Abstract
Study Design
A retrospective analysis of the posterolateral fusion in degenerative spondylolisthesis.
Objectives
Posterolateral fusion has been performed for patients about Meyerding grade1, 2 with degenerative spondylolisthesis in L4- 5. We evaluated the prognostic factors of posterolateral fusion, alone for degenerative spondylolisthesis.
Summary of Literature Review
It is reported that posterolateral fusion has almost equal postoperative clinical and radiographic results with the interbody or circumferential fusion for spondylolisthesis. However, there have been some unsatisfactory results after posterolateral fusion alone and the causes are yet unknown.
Material and Methods
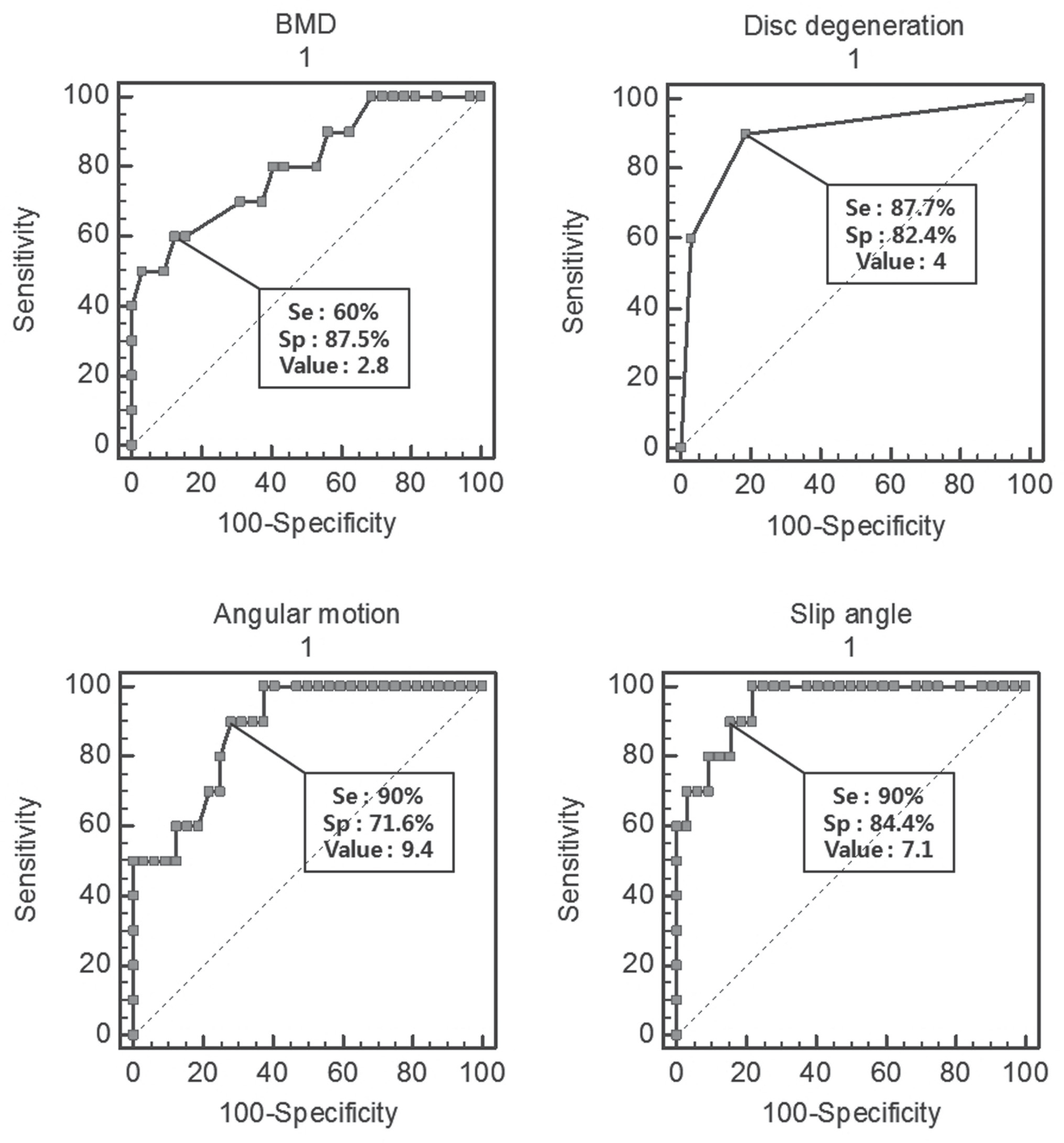
From January 2002 to July 2008, we analyzed postoperative clinical outcomes of 42 patients who were diagnosed with Meyerding 1 or 2 grade degenerative spondylolisthesis at L4-5. All the patients were classified into group I and group II, based on the clinical outcome evaluation method by Kirkaldy-Willis. Ten patients (Group I) were found to have poor or fair clinical outcomes, while 32 patients (Group II) were found to have excellent or good clinical outcomes. The mean duration of the follow up was 16.3 (12-23) months. We looked into postoperative body mass index and bone mass density, and found degenrative lumbar disc through preoperative MRI, retrospectively. We measured angular motion by dynamic radiographs and preoperative slip angle through a Taillard method.
Results
In group I, the average preoperative BMI was 25.7 (21.2~31.4) and the average T score of bone density was -3.0 (-1.9~-4.2). There was 1 case of Grade 3, 3 cases of Grade 4 and 6 cases of Grade 5 by preoperative Pfirmann classification. The average angular motion was 11.8 (9.1~14.2) and the average preoperative slip angle was 8.4 (6.9-9.6). In group II, the average preoperative BMI was 24.3 (20.72~28.1) and the average T score of bone density was -2.1 (-0.9~-3.1). There were 26 cases of Grade 3, 5 cases of Grade 4 and 1 case of Grade 5 by preoperative Pfirmann classification. The average angular motion was 8.8 (6.2~12.1) and the average preoperative slip angle was 6.2 (3.6-7.9). There were statistically significant differences between the two groups in BMI, stage of disc degeneration, preoperative angular motion, and slip angle. (p=0.04, 0.04, 0.05, 0.03, respectively)
REFERENCES
1.Lionel N. Metz, BS Vedat Deviren. Low-grade spondylo-listhesis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2007. 18:237–48.
2.Agazzi S., Reverdin A., May D. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cages: an independent review of 71 cases. J Neurosurg. 1999. 91(suppl):186–92.

