Abstract
Objectives
To report a rare case of a surgically treated tuberculous myelitis and arachnoiditis patient with incomplete paraplegia.
Summary of Literature Review
Tuberculous myelitis and arachnoiditis is a rare disease with a high rate of neurologic deficit. This condition is treated using antituberculous medication and high-dose steroid therapy, but surgical treatment has rarely been reported and the outcomes vary.
Material and Methods
A 29-year-old female had tuberculous myelitis and arachnoiditis. The patient was treated with antituberculous medication and high-dose steroid therapy, but the treatment failed and the patient could not walk because of incomplete paraplegia. The surgical treatment was performed twice; we decompressed by total laminectomy and debrided the infected arachnoid membrane. Four months after surgery, we performed anterior interbody fusion due to the development of spondylitis with kyphosis.
REFERENCES
2. Solanki GA. Spinal arachnoiditis. Palmer manual of neurosurgery. London: Churchill & Livingstone;1996. p. 769–74.
3. Zuger A, Lowy FD. Tuberculosis of the brain, me-ninges, and spinal cord. Tuberculosis. Boston: Little & Brown;1996. p. 541–56.
4. Jain AK. Treatment of tuberculosis of the spine with neurologic complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; 398:75–84.

5. Jain AK, Dhammi IK. Tuberculosis of the spine: a review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 460:39–49.
6. Hristea A, Constantinescu RV, Exergian F, et al. Paraplegia due to non-osseous spinal tuberculosis: report of three cases and review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis. 2008; 12:425–9.

7. Poon TL, Ho WS, Pang KY, et al. Tuberculous meningitis with spinal tuberculous arachnoiditis. Hong Kong Med J. 2003; 9:59–61.
8. Dastur H. Diagnosis and neurosurgical treatment of tuberculous disease of the CNS. Neurosurgical review. 1983; 6:111–7.

9. Chotmongkol V, Kitkuandee A, Limpawattana P. Tuberculous radiculomyelitis (arachnoiditis) associated with tuberculous meningitis. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2005; 36:722–4.
10. Rand C, Smith MA. Anterior spinal tuberculosis: paraplegia following laminectomy. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1989; 71:105–9.
Figures and Tables%
Fig. 1.
Preoperative magnetic resonance images. (A) Sagittal T2-weighted image of T6-T11 demonstrates tuberculous myelitis and arachnoiditis. (B) Axial T2-weighted images show the cord swelling and thickening of the dural sac.

