Abstract
Objectives
The aim of the study was to discuss treatment strategies by understanding of emerging problems related to spinal tuberculosis.
Summary of Literature Review
Owing to modern diagnostic modalities, development of prevention and chemotherapy, the incidences of tuberculosis infection including spinal tuberculosishave been decreasing. Moreover, these medical these improvements of medical and surgical treatments the improvement of surgical techniques for spinal tuberculosis reduced the incidence of kyphosis or neurologic complications such as Pott's paralysis.
REFERENCES
1. Joint committee for the development of guidelines for tuberculosis, Korea centers for disease control and prevention. Korea guidelines for tuberculosis first edition. 2011.
2. Kang M, Gupta S, Khandelwal N, Shankar S, Gulati M, Suri S. CT-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of spinal lesions. Acta Radiol. 1999; 40:474–8.

3. Francis IM, Das DK, Luthra UK, Sheikh Z, Sheikh M, Bashir M. Value of radiologically guided fine needle aspiration cytology(FNAC) in the diagnosis of spinal tuberculosis: a study of 29 cases. Cytopathology. 1999; 10:390–401.
4. Currie S, Galea-Soler S, Barron D, Chandramohan M, Groves C. MRI characteristics of tuberculous spondylitis. Clin Radiol. 2011; 66:778–87.

5. Jung NY, Jee WH, Ha KY, Park CK, Byun JY. Discrimination of tuberculous spondylitis from pyogenic spondylitis on MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004; 182:1405–10.

6. Jain AK. Tuberculosis of the spine: a fresh look at an old disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010; 92:905–13. Oz B. Intramedullary tuberculous abscess: a case report. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1996; 21:766–9.
8. Jahng J, Kim YH, Lee KS. Tuberculosis of the lower lumbar spine with an atypical radiological presentation - a case mimicking a malignancy. Asian Spine J. 2007; 1:102–5.
9. Babhulkar SS, Tayade WB, Babhulkar SK. Atypical spinal tuberculosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984; 66:239–42.

10. Caminero JA. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: epidemiology, risk factors and case finding. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2010; 14:382–90.
11. Ki SC, Kim KS, Kim YH, Choi YS. Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis spondylitis. A case report. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2008; 15:102–5.
12. Jain AK, Jain S. Instrumented stabilization in spinal tuberculosis. Int Orthop. 2011; 36:285–92.

13. Rajasekaran S. The natural history of post-tubercular kyphosis in children. Radiological signs which predict late in-crease in deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2001; 83:954–62.
14. No authors listed. A 15-year assessment of controlled trials of the management of tuberculosis of the spine in Korea and Hong Kong. Thirteenth Report of the Medical Research Council Working Party on Tuberculosis of the Spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998; 80:456–62.
15. Moon MS, Woo YK, Lee KS, Ha KY, Kim SS, Sun DH. Posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculous kyphosis of dorsal and lumbar spines. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1995; 20:1910–6.

16. Tuli SM. Treatment of neurological complications in tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969; 51:680–92.

17. Kotil K, Alan MS, Bilge T. Medical management of Pott disease in the thoracic and lumbar spine: a prospective clinical study. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007; 6:222–8.

18. Ha KY, Chung YG, Ryoo SJ. Adherence and biofilm formation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis on various spinal implants. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:38–43.

19. Moon MS, Moon JL, Moon YW, et al. Pott's paraplegia in patients with severely deformed dorsal or dorsolumbar spines: treatment and prognosis. Spinal Cord. 2003; 41:164–71.

20. Wong YW, Leong JC, Luk KD. Direct internal kyphectomy for severe angular tuberculous kyphosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007; 460:124–9.

