Abstract
Objectives
The recent evolution of mobile devices has opened new possibilities of providing strongly integrated mobile services in healthcare. The objective of this paper is to describe the decision driver, development, and implementation of an integrated mobile Electronic Health Record (EHR) application at Ulsan University Hospital. This application helps healthcare providers view patients' medical records and information without a stationary computer workstation.
Methods
We developed an integrated mobile application prototype that aimed to improve the mobility and usability of healthcare providers during their daily medical activities. The Android and iOS platform was used to create the mobile EHR application. The first working version was completed in 5 months and required 1,080 development hours.
Results
The mobile EHR application provides patient vital signs, patient data, text communication, and integrated EHR. The application allows our healthcare providers to know the status of patients within and outside the hospital environment. The application provides a consistent user environment on several compatible Android and iOS devices. A group of 10 beta testers has consistently used and maintained our copy of the application, suggesting user acceptance.
Hospitals are increasingly using Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems. Such systems have numerous advantages, such as easier access to patient data, structured information, and improved patient safety through decision support and better access to information [1]. While dematerialization is one of the major advantages of computerization, it is surprisingly often associated with decreased mobility. This apparent contradiction is strongly observed in clinical settings with a heavy dependence on computers [2].
Working in a medical environment requires free mobility and usability. This is important for healthcare professionals who provide patient care in various situations. Since the induction of hospital information systems, this mobility has often been considered hindered by interaction with computers [3]. The use of personal mobile assistants, such as smartphones, makes it possible to gain access to clinical data anywhere quickly and easily.
Ulsan University Hospital (UUH) is a secondary general hospital located in Ulsan metropolitan city; it opened in March 1997. In 2009, UUH successfully launched a self-developed EHR system with the mission of improving the quality of medical care given to patients. The recent evolution of mobile devices has opened new possibilities of providing strongly integrated mobile services in healthcare. As the demand for mobile applications for healthcare providers have been increasing in UUH, we considered the deployment of mobile clinical EHR for healthcare provider in 2013.
This paper briefly describes the major components and features of the UUH mobile EHR application.
After opening in 1997 as university hospital, UUH opened a regional emergency medical center with a self-developed EMR system in 2009. In December 2012, the cancer center opened, and UUH expanded to 1,050 beds from 736 beds. A novel and cost efficient solution was necessary to improve clinician access to the hospital information system. The hospital director and manager decided to develop an integrated mobile EHR system to meet the needs of healthcare providers.
The UUH mobile EHR project was initiated to provide a convenient way to access the UUH hospital information system quickly and easily. We expect the mobile EHR application to improve the quality of individual patient care and the efficiency of care provision.
The mobile EHR task force team (TFT) decided to benchmark the source code of a commercial mobile EHR solution from BIT Computer Co., Ltd., Seoul, Korea and to develop a new one to meet our goals to shorten the time to develop the application. For a month, the mobile TFT identified an initial set of user needs through a healthcare provider survey, and the held meetings with every department to define the final set of user requirements.
In May 2013, the first beta working version was completed in 5 months, requiring 1,080 development hours. A group of 10 beta testers has consistently used and maintained our copy of the application, suggesting user acceptance.
In June 2013, the Mobile-Ulsan University Hospital Medical Information System (M-UMIS) was officially launched.
UUH has been establishing its hospital information management system through a medical computational team under the chief information officer (CIO). The mobile EHR TFT was organized to develop the application in Dec 2012. The TFT was composed of doctors from internal medicine, emergency medicine, and surgery as well as IT technicians, including developers and graphic designers. The mobile TFT comprises strategic planning, medical information management, and development teams.
The integrated mobile EHR application operating TFT includes the Electronic Medical Record (EMR), laboratory information system (LIS), picture archiving and communication system (PACS), nurse information system (NIS), and standardization TFT that make operational policy and decisions for the improvement of information systems for total quality control.
We developed an integrated mobile application prototype that is intended to improve the mobility and usability of medical records and information for healthcare providers during their daily medical activities. The Android and iOS platforms were used to create the mobile EHR application. M-UMIS was built in native Java programming and Objective-C. The specific features and design of M-UMIS are detailed in relationship to the requirements that drove developments: inpatient, outpatient, and emergency patient information; operation schedule; verbal orders; medical consultation; searching patients; on-duty scheduling views; salary views; cafeteria menu; telephone directory; and group ware board.
JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) was adapted for the Web-service protocol between mobile devices and server. For security, all data transmissions were carried over encrypted Internet connections as HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTPS) over Secure Sockets Layer within and outside the hospital.
