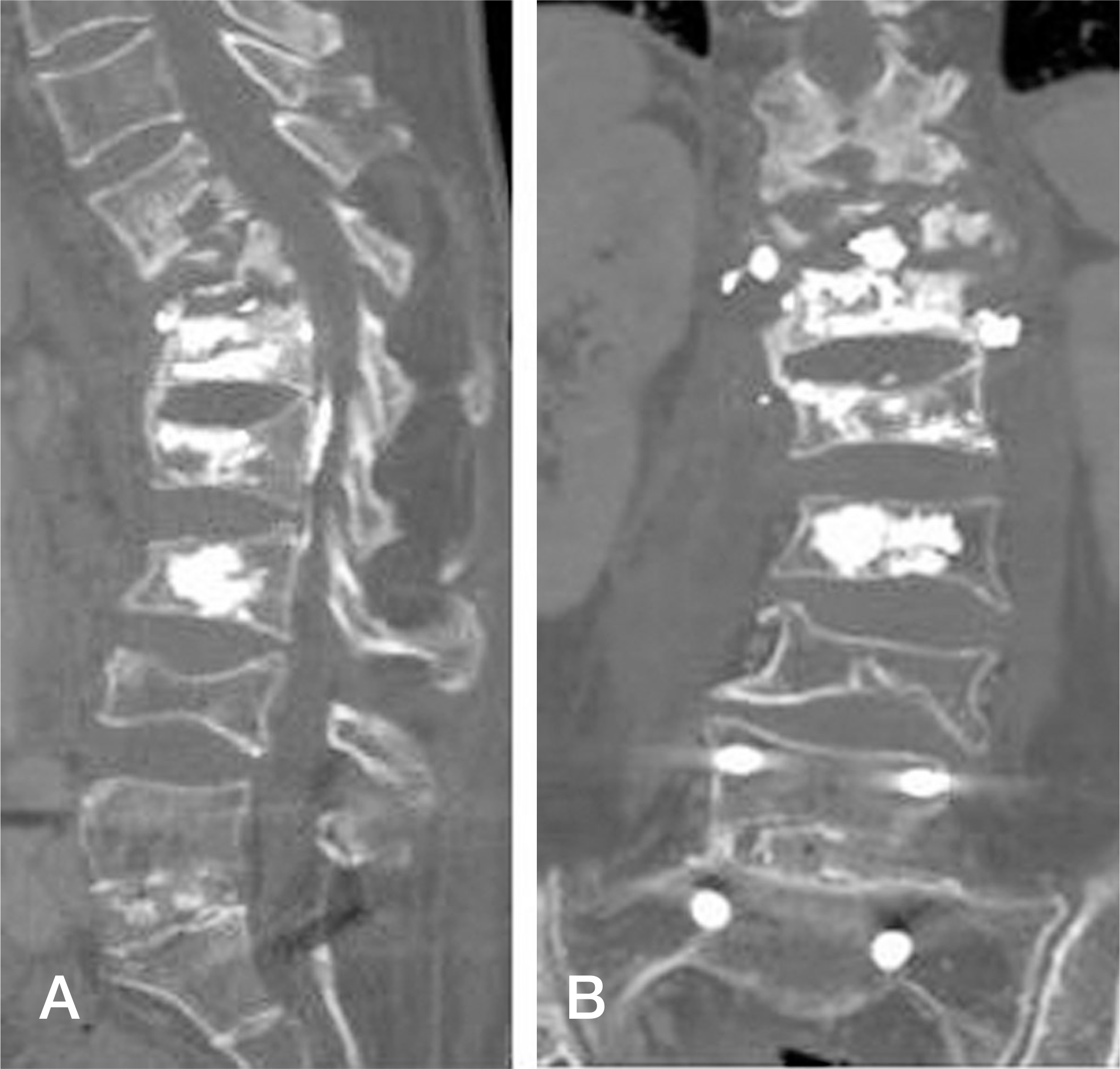
Fig. 4.
MRI images show a few cement masses floating in the T12 body surrounded by fluid collection (A-C).
