Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the three-plus year followup results of patients who underwent posterior lumbar interbody fusion with PEEK cage and pedicle screw fixation for lumbar degenerative disease.
Summary of Literature Review
There are few previous reports addressing posterior lumbar interbody fusion using PEEK cage with midterm follow up periods.
Materials and Methods
260 patients who underwent posterior lumbar interbody fusion with PEEK cage and pedicle screw fixation for lumbar degenerative disease were enrolled. We classified patients into three groups according to their fusion level: group A (n=151) had one-level fusion, and group B (n=91) had two-level fusion, and group C (n=18) had three-level fusion. Clinical outcomes were evaluated by pre- and postoperative Visual analogue scale (VAS) scores, the Oswestry Disability Index (ODI), and complication and reoperation rates. Radiologic outcomes were measured by the fusion rate, sagittal alignment, disc height and changes.
Results
VAS (pre-operative to final followup) changed from 7.62±2.03 (5-10) to 3.19±1.94 (1-8) in group A, from 6.83±2.28(4-9) to 4.51±2.18(2-9) in group B and from 7.17±2.46 (5-10) to 4.63±1.97(1-9) in group C. Final followup ODI also decreased in group A (17.6±8.56%), group B (15.4±5.46%) and group C (24.7±7.46%). This corresponds to scores of 94.7% in group A, 92.3% in group B and 94.4% in group C. There were significant differences between preoperative, postoperative and final followup lumbar lordosis [p=0.042(group A), 0.036(group B), 0.045(group C)], segmental lordosis [p=0.036(group A), 0.039(group B), 0.047(group C)]. Reoperation was performed in patients 8 group A, 4 group B, and 1 group C, and there is no significant diffrence between groups. Adjacent segmental change was found in all reoperation patients, but showed no correlation with clinical results.
REFERENCES
1. Brantigan JW, Steffee AD, Geiger JM. A carbon fiber implant to aid interbody fusion. Mechanical testing. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1991; 16(6 Suppl):S277–82.
2. Brantigan JW, Steffee AD, Lewis ML, Quinn LM, Persenaire JM. Lumbar interbody fusion using the Brantigan I/F cage for posterior lumbar interbody fusion and the variable pedicle screw placement system: two-year results from a Food and Drug Administration investigational device exemption clinical trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000; 25:1437–46.
3. Brodke DS, Dick JC, Kunz DN, McCabe R, Zdeblick TA. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion. A biomechanical comparison, including a new threaded cage. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22:26–31.
4. Csé csei GI, Klekner AP, Dobai J, Lajgut A, Sikula J. Posterior interbody fusion using laminectomy bone and transpedicular screw fixation in the treatment of lumbar spondylolisthesis. Surg Neurol. 2000; 53:2–6.
5. Elias WJ, Simmons NE, Kaptain GJ, Chadduck JB, Whitechill R. Complications of posterior lumbar interbody fusion when using a titanium threaded cage device. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93(1 Suppl):45–52.

6. Mardjetko SM, Connolly PJ, Shott S. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. A meta-analysis of literature 1970-1993. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1994; 19(20 Suppl):2256S–65S.
7. Park JT, Shin YS, Yang JH, Seo BG. The fusion rate and clinical effect of PLIF with laminected lamina and spinous process. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1998; 5:79–85.
8. Schlegel KF, Pon A. The biomechanics of posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) in spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985; 193:115–9.

9. Shin BJ, Kim GJ, Ha SS, Chung SH, Kwon H, Kim YI. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion using laminar bone block. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1999; 6:110–6.
10. Steffee AD, Sitkowski DJ. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion and plates. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; 227:99–102.

11. Kim KT, Suk KS, Kim JM. Fusion development of interbody fusion cages. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2001; 8:386–91.
12. Glaser J, Stanley M, Sayre H, Woody J, Found E, Spratt K. A 10-year followup evaluation of lumbar spine fusion with pedicle screw fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:1390–5.

