Abstract
Objectives
To evaluate the effectiveness of unilateral extrapedicular approach in the treatment of osteoporotic compression fracture, as compared to transbipedicular approach.
Materials and Methods
115 patients presenting with percutaneous vertebroplasty between Mar. 2002 and Feb. 2009, were divided into three groups: Group A (43 vertebrae; 29 patients) who were treated with bipedicular approach, Group B (66 vertebrae; 47 patients) treated with early cases of unilateral extrapedicular approach, and Group C (43 vertebrae; 39 patients) treated with late cases of unilateral extrapedicular approach. We analyzed radiological test results including the volume of injected cement and the distribution of intravertebral body, cement leakage, height restoration and kyphosis correction. Statistical analysis was done using SPSS. Clinical results were analyzed using VAS scores.
Results
The mean followup period varied from one year at minimum to seven years and six months at maximum. The mean volume of injected cement was 3.39cc/5.39cc/3.79cc for groups A, B and C respectively. Cement leakage was at 13.4/34.8/12.8% in each group. Cement leakage was higher in group B, but most leakage took place in early cases that we tried to inject more and more cement in early inexperienced period. Bilaterally well distributed cement in the vertebral body was at 85.7/76.9% in groups B and C respectively. VAS scores improved from 8.4/8.3/8.5 preoperatively to 2.0/2.0/1.6 postoperatively.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, Le Gars D. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty. Neurochirurgie. 1987; 33:166–8.
2. Deramond H, Depriester C, Galibert P, Le Gars D. Percutaneous vertebroplasty with polymethylethacrylate. Technique, indications, and results. Radiol Clin N Am. 1998; 36:533–6.
3. Kallmes DF, Schweickert PA, Marx WF, Jensen ME. Vertebroplasty in the mid- and upper thoracic spine. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1117–20.
4. Cotten A, Boutry N, Cortet B, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty: state of the art. Radiographics. 1998; 18:311–20.

5. Molloy S, Mathis JM, Belkoff SM. The effect of vertebral body percentage fill on mechanical behavior during percutaneous vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003; 28:1549–54.

6. Diamond TH, Champion B, Clark WA. Management of acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a nonrandomized trial comparing percutaneous vertebroplasty with conservative therapy. Am J Med. 2003; 114:257–65.

7. Belkoff SM, Mathis JM, Jasper LE, Deramond H. The biomechanics of vertebroplasty. The effect of Cement Volume on Mechanical Behavior. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:1537–41.
8. Molloy S, Riley III, Belkoff SM. Effect of Cement Volume and Placement on Mechanical-Property Restoration Resulting from Vertebroplasty. AJNR Am Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:401–4.
9. Liebschner MA, Rosenberg WS, Keaveny TM. Effects of bone cement volume and distribution on vertebral stiffness after vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:1547–54.

10. Steinmann J, Tingey CT, Cruz G, Dai Q. Biomechanical comparison of unipedicular versus bipedicular kyphoplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:201–5.

11. Tohmeh AG, Mathis JM, Fenton DC, Levine AM, Belkoff SM. Biomechanical efficacy of unipedicular versus bipedicular vertebroplasty for the management of osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1999; 24:1772–6.

12. Padovani B, Kasriel O, Brunner P, Peretti-Viton P. Pulmonary embolism caused by acrylic cement: a rare complication of percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:375–7.
13. Ratliff J, Nguyen T, Heiss J. Root and spinal cord compression from methylmethacrylate vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:E300–2.

14. Yang JY, Lee JK, Cha SM, Joo YB. Clinical Results of Unilateral Partial Vertebroplasty(UPVP) in Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 2011; 18:64–9.