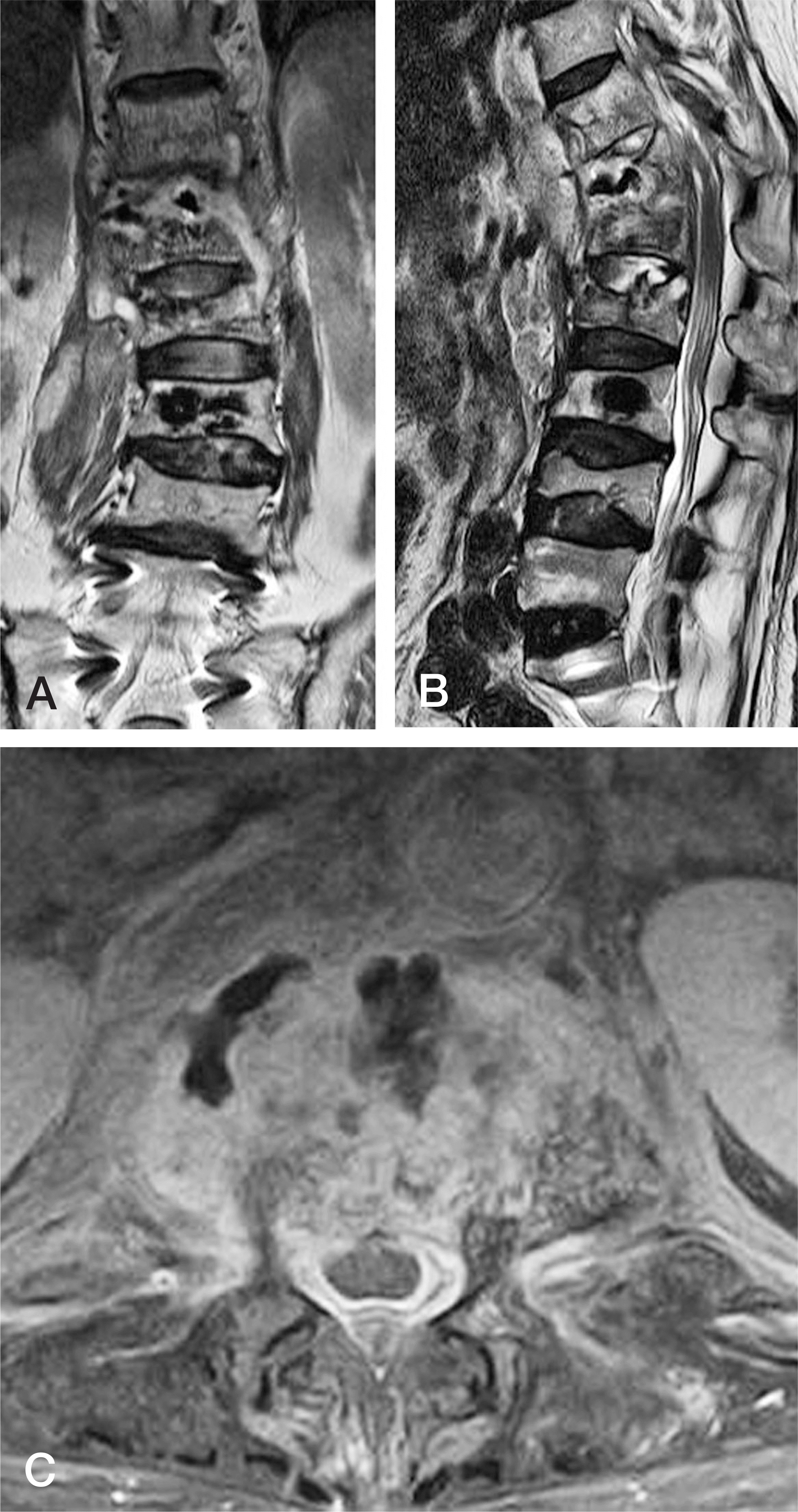
Fig. 5.
Via an anterior approach, the T12 body was explored so that all the cement material was removed. A strut graft taken from the iliac crest and pieces of a rib that had been resected for the anterior approach were inserted into the empty T12 body space.