13. Agazzi S, Reverdin A, May D. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion with cages: an independent review of 71 cases. J Neurosurg. 1999; 91(2 Suppl):186–92.

14. Shin BJ, Lee JJ. Results of decompression and internal fixation for spinal stenosis more than 5 year followup. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1998; 2:272–7.
15. Brantigan JW, Neidre A, Toohey JS. The lumbar I/F cage for posterior lumbar interbody fusion with the variable screw placement system: 10-year results of a Food and Drug Administration clinical trial. Spine J. 2004; 4:681–8.

16. Fischgrund JS, Mackay M, Herkowitz HN, Brower R, Montgomery DM. 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: a prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22:2807–12.
17. Thomsen K, Christensen FB, Eiskjaer SP, Hansen ES, Fruensgaard S, Bunger CE. 1997 Volvo Award winner in clinical studies. The effect of pedicle screw instrumentation on functional outcome and fusion rates in posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion: a prospective, randomized clinical study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1997; 22:2813–22.
18. Herno A, Saari T, Suomalainen O, Airaksinen O. The degree of decompressive relief and its relation to clinical outcome in patients undergoing surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24:1010–4.

19. Cho KJ, Moon KH, Kim MK, et al. Changes of Clinical Outcomes after Decompression and Fusion for Spinal Stenosis during 2-Year Followup Periods. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2003; 10:113–8.

20. Brantigan JW, Neidre A, Toohey JS. The lumbar I/F cage for posterior lumbar interbody fusion with the variable screw placement system: 10-year results of a Food and Drug Administration clinical trial. Spine J. 2004; 4:681–8.