Figure 1 shows the link between our mobile application and the current hospital electronic system. The main configuration of M-UMIS is shown in Figure 2.
The M-UMIS user interface can handle the various screen sizes or resolutions on Android or iOS devices. The user interface was chronologically structured to view time-based items (Figure 3).
Using the EHR application, most medical records can be electronically viewed to know the status of patients within and outside hospital. The various types of medical records can be viewed on the EHR application, including patient medical records; nursing charts; and clinical observation charts, including vital signs, medical consultation, and doctor's orders (Figure 4).
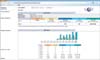
Figure 5 shows the total privilege management interface of the UUH hospital information system on a personal computer. This involves defining the appropriate administrators (which includes assigning the proper privileges and permission levels for security) and then setting up notification assignments based on their defined roles and domain ownership within our organization. If an installed device is lost or the user's account needs to be controlled, an administrator can respond promptly through this management system.
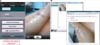
To support information to treat patients, this application helps medical staff work quickly to find important information, such as laboratory findings, electrocardiography results, and radiologic and diagnostic images. M-UMIS is particularly equipped with the ability to automatically convert the patient's electrocardiography results into JPG images on the self-developed transformation module (Figure 6).
M-UMIS enables nursing staff to simplify and automate round preparation and other daily tasks. Nurses can access patient information and nursing charts from anywhere with this application; thus, the mobile environment can reduce the workload.
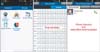
In 2013, UUH had to prepare for the Hospital Certification designated by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Korea. Many changes were required to establish proper healthcare service policies to allow the hospital to be certified. In many policies, the principle of verbal order processing must be settled without much difficulty. The mobile TFT decided to include the verbal orders processing system in the mobile application (Figure 7).
M-UMIS enables users to transfer patient images shot with built-in cameras on smartphone devices to patient medical records simply. M-UMIS also allows users to browse and playback images stored on their own devices. Uploaded photos allow healthcare providers to check the status of patients quickly and easily (Figure 8).
After the open beta test, the mobile TFT obtained feedback from beta testers and included the miscellaneous functions in the mobile EHR application. For example, this application provides operation schedule, medical consultation, searching patients, on-duty scheduling views, salary views, hospital cafeteria menu, telephone directory, and group ware board to healthcare providers (Figure 9).
In this paper, we introduced our experience of the development of an integrated mobile EHR application. Smartphones have already become an everyday part of many doctors' working lives. Health application can improve the quality of care and patient safety [5]. We also considered the integrated mobile EHR to improve the quality of individual patient care and the efficiency of care provision with hospital bed expansion.
The chief issues raised and resolved by this study, however, are the time required for development and costs. The increased costs and the time required could impede development of the application. The investment and adoption of a mobile platform technology in a hospital requires drastic innovation and support from hospital managers [6]. Our hospital manager considered mobile application development in relation to the high costs and long time required for its development. However, we could reduce the development time and costs of developing the final release version through simultaneously development and testing.
In the early stages of development, our hospital was concerned about the adoption of a commercial mobile application. The large volume and slow performance of commercial applications are inappropriate for a hospital setting. Therefore, the mobile TFT considered the practices of other hospitals and decided to develop an application on our own [7,8]. We also thought about an application suitable for quick information sharing between every healthcare provider. M-UMIS written in native codes supports healthcare providers from every compatible Android and iOS devices.
Our Mobile EHR application places emphasis on urgent and important tasks that need to be processed, reflecting the opinion of healthcare providers. Before development starts, we have defined user requirements through extensive surveys. M-UMIS has several features that appeal to users for sustainable usage. On-line analytical process tools were used to compensate systems to view the usage of data by application [9]. We periodically monitored the usage of the application and the number of log-ins to suit the changing needs and tasks of users. A gradual increased in data accessing via M-UMIS has been confirmed by the analytical tools.
As a limitation, it must be noted that, although we successfully developed the mobile EHR application, further evaluation of the application through its use by more healthcare providers seems to be needed.
We are developing the integrated mobile EHR application with the goals of implementing an environment that is user-friendly, implementing a patient-centered system, and increasing the hospital's competitiveness. Based on this vision, we will expand mobile EHR systems to enable our patients to access their medical information online.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Communication architecture between mobile application and the existing hospital information system. DMZ: demilitarized zone, PoE: power over Ethernet, AP: access point, DB: database, LAN: local area network.