Fig. 2.
Sagittal T1-weighted image wth gadolinium enhancement of tuberculous spondylitis involving L1 and L2.
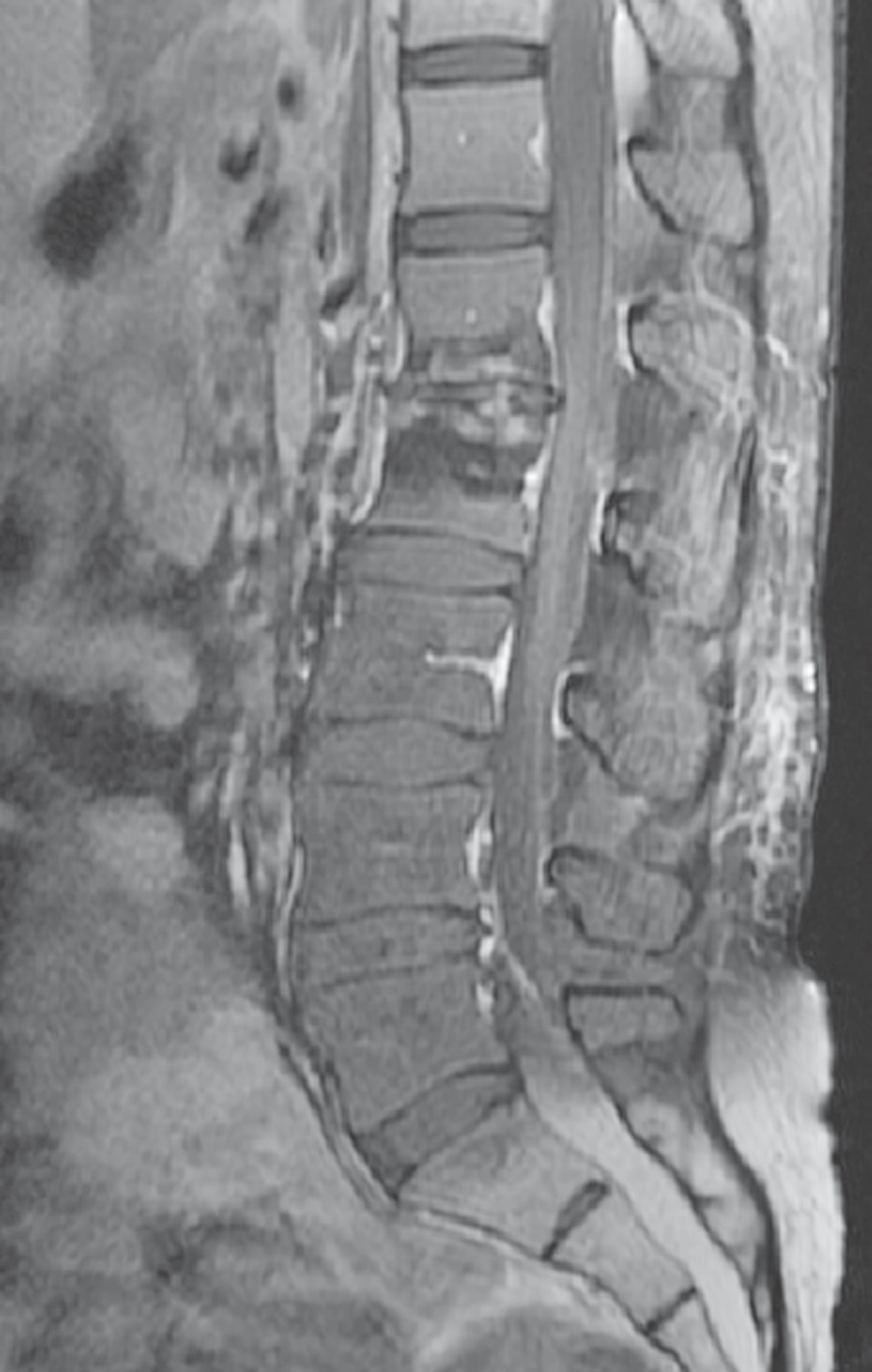
Fig. 3.
Intraoperative photography. After incision of dura, the severe ad-hesion between dura mater and arachnoid mater was observed.
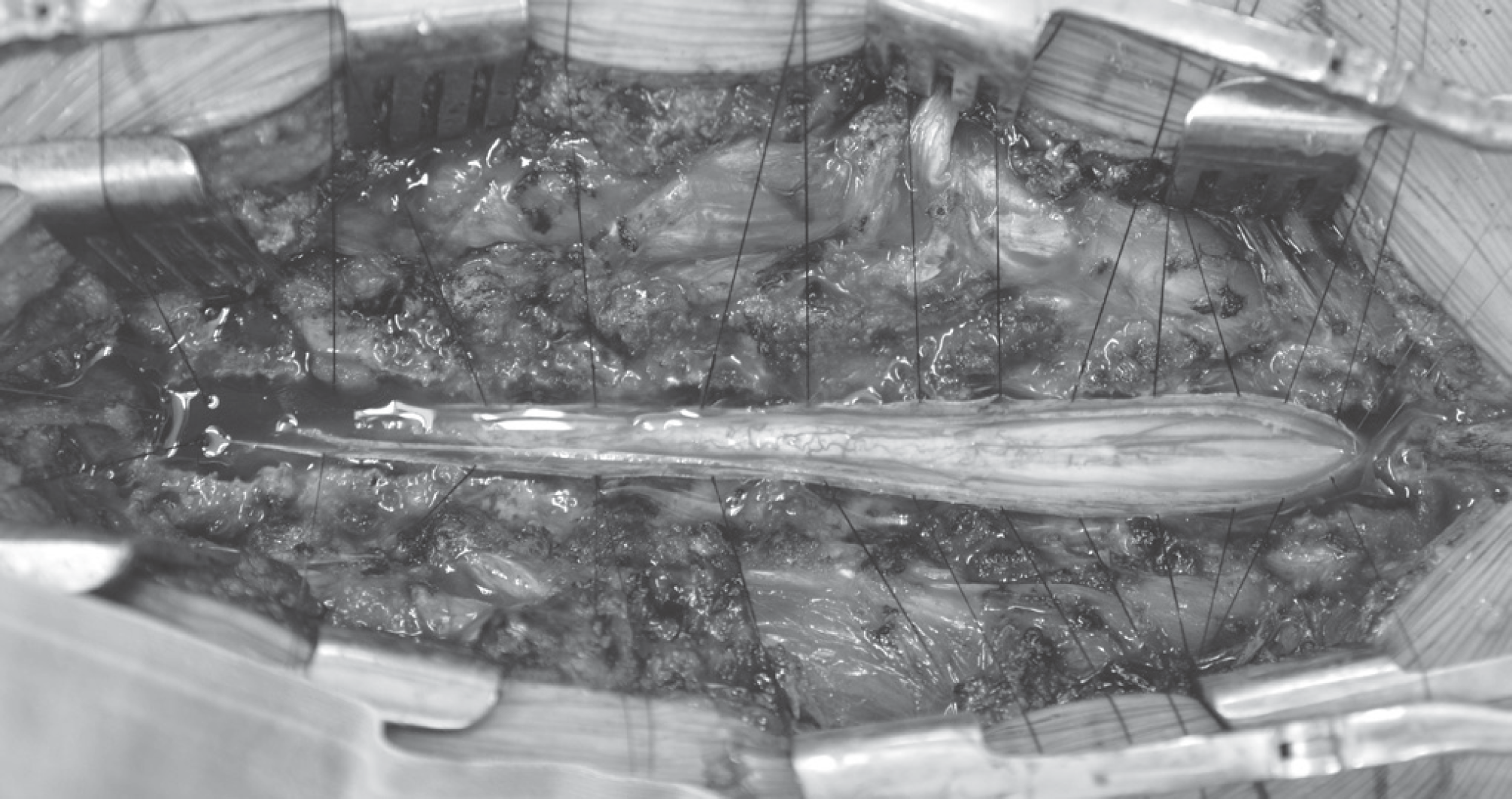
Fig. 4.
Preoperative lateral radiograph shows severe progression of kyphosis (Cobb's angle:30°) and sagittal T2-weighted image of tuberculous spondylitis involving L1 and L2.

