Abstract
Objectives
We analyzed clinical symptom, findings of MRI, and surgical outcome of spinal intradural tumor.
Summary of Literature Review
Intradural tumors are not commonly reported and they show non-specific clinical features.
Materials and Methods
In this study, 18 patients who underwent surgical treatment and radiologically and pathologically diagnosed as spinal intradural tumor from 1997 to 2009 were reviewed. We evaluated pain, neurological symptoms, location of tumor as well as degrees of signal intensity and its enhancement of MRI(T1 and T2). And clinical outcomes were analyzed according to Klekamp-Samii scoring system and Visual Analogue Scale(VAS).
Results
All patients were clinically suffered from back pain and radiating pain of lower extremity including 3 patients with neurological symptoms. We radiologically found single tumor in 16 cases and masses more than two lesion in 2 cases. 1 case was located on cord level(T7), 14 cases cauda equine level, and 3 cases sacral level. We performed laminectomy in 18 cases and posterior instrumentation was applied to 8 cases. In clinical features, mean Klekamp-Samii score was improved from 21.6 to 23.5(p<0.05) and VAS was recovered from 5.2 to 3.0 (p<0.05).
REFERENCES
1. Ahn SJ, Song MH, Yoo SH, Lee MS, Kang SW, Kim BJ. Solitary intradural metastatic tumor from renal cell carcino-ma. A case report. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2009; 16:299–303.

2. Ha KY, Ryoo SJ, Lee JS, Cho YH. Distant intradural metastasis by direct seeding through dural opening from the metastasis of rectal cancer. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2005; 12:83–6.

3. Van Goethem JW, van den Hauwe L, Ozsarlak O, De Schepper AM, Parizel PM. Spinal tumors. Eur J Radiol. 2004; 50:159–76.

4. Conti P, Pansini G, Mouchaty H, Capuano C, Conti R. Spinal neurinomas: retrospective analysis and longterm outcome of 179 consecutively operated cases and review of the literature. Surg Neurol. 2004; 61:34–43.

6. el-Mahdy W, Kane PJ, Powell MP, Crockard HA. Spinal intradural tumours: Part I–Extramedullary. Br J Neurosurg. 1999; 13:550–7.

7. Shin BJ, Lee JC, Yoon TK, et al. Surgical treatments of intradural extramedullary tumor. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2002; 9:230–7.

8. Jinnai T, Koyama T. Clinical characteristics of spinal nerve sheath tumors: analysis of 149 cases. Neurosurgery. 2005; 56:510–5.

9. Friedman DP, Tartaglino LM, Flanders AE. Intradural schwannomas of the spine: MR findings with emphasis on contrast-enhancement characteristics. AJR Am J Roent-genol. 1992; 158:1347–50.

10. Roux FX, Nataf F, Pinaudeau M, Borne G, Devaux B, Meder JF. Intraspinal meningiomas: review of 54 cases with discussion of poor prognosis factors and modern therapeutic management. Surg Neurol. 1996; 46:458–63.

11. Gezen F, Kahraman S, Canakci Z, Beduk A. Review of 36 cases of spinal cord meningioma. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:727–31.

12. Harry N. The spine. The textbook of spinal surgey. 4th. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co;1998. p. 1366.
13. Stein BM, McCormick PC. Intramedullary neoplasms and vascular malformations. Clin Neurosurg. 1992; 39:361–87.
14. Kane PJ, el-Mahdy W, Singh A, Powell MP, Crockard HA. Spinal intradural tumours: Part II–Intramedullary. Br J Neurosur. 1999; 13:558–63.

15. Miller DC. Surgical pathology of intramedullary spinal cord neoplasms. J Neurooncol. 2000; 47:189–94.
16. Traul DE, Shaffrey ME, Schiff D. Part I: spinal-cord neo-plasms-intradural neoplasms. Lancet Oncol. 2007; 8:35–45.