Fig. 6.
CT images at postoperative 6 months show ongoing fusion around the graft bones in both the coronal (A) and sagittal (B) plane.
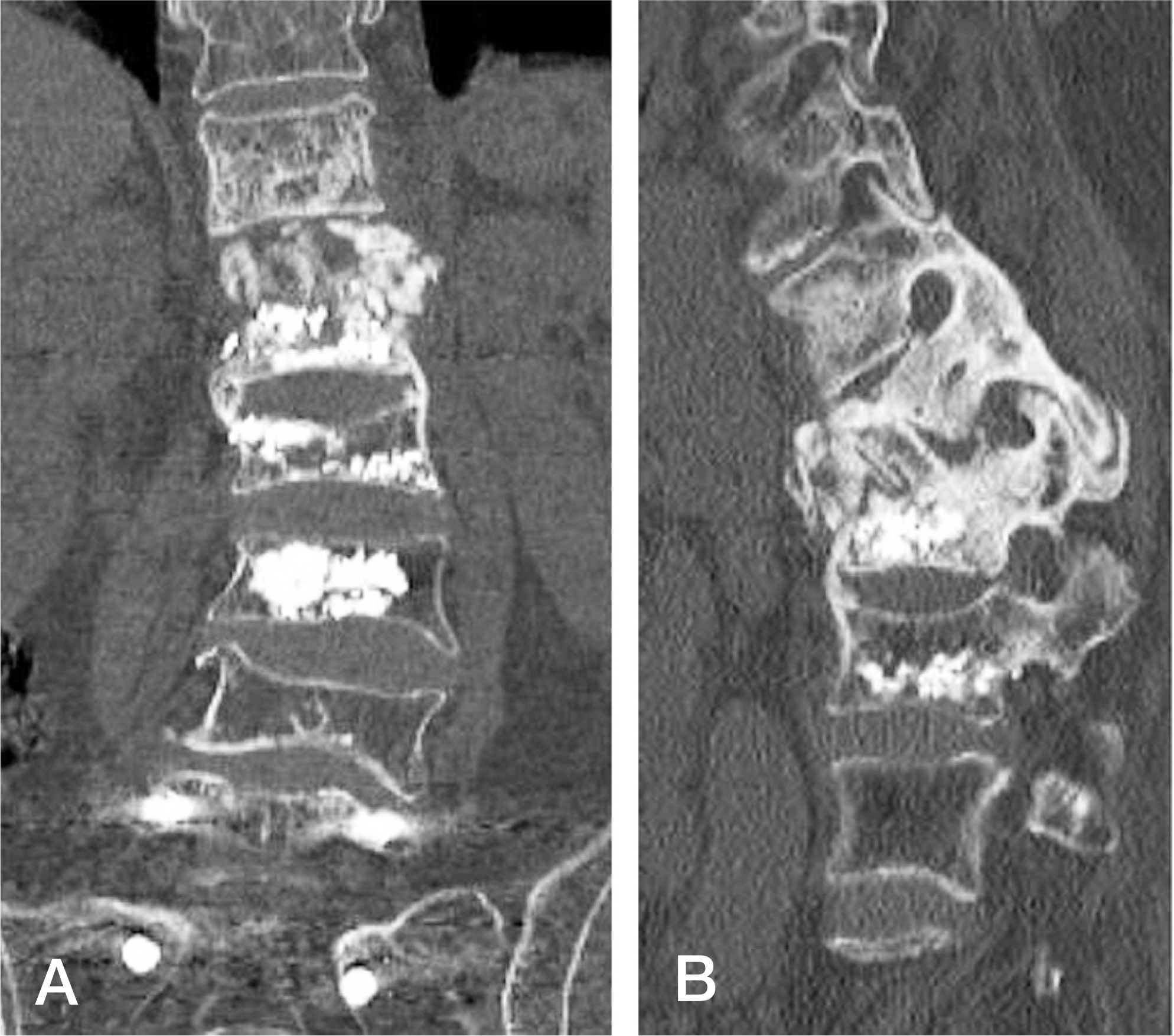
Fig. 7.