21. Christensen FB, Hansen ES, Laursen M, Thomsen K, Bunger CE. Longterm functional outcome of pedicle screw instrumentation as a support for posterolateral fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002; 27:1269–77.
22. Rahm MD, Hall BB. Adjacent-Segment Degeneration After Lumbar Fusion with Instrumentation: A Retrospective Study. J Spinal Disord. 1996; 9:392–400.
Figures and Tables%
Fig. 1.
A 69-year-old female presented with back pain, sciatica and neurogenic claudication.(A) Plain lateral radiograph shows degenerative changes on L4-5 lumbar disc space.(B) T2-weighted MRI(sagittal, axial view) shows that dural sac was compressed by extruded disc material and hypertrophied ligamentum flavum on L4-5. (C) Postoperative radiograph shows posterior lumbar interbody fusion with PEEK cage and pedicle screw fixation on L4-5. (D) 3 years after surgery, radiograph shows solid fusion mass on L4-5.
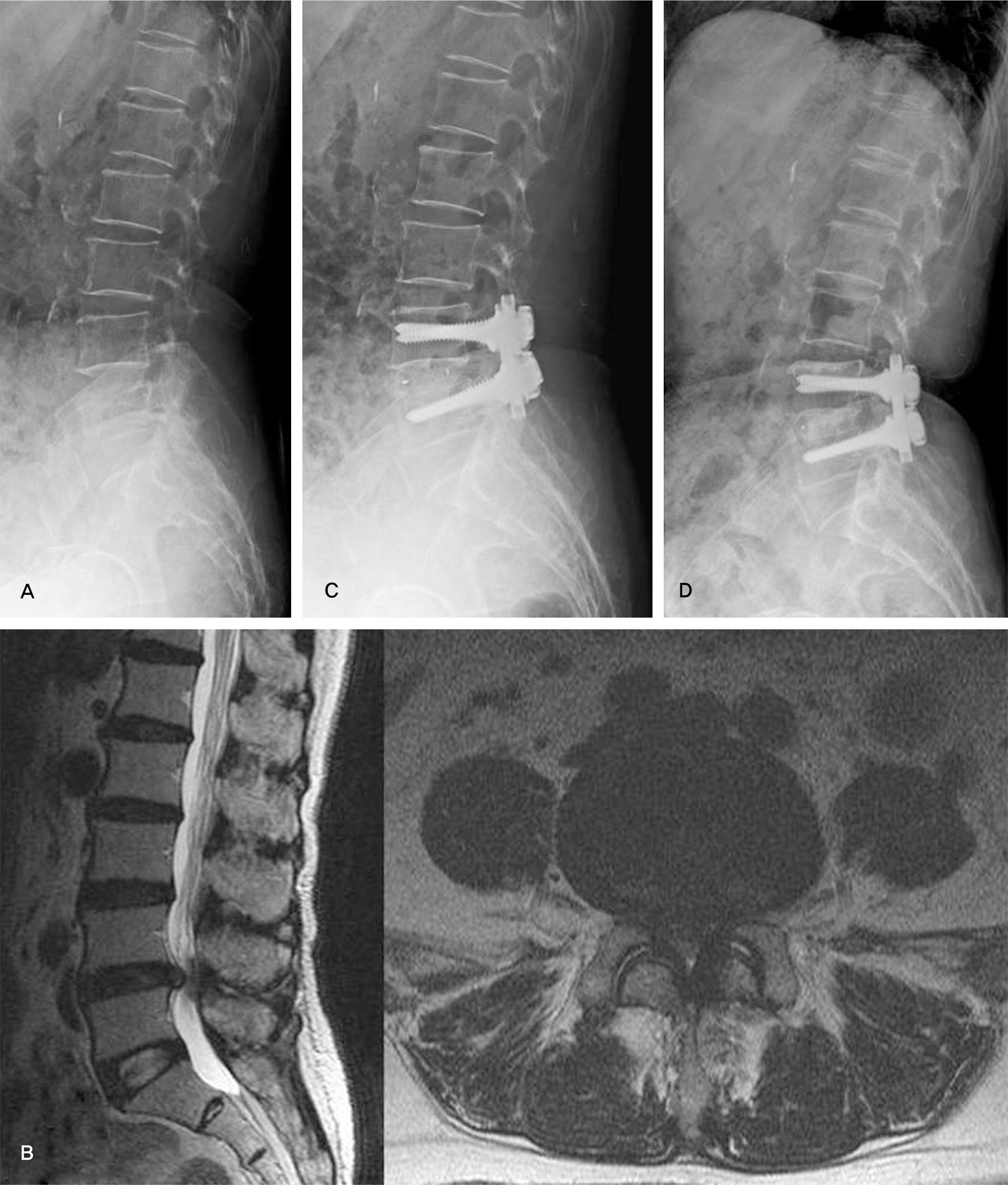
Fig. 2.