17. Cushing H, Eisenhardt L. Meningiomas: their classification, regional behavior, life history and surgical end results. 1st. Ilinois, Spingfield: Charles C Thomas;1938. p. 735.
18. McCormick PC. Anatomic principles of intradural spinal surgery. Clin Neurosurg. 1994; 41:204–23.
Figures and Tables%
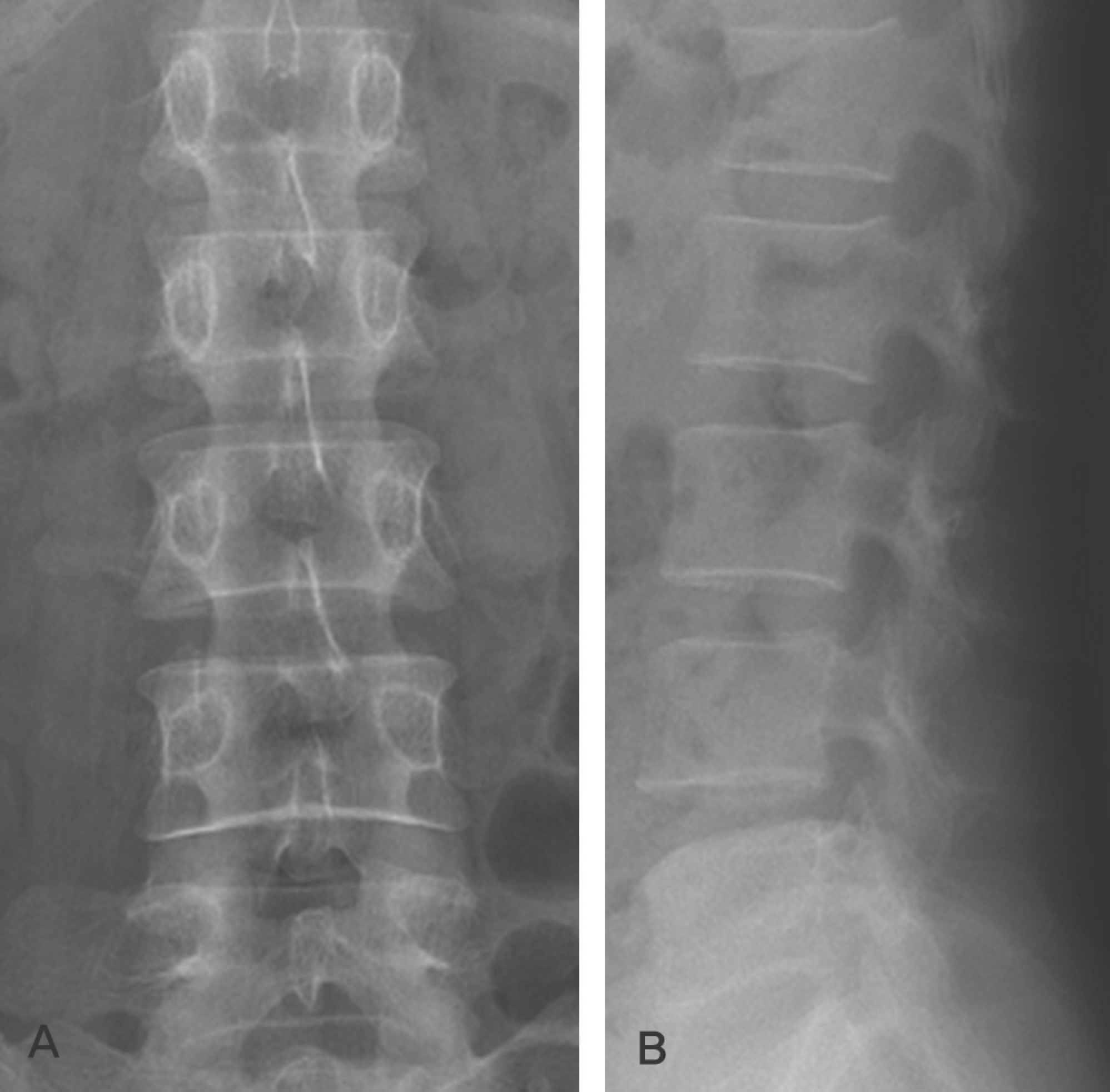
Fig. 2.
There are well-defined masses lesion with intermediate signal intensity on both T1(A) and T2 weighted images(B) at the level of L1 and L4, re-spectively. The lesions show homogenous, strong enhancement(C).

Fig. 3.
Intraoperative photograph shows totally encapsulated intradural mass(A). Two encapsulated tumors are resected from different locations(B, C).

Fig. 5.
Enhanced MRI show schwannoma with peripheral enhancement on sagittal (A) and axial(B) images.

Table 1.
Klekamp-Samii neurological scoring system.
Table 2.
Intradural spinal cord neoplasms.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download