21. Yau AC, Hsu LC, O'Brien JP, Hodgson AR. Tuberculous kyphosis: correction with spinal osteotomy, halo-pelvic distraction, and anterior and posterior fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1974; 56:1419–34.
Fig. 1.
A 29-year-old male with back pain. A typical tuberculous spondylitis T2-weighted-fat-suppression MR image shows high signal intensity at the 11 th and 12 th thoracic spine and the 2 nd and 3 rd lumbar spine. And there are epidural abscess at the thoracic spine and sub-ligamentous abscess extension at the lumbar spine.
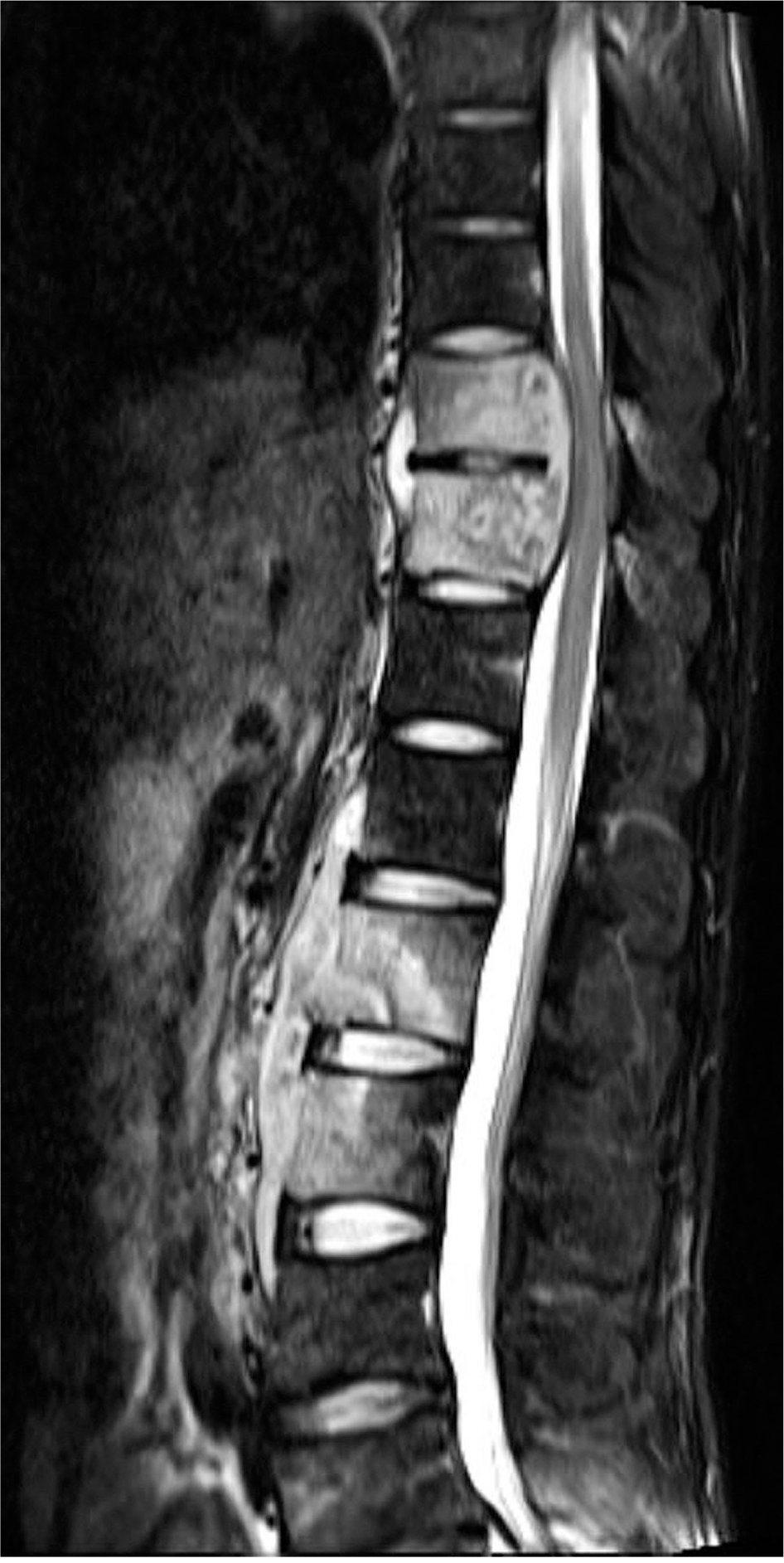
Fig. 2.
A 44-year-old male with old tuberculous spondylitis history. Severe kyphosis was noted at the upper thoracic spine.
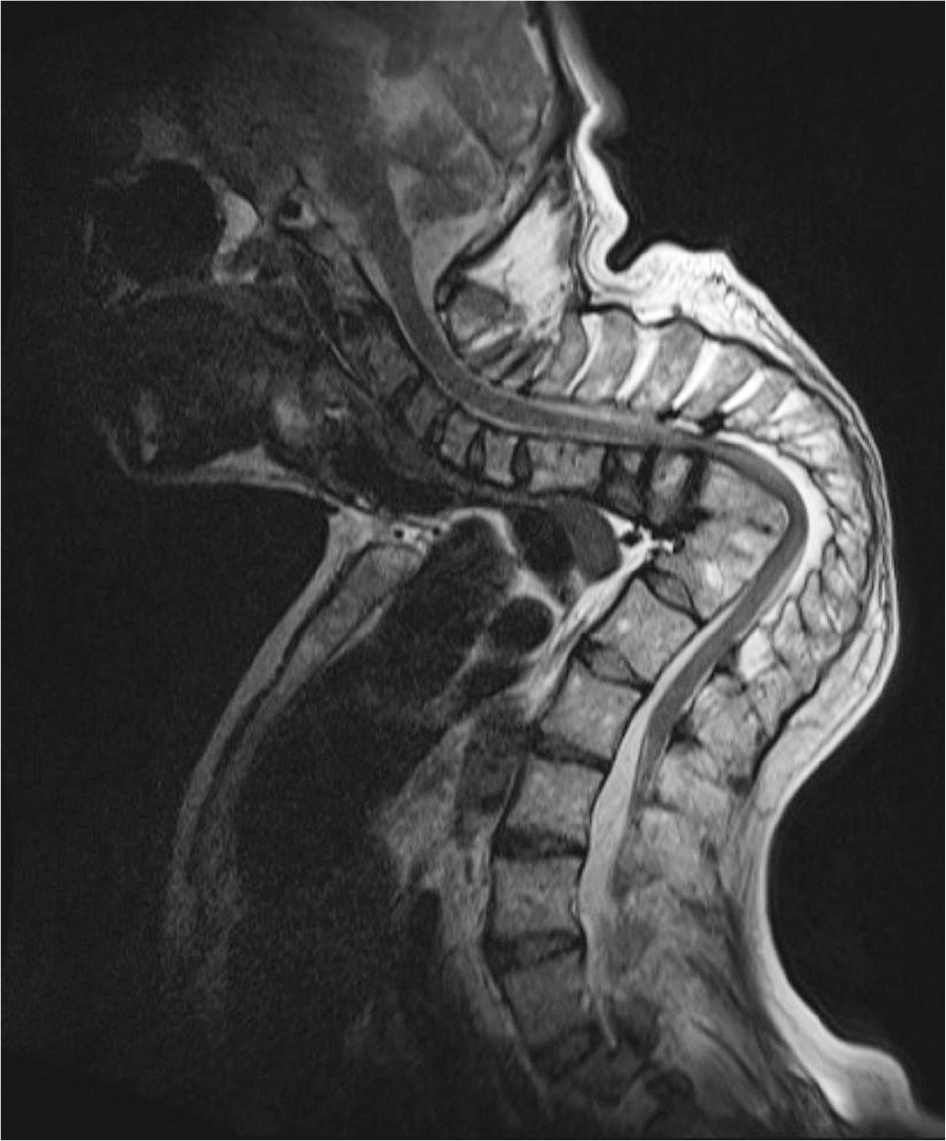
Fig. 3.
A 60-year-old female (A) Tuberculous spondylitis was occurred at the 7 th and 8 th thoracic spine, and there was associated compression fracture at the 8 th thoracic spine. (B) After 8-month of chemotherapy, suc-cessful recovery was achieved with mild kyphosis sequel.
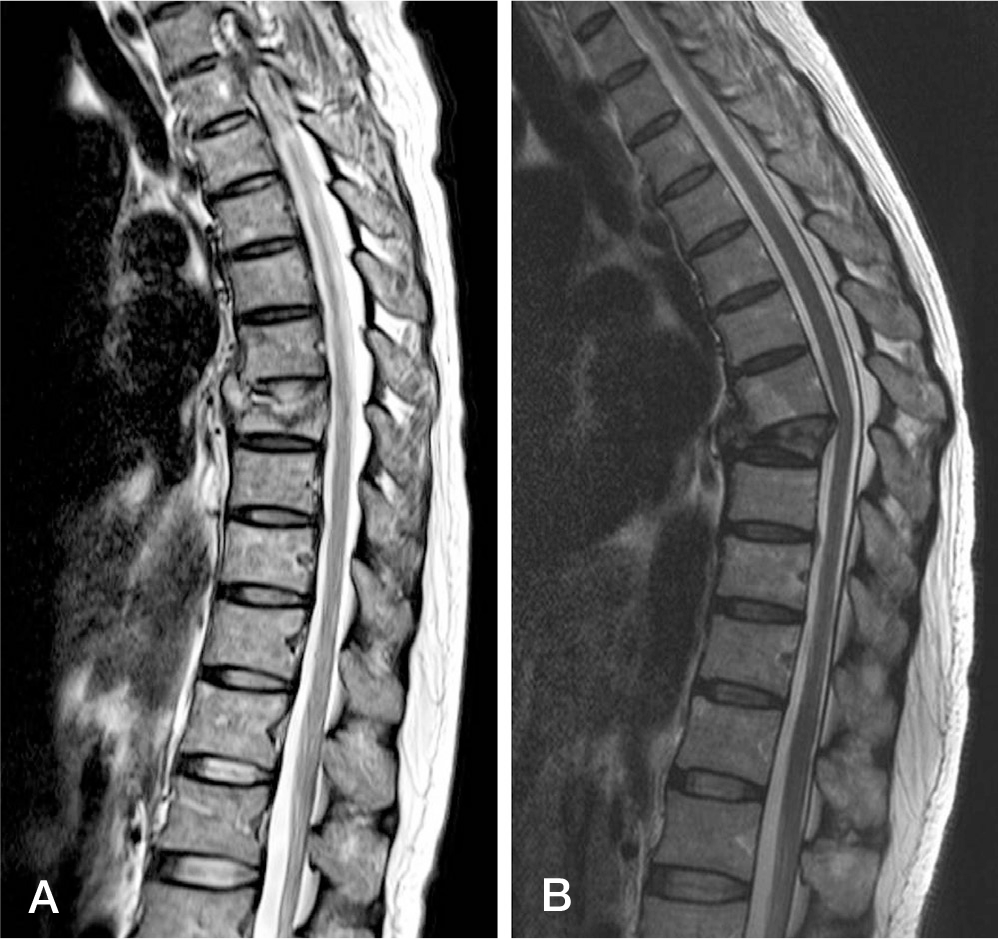
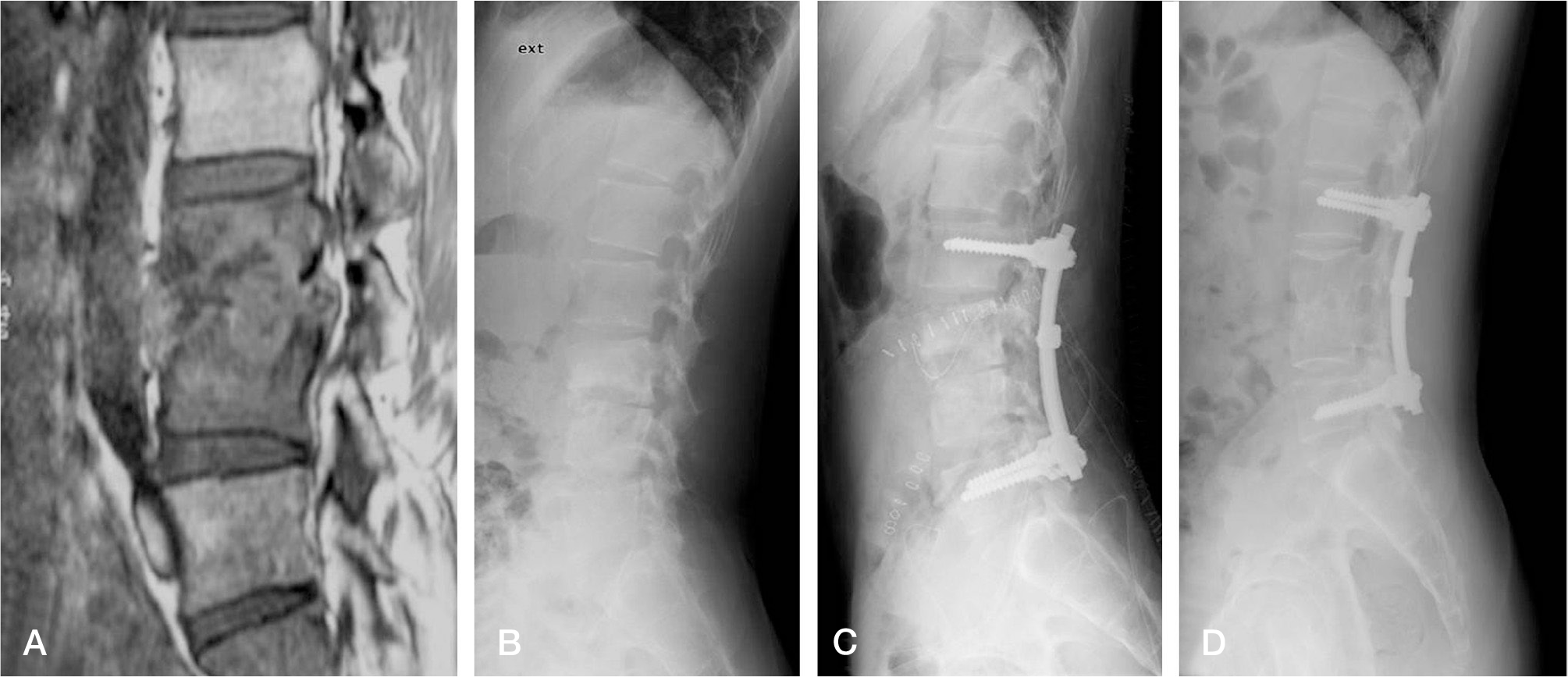
Fig. 4.
A 25-year-old male with tuberculous spondylitis at the 3 rd and 4 th lumbar spine. (A) A preoperative T1 weighted sagittal MR image shows destructive lesion involving the lumbar spine with paraspinal abscess. (B) Preoperative lateral X-ray shows destructive bony lesion with kyphosis.(C) Postoperative lateral X-ray showing anterior and posterior fusion (Hong-Kong method) status. (D) After 3-year followup, eradication of tuberculosis and bony union were achieved.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download