3.Song KJ., Kim SJ. Surgical treatment for the low grade lumbar isthmic spondylolisthesis: comparison between posterolateral fusion and posterior lumbar interbody fusion. J Kor Soc Spine Surg. 1999. 6:96–103.
4.Herkowitz HN., Kurz ST. Degenerative lumbar spon-dylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991. 73:802–8.
5.Charles Dean Ray. Threaded titanium cages for lumbar interbody fusions. Spine. 1997. 22:667–79.
6.Gyorgy I., Csecsei ph D., Almos P. Klekner Jozsef Dobal. Posterior interbody fusion using laminectomy bone and transpedicular screw fixation in the treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine. 2000. 53:2–7.
7.Zhao Jie., Yong Hai., Nathaniel R. Ordway, Choon Keun. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using posterolateral placement of a single cylindrical threaded cage. Spine. 2000. 25:425–30.
8.Suk KS., Jeon CH., Lee HM., Kim NH., Kim HC. Compari-son between posterolateral fusion with pedicle screw fixation and anterior interbody fusion with pedicle screw fixation in sondylolisthesis of the lumbar spine. J Kor Soc Spine Surg. 1999. 6:397–406.
9.Ricciard JE., Pflueger PC., Isaza JE., Whitecloud TS 3rd. Transpedicular fixation for the treatment of isthmic spon-dylolisthesis. Spine. 1995. 10:821–27.
10.Shin BJ., Min KD., Kwon H, et al. Surgical results of isthmic spondylolisthesis-Comparison of posterolateral fusion vs. PLIF. J Kor Soc Spine Surg. 1996. 3:61–8.
11.Csecsei G., Klekner AP., Dobai J., Lajgut A., Sikula J. Posterior interbody fusion using laminectomy bone and transpedicular screw fixation in the treatment of lumbar spondylolis-thesis. Surg Neural. 2000. 53:2–6.
12.Christian WA. Pfirmann, Alexander Metzdorf: Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 2001. 26:1873–8.
13.Kirkaldy-Willis WH., Panie KWR., Cauchoix J., McIvor G. Lumba spinal stenosis. Clin Orthop. 1974. 99:30–52.
14.Crenshaw AH. Spondylolisthesis. Campbell's operative or-thopedics. 8th ed. 1992. 14:3243–51.
15.Kim YT., Lee CS., Na HY., Lee CW. A comparison of surgical treatment in isthmic and degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1998. 33:1627–34.

16.Lombardi JS., Wiltes LL., Reynolds J., Widell EH. Treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1985. 10:821–27.

17.Dilip K. Sengupta, Hnarry N. Herkowitz. Degenerative spondylolisthesis. 2005. 30(suppl):71–81.
18.Lenke LG., Birdwell KH., Bullis D., Betz RR., Baldus C. Results of in situ fusions for isthmics spondylolisthesis. J Spinal Disorder. 1992. 5:433–41.
19.Kim SS., Denis F., Lonstein JE., Winter RE. Factors affecting fusion rate in adult spondylolisthesis. Spine. 1990. 15:979–84.

20.Halvorson TL., Kelley LA., Thomas KA., Whitecloud TS 3rd., Cook SD. Effects of bone mineral density on pedicle screw fixation. Spine. 1994. 19:2415–20.

21.O'Brien MF. Low-grade isthmic/lytic spondylolisthesis in adults. Inst Course Lect. 2003. 52:511–24.
22.Montgomery DM., Fischgrund JS. Passive reduction of spondylolisthesis on the operating room table: a prospective study. J Spinal Disord. 1994. 7:167–72.
Table 1.
Analyzation and comparision between each groups




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download