15. Garfin S, Lin G, Lieberman I, et al. Retrospective analysis of the outcome of balloon kyphoplasty to treat vertebral compression fracture refractory to medical management. Eur Spine J. 2001; 10(Supple):7.
Go to : 
Figures and Tables%
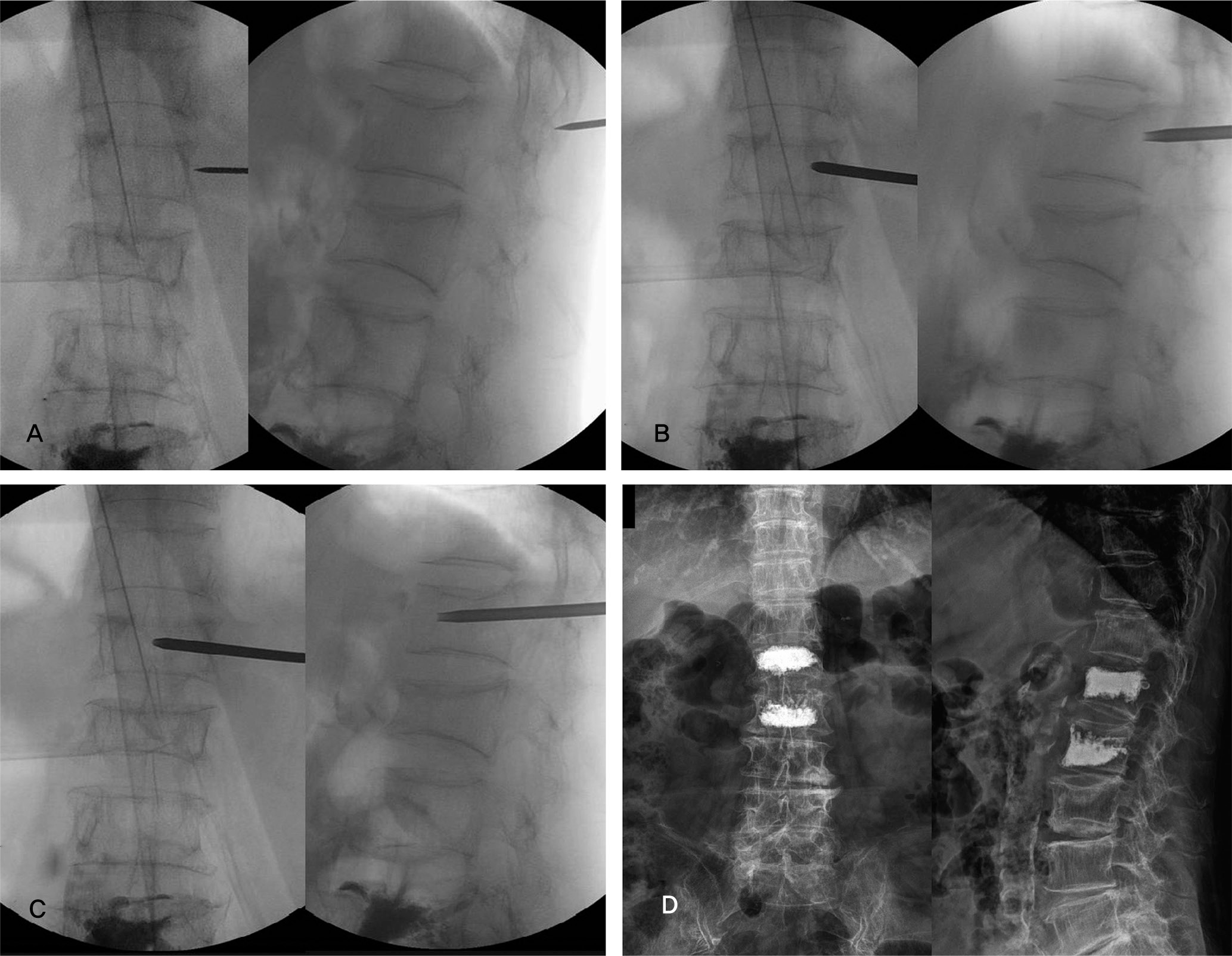 | Fig. 1.(A) Entry Point: in the AP spot, just lateral 0.5-1cm superolateral to vertebral body. in the lateral spot, needle should be located at junction of transverse process and facet joint or rib.(B) Needle should be inserted with appropriate convergency. Proper convergency is that needle tip is located at medial wall of pedicle in the AP spot. And 5mm anterior to posterior sagittal line in the lateral spot. (C) Recommandable final needle position is closer to midline of vertebral body in the AP spot. and anterior 3/4 of body in the lateral spot. (D) The postoperative plain film shows successful cement injection with bilateral distribution evenly. |
Table 1.
Height restoration of vertebral body in each groups. (unit:%)
Table 2.
Correction of local kyphotic angle in each groups. (unit: degree)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download