Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the effectiveness of microdiscectomy under local anesthesia in comparison with general anesthesia.
Summary of Literature Review
No comparative studies regarding the outcomes of microdiscectomy under local and general anesthesia could be found in the literature.
Materials and Methods
Between May 2000 and June 2004, 88 patients who underwent microdiscectomy under local anesthesia (n=50, local anesthesia group) or under general anesthesia (n=38, general anesthesia group) were selected and included in this study with a follow up period more than 3 years. The operation time and duration of hospital stay were documented. The Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) were used to evaluate the degree of symptom relief. The patient satisfaction was evaluated using the MacNab's criteria and postoperative complications.
Results
Between both groups there is no significant operation time difference. However, the average hospital stay duration in the general anesthesia group was 7.3 days, while it was 4.7 days in the local anesthesia group (P<0.05). The VAS and ODI scores were improved in both groups. Thirty-two cases (84.2%) of the general anesthesia group and 40 cases (80%) of the local anesthesia group showed satisfied results by the MacNab's criteria with no statistically significant difference (P>0.05). Three patients in the general anesthesia group and 7 patients in the local anesthesia group needed a reoperation.
Conclusions
A microdiscectomy under local anesthesia shows faster recovery period. But it shows also a relative high revision rate. In patients with old age and underlying disease, local anesthesia can be used for the microdiscectomy selectively and careful exploration of the herniated disc is required.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Caspar W. A new surgical procedure for lumbar disc herniation causing less tissue damage through a microsurgical approach. Adavance in Neurosurgery. 1977; 4:74–80.

2. Williams RW. Microlumbar disectomy: A conservative surgical approach to the virgin herniated lumbar disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1978; 3:175–82.
3. Williams RW. Microlumbar discectomy. A 12-year statistical review. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1986; 11:851–2.
4. Asch HL, Lewis PJ, Moreland DB, et al. Prospective multiple outcomes study of outpatient lumbar microdiscectomy: should 75 to 80% success rates be the normal? J Neurosurg. 2002; 96(1 Suppl):34–44.
5. Chen HT, Tsai CH, Chao SC, et al. Endoscopic discectomy of L5-S1 disc herniation via an interlaminar approach: Prospective controlled study under local and general anesthesia. Surg Neurol Int. 2011; 2:93.

6. Ebeling U, Reichenberg W, Reulen HJ. Results of microsurgical lumbar discectomy. Review of 485 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1986; 81:45–52.
7. Hudgins WR. The role of microdisectomy. Orthop Clin North Am. 1983; 14:589–603.
8. Maroon JC, Abla AA. Microlumbar discectomy. Clin Neurosurg. 1986; 33:407–17.
9. Wilson DH, Kenning J. Microsurgical lumbar discectomy: preliminary report of 83 consecutive cases. Neurosurgery. 1979; 4:137–40.
10. Andrews DW, Lavyne MH. Retrospective analysis of microsurgical and standard lumbar discectomy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1990; 15:329–35.

12. Shim DM, Kim SS, Lee BC, Choi ES. Clinical analysis and comparative study of standard and microsurgical lumbar discectomy. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1994; 1:87–92.
13. Shim DM, Kim SS, Kim TK, Song HH, Choi SH. Results of microscopic discectomy in lumbar disc herniation: A 5-years follow up. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2000; 7:22–8.
14. Wilson DH. Harbaugh R. Microsurgical and standard re-moval of the protruded lumbar disc: A comparative study. Neurosurgery. 1981; 4:422–5.
15. Kundra P, Gurnani A, Bhattacharya A. Preemptive epidural morphine for postoperative pain relief after lumbar laminectomy. Anesth Analg. 1997; 85:135–8.

16. Kang H, Jung HJ, Lee JS, Yang JJ, Shin HY, Song KS. Early postoperative analgesic effects of a single epidural injection of ropivacaine administered preoperatively in posterior lumbar interbody spinal arthrodesis. JBJS Am. 2013; 95:393–9.

17. Sekar C, Rajasekaran S, Kannan R, Reddy S, Shetty TA, Pithwa YK. Preemptive analgesia for postoperative pain relief in lumbosacral spine surgeries: a randomized controlled trial. Spine J. 2004; 4:261–4.

18. Torun F, Mordeniz C, Baysal Z, et al. Intraoperative perineural infiltration of lidocaine for acute postlaminectomy pain: preemptive analgesia in spinal surgery. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010; 23:43–6.
19. Lee CS, Chung SS, Park MS, Chung KH, Kim JH. Survivor ship analysis of lumbar microdiscectomy. J Korean Orthop Surg. 2002; 37:781–6.