Figure 2
Main configuration of Mobile-Ulsan University Hospital Medical Information System (M-UMIS) service. UUH: Ulsan University Hospital, LIS: laboratory information system, PACS: picture archiving and communication system, EMR: Electronic Medical Record.
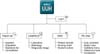
Figure 3
Basic layout of user interface of Mobile-Ulsan University Hospital Medical Information System. (A) Single sign-on login screen, (B) initial screen page, and (C) submenu screen.

Figure 4
Screen shots of Mobile-Ulsan University Hospital Medical Information System. (A) Medical records, (B) nurse transition chart, and (C) clinical observation chart.
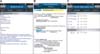
Figure 5
Total privilege management interface on a computer screen in the Ulsan University Hospital electronic system.
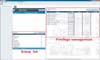
Figure 6
Laboratory information system and picture archiving and communication system (PACS) on Mobile-Ulsan University Hospital Medical Information System (M-UMIS). (A) Patient's electrocardiography, (B) PACS on M-UMIS.
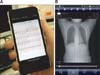
Figure 7
Verbal orders processing system in our hospital electronic system. M-UMIS: Mobile-Ulsan University Hospital Medical Information System.

Acknowledgments
We would like to thank BIT Computer Corporation for helping develop the proposed application.
References
1. Walker JM, Carayon P, Leveson N, Paulus RA, Tooker J, Chin H, et al. EHR safety: the way forward to safe and effective systems. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2008; 15(3):272–277.

2. Zhao QA, Stasko JT. Evaluating image filtering based techniques in media space applications. In : Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work; 1998 Nov 14-18; Seattle, WA. p. 11–18.
3. Ehrler F, Wipfli R, Teodoro D, Sarrey E, Walesa M, Lovis C. Challenges in the implementation of a mobile application in clinical practice: case study in the context of an application that manages the daily interventions of nurses. JMIR mHealth uHealth. 2013; 1(1):e7.

4. Destailleur L. AWStats logfile analyzer documentation [Internet]. Boulogne Billancourt, France: NLTechno;2005. cited at 2013 Oct 1. Available from: http://awstats.sourceforge.net/docs/.
6. Lee OF, Meuter ML. The adoption of technology orientation in healthcare delivery: case study of a large-scale hospital and healthcare system's electronic health record. Int J Pharm Healthc Mark. 2010; 4(4):355–374.
7. Choi JS, Yi B, Park JH, Choi K, Jung J, Park SW, et al. The uses of the smartphone for doctors: an empirical study from Samsung Medical Center. Healthc Inform Res. 2011; 17(2):131–138.

8. Choi J, Kim JW, Seo JW, Chung CK, Kim KH, Kim JH, et al. Implementation of consolidated HIS: improving quality and efficiency of healthcare. Healthc Inform Res. 2010; 16(4):299–304.

9. Srivastava J, Cooley R, Deshpande M, Tan PN. Web usage mining: discovery and applications of usage patterns from Web data. ACM SIGKDD Explor. 2000; 1(2):12–23.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download