Anteroposterior (A) and lateral (B) X-ray images reveal perfect fusion from T11 to L1 across the graft bones.
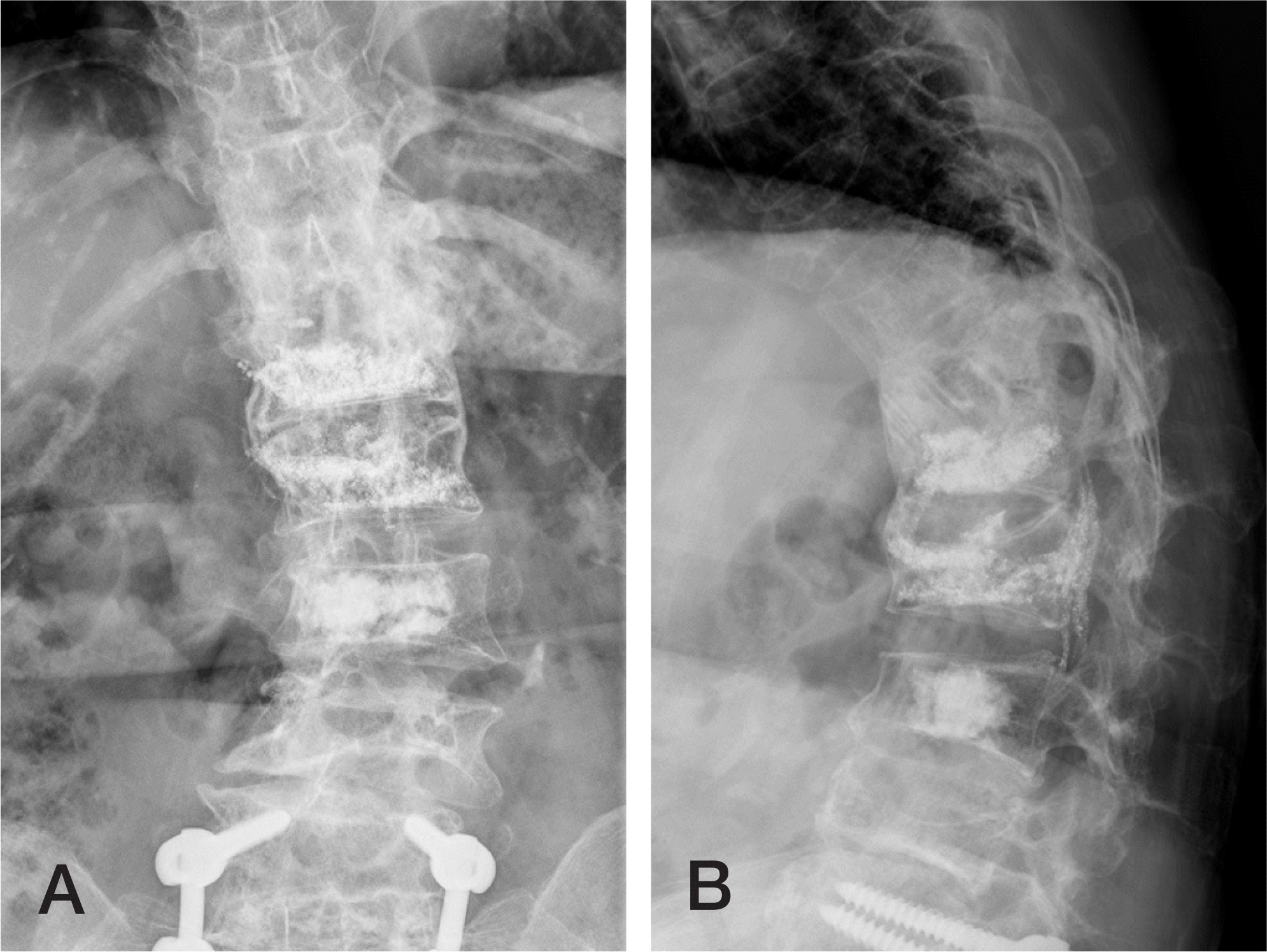
Table 1.
Reported cases of late infection after vertebroplasty




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download