Abstract
Study Design
A review of literature including definition, diagnosis and treatment of neuropathic pain.
Summary of Literature Review
Neuropathic pains are characterized by partial or complete somatosensory change caused by various disorders affecting central and peripheral nervous system, and are especially problematic because of their severity, chronicity and resistance to simple analgesics.
Results
Tricyclic antidepressants and the anticonvulsants gabapentin and pregablin were recommended as first-line treatments for neuropathic pain. Opioid analgesics and tramadol were recommended as second-line treatments that can be considered for first-line use in selected clinical circumstances. Other medications such as dual reuptake inhibitors of both serotonin and norepinephrine would be used in severe cases. More invasive interventions (e.g., spinal cord stimulation) may sometimes be helpful.
REFERENCES
1. Merskey H, Bodguk N. Lumbar zygapophysial joint pain syndromes and definition of pain terms. 2nded.Seattle: IASP Press;1994. p. 181–2.
2. Hansson P. Neuropathic pain: clinical characteristics and diagnostic workup. Eur J Pain. 2002; 6(suppl A):47–50.

4. Jensen TS, Sindrup SR, Bach FW. Test the classification of pain: reply to Mitchell Max. Pain. 2002; 96:407–8.
6. Dworkin RH, Backonja M, Rowbotham MC, et al. Advances in neuropathic pain: diagnosis, mechanisms, and treatment recommendations. Arch Neurol. 2003; 60:1524–34.
7. Cruccu G, Anand P, Attal N, et al. EFNS guidelines on neuropathic pain assessment. Eur J Neurol. 2004; 11:153–62.

8. Woolf CJ, Mannion RJ. Neuropathic pain. Etiology, symptoms, mechanisms, and management. Lancet. 1999; 353:1959–64.
9. Treede RD, Jensen TS, Campbell JN, et al. Neuropathic pain: redefinition and a grading system for clinical and research purposes. Neurology. 2008; 29:1630–5.

10. Bennett M, Smith B, Torrance N, et al. The S-LANSS score for identifying pain of predominantly neuropathic origin: Validation for use in clinical and postal research. J Pain. 2005; 6:149–58.

11. Gilron I, Bailey JM, Tu D, et al. Morphine, gabapentine, or their combination for neuropathic pain. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1324–34.
12. Dworkin RH, O'Connor AB, Backonja M, et al. Parmacologic management of neuropathic pain: evidence-based recommendations. Pain. 2007; 132:237–51.
13. Gilron I, Bailey JM, Holden RR, et al. Morphine, gabapentin. or their combination for neuropathic pain N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1324–34.
14. Raja SN, Haythornthwaite JA, Pappagallo M, et al. Opioids versus antidepressants in postherpetic neuralgia: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Neurology. 2002; 59:1015–21.

15. Finnerup NB, Otto M, McQuay HJ, et al. Algorithm for neuropathic pain treatment: an evidence based proposal. Pain. 2005; 118:289–305.

16. Bel S, Bauer BL. Dorsal column stimulation (DCS): cost to benefit analysis. Acta Neurchir Suppl(Wien). 1991; 52:121–3.

17. Kumar K, Hunter G, Demeria D. Spinal cord stimulation in treatment of chronic benign pain: challenges in treatment planning and present tatus, a 22-year experience. Neurosurgery. 2006; 58:481–96.
18. Kumar K, Malik S, Demeria D. Treatment of chronic pain with spinal cord stimulation versus alternative therapies;cost-effectiveness analysis. Neurosurgery. 2002; 51:106–15.
19. North RB, Kidd D, Shipley J, et al. Spinal cord stimulation versus reoperation for failed back surgery syndrome; a cost effectiveness and cost utility analysis based on a randomized, controlled trial. Neurosurgery. 2007; 61:361–8.

20. De Vries J, De Jongste MJ, Spincemaille G, et al. Spinal cord stimulation for ischemic heart disease and peripheral vascular disease. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg. 2007; 32:63–89.

21. Horsch S, Schulte S, Hess S. Spinal cord stimulation in the treatment of peripheral vascular disease; results of a single center study of 258 patients. Angiology. 2004; 55:111–8.
22. Harke H, Gretenkort P, Ladleif HU, et al. Spinal cord stimulation in sympathetically maintained complex regional pain syndrome type I with severe disability. A prospective clinical study. Eur J Pain. 2005; 9:363–73.

23. Taylor RS, Van Buyten JP, Buchser E. Spinal cord stimulation for complex regional pain syndrome: a systematic review of the clinical and cost-effectiveness literature and assessment of prognostic factors. Eur J Pain. 2006; 10:91–101.

24. Daousi C, Benbow J, MacFarlane IA. Electrical spinal cord stimulation in the longterm treatment of chronic painful diabetic neuropathy. Diabet Med. 2005; 22:393–8.

Figures and Tables%
Fig. 1.
This algorithm shows the management of neuropathic pain in primary care. Topical antineuralgics such as lidocaine patch is useful for focal neuropathy such as postherpetic neuralgia.
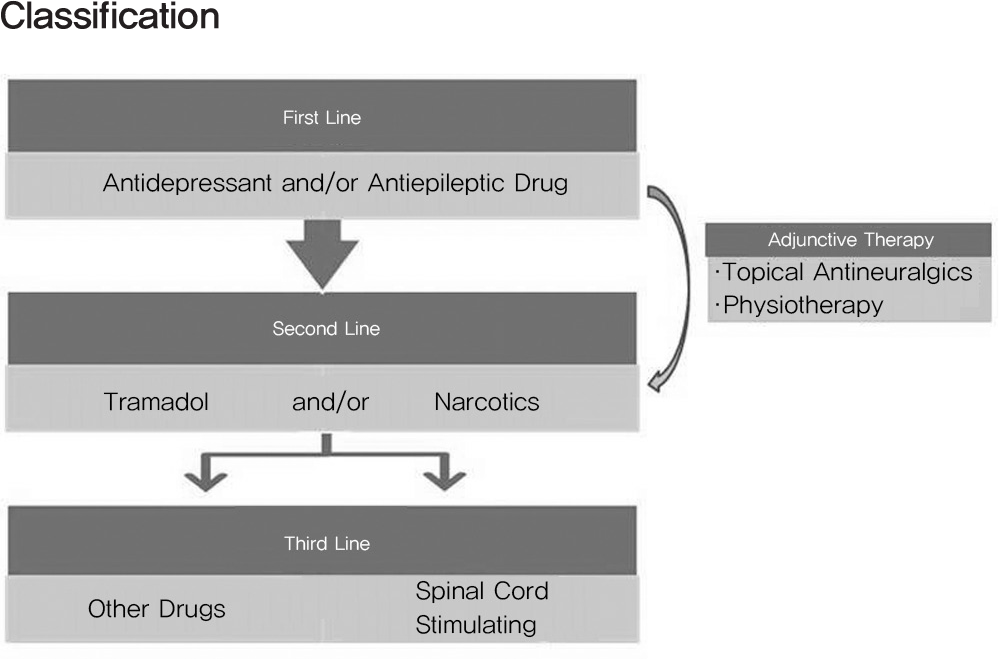
Table 1.
Classification of neuropathic pain by anatomical location and etiology.
Table 2.
Grading system for neuropathic pain.9)
Table 3.
Neuropathic pain medications.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download