I. Introduction
II. Methods
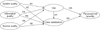
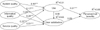
1. Research Model
System quality: This is said to measure the desirable characteristics of an information system. Several IS studies have measured this using such characteristics as perceived ease of use, system features, response time, and flexibility [9]. However, this study assessed system quality by examining the ease of use associated with hospital information systems as well as functionality and flexibility.
Information quality: This has to do with content issues and characteristics of the information systems output. It has been measured by examining the output of an information system in terms of timeliness, accuracy, reliability, and trustworthiness [9]. This study operationalized information quality in terms of the correctness, usefulness and timeliness of the information generated by the hospital information system in use.
Service quality: This is measured in terms of the quality of support rendered by the information system's developer. Studies have assessed this using service quality dimensions, such as assurance and responsiveness by the systems support department, as well as the provision of user training [9]. In this study, service quality was measured by examining the technical support in place for users of a hospital information system, the network infrastructure in place, and the reliability of the system.
Intention to use/Use: This is concerned with assessing the manner in which an information system is used. Various studies have measured this by examining actual usage or sometimes, the frequency of use [9]. The intention to use is said to be an alternative measure to use for some other context, depending on the nature of the information system [4]. Since most institutions having a hospital information system in place expect and mandate their employees to use the system, this study assessed use from the angle of perceived usefulness, as studies have pointed out measuring actual use, in this case, may be pointless [11].
User satisfaction: This is considered one of the most important measures of systems success, often measured by overall user satisfaction [49]. It was assessed in the study by capturing overall user satisfaction with the hospital information system.
Net benefits: This is also regarded as one of the most important measures of IS success, and it constitutes the extent to which an IS contributes to the success of various stakeholders, whether positive or negative. It has been measured by sometimes assessing individual impact or organizational impact [9]. This study, however, examined net benefits as perceived net benefits, since primary users of the hospital information system were surveyed in this study.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download