Fig. 5.
Postoperative radiograph of anterior interbody fusion with an autogenous rib strut bone graft.
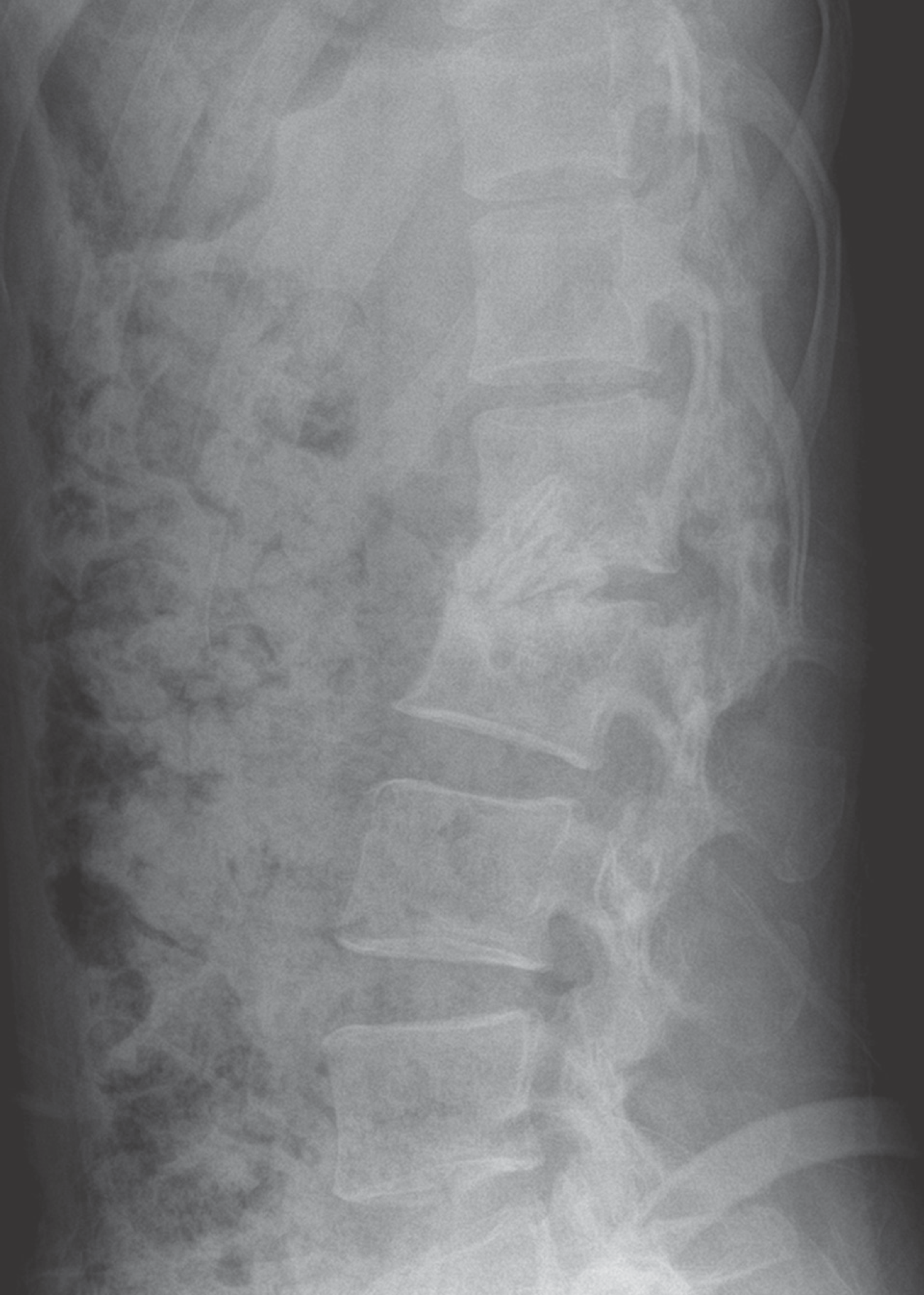
Table 1.
Previously Reported Cases Of TUberculous Meningitis with Spinal Tuberculous ArachnoiditiS




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download