Go to : 
Figures and Tables%
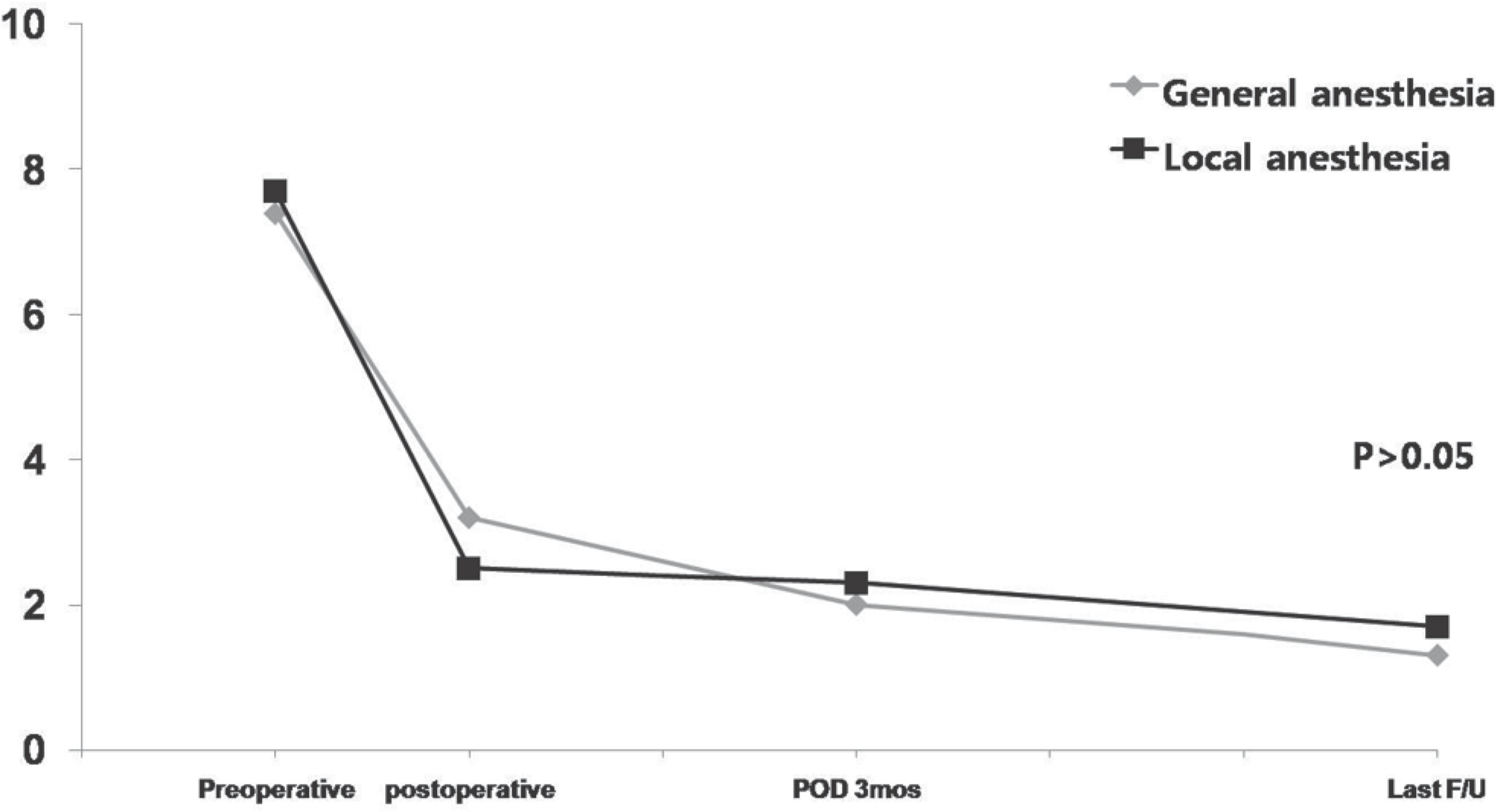 | Fig. 1.Visual Analogue Scale(VAS) score after microdiscectomy. Early postoperative VAS score of the local anesthesia group is lower than the general anesthesia group. But, there is no statistical difference between general anesthesia group and local anesthesia group(P=0.082). |
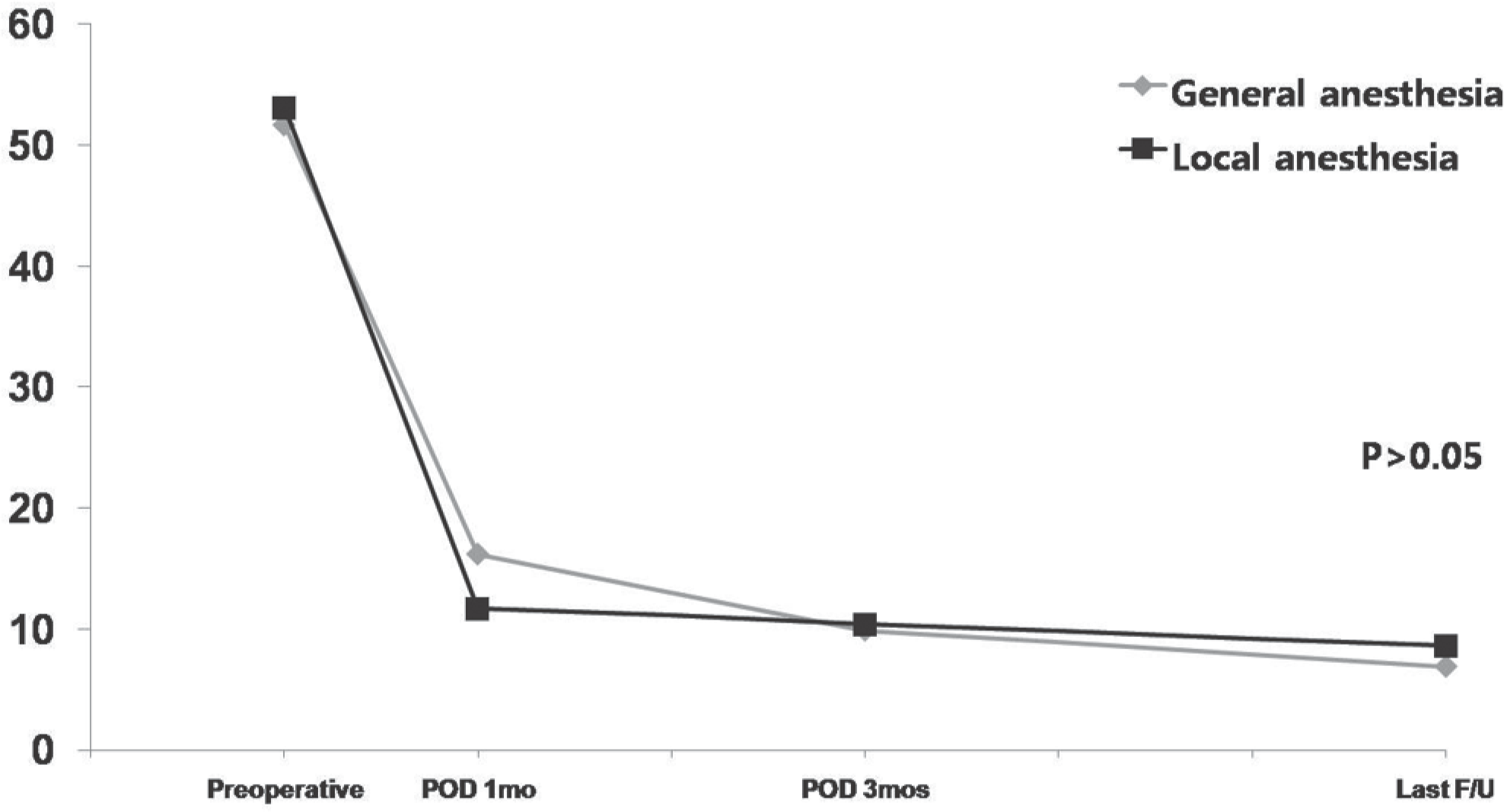 | Fig. 2.Graph showing the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) score after microdiscectomy. There is no statistical difference between general anesthesia group and local anesthesia group(P=0.088). |
Table 1.
Demographic Data of Patients.
| General anesthesia | Local anesthesia | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 44.9 years (13-79) | 46.1 years (17-78) | |
| Gender | M : F=24 : 14 | M : F=28 : 22 | |
| Followup duration | 42 months (36-73) | 47 months (36-111) | |
| L3 – 4 : 1 case | L3 – 4 : 5 cases | ||
| Disc herniation level | L4 – 5 : 27 cases | L4 – 5 : 31 cases | |
| L5 – S1 : 11 cases | L5 – S1 : 15 cases | ||
| Preoperative *VAS score | 7.4 ± 1.3 | 7.7 ± 1.1 | 0.346 |
| Preoperative † ODI score | 51.7 ± 7.5 | 53.1 ± 8.1 | 0.393 |
Table 2.
Results of microdiscectomy under general and local anesthesia




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download