A 61-year-old female presented with back pain and sciatica.(A) Plain lateral radiograph shows degenerative changes and isthmic spondylolisthesis on L4-5 lumbar disc space.(B) T2-weighted MRI(sagittal, axial view) shows spinal stenosis and on L3-4 and L4-5. (C) Postoperative radiograph shows posterior lumbar interbody fusion with PEEK cage and pedicle screw fixation on L3-4 and L4-5. (D,E) 2 years after surgery, radiograph shows adjacent segmental degeneration on L1-2 and L2-3.(F) Revision surgery was performed.
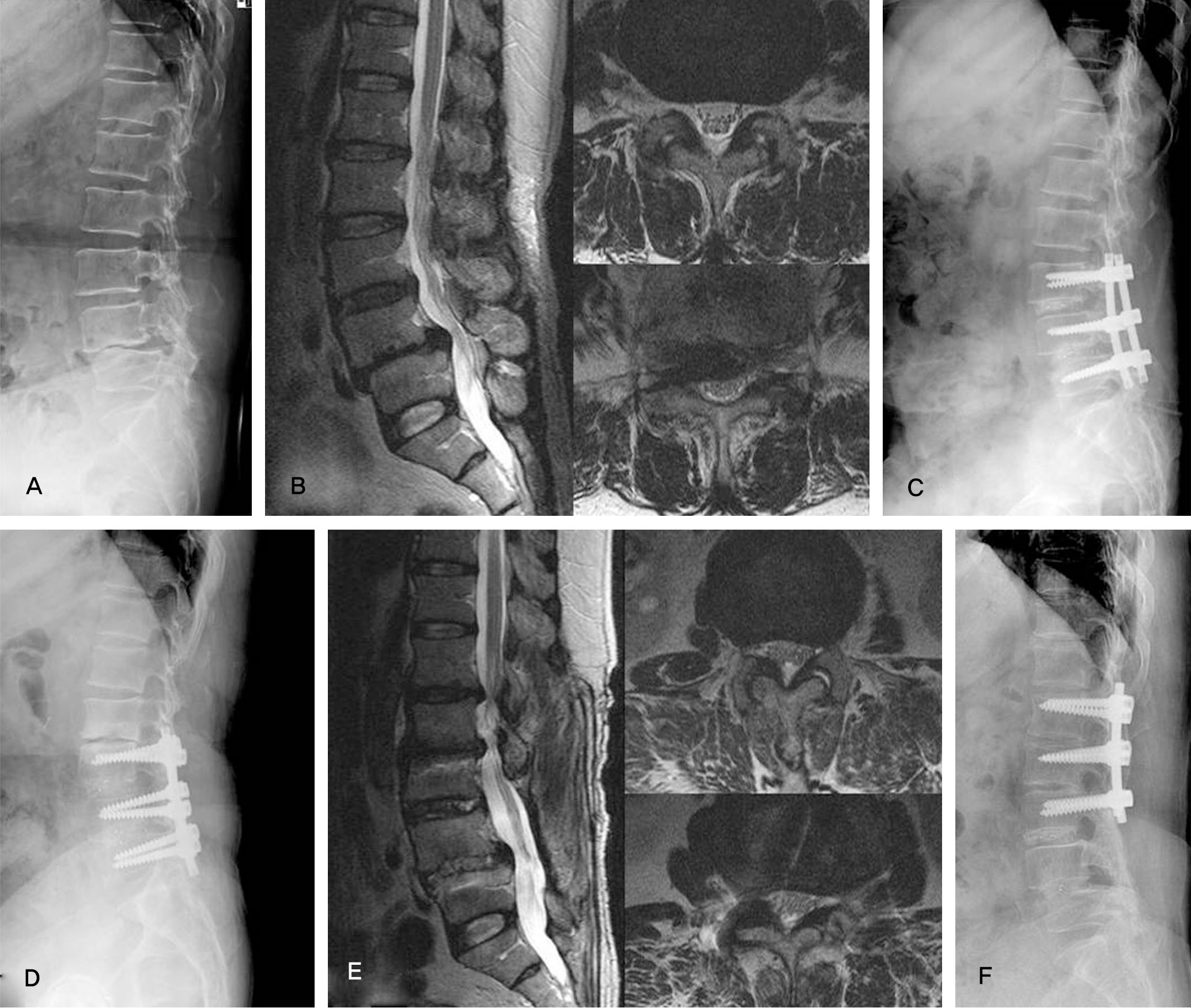
Table 1.
Demography of Patients
| Group A | Group B | Group C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case(No) | 151 | 91 | 18 |
| Sex(M:F) | 67:84 | 38:53 | 7:11 |
| Age(years) | 58.73±8.13 | 61.24±6.51 | 64.47±9.08 |
| Preoperative Diagnosis | |||
| LSS * | 101 | 64 | 16 |
| SLT † | 25 | 7 | 0 |
| LSS with SLT | 7 | 19 | 2 |
| HLD ‡ | 18 | 1 | 0 |
Table 2.
Changes of disc height, Lumbar lordosis, segmental lordosis, visual analog scale (VAS) and Oswestry disability index (ODI)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download