Abstract
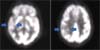
Plasmodium vivax malaria is an endemic disease in Korea, which rarely causes severe complications including those occurring in the cerebrum. There are limited numbers of complicated cases that have been reported around the world. We experienced a case of vivax malaria with cerebral complication: cognitive impairment and ataxia. A 55-year-old female with diabetes mellitus presented to the emergency department with acute fever of two days' duration. She did not have any history of travelling abroad or receiving blood transfusions. Peripheral blood smear revealed vivax malaria with parasitemia density of 0.53 percent. She demonstrated loss of orientation, especially regarding time and place, and ataxia. Although the initial hydroxychloroquine treatment for malaria was successful, cognitive impairment and ataxia persisted and were not recovered. Brain MRI showed no structural abnormality. Brain PET showed diffuse hypometabolism in right parieto-temporal lobe of the brain.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Statistics of infectious diseases. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. [cited July 27 2009]. Available from: URL:
http://stat.cdc.go.kr/index_List.aspx.
2. Park SW, Kim DW, Park JW, Lee SI, Shin YH, Kim EC, Oh MD, Choe KW. A case of fatal Plasmodium vivax malaria with multi-organ failure. Infect Chemother. 2005. 37:111–115.
3. Yoon SG, Kim MH, Jung ES, Han KH, Kwak YG, Cho CR, Um TH, Kim ES. A case of vivax malaria with seizure and shock. Infect Chemother. 2007. 39:226–229.
4. You JS, Lee JH, Chung SP, Goo HD, Park IC. Cardiac arrhythmia and pericardial effusion during Plasmodium vivax infection. Infect Chemother. 2006. 38:407–410.
5. Kim SA, Kim ES, Rhee MY, Choi SI, Huh HJ, Chae SL. A case of myocarditis associated with Plasmodium vivax malaria. J Travel Med. 2009. 16:138–140.

6. Severe falciparum malaria. World Health Organization, Communicable Diseases Cluster. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2000. 94:Suppl 1. S1–S90.
7. Idro R, Jenkins NE, Newton CR. Pathogenesis, clinical features, and neurological outcome of cerebral malaria. Lancet Neurol. 2005. 4:827–840.

8. Beg MA, Khan R, Baig SM, Gulzar Z, Hussain R, Smego RA Jr. Cerebral involvement in benign tertian malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2002. 67:230–232.

9. Kochar DK, Shubhakaran , Kumawat BL, Kochar SK, Halwai M, Makkar RK, Joshi A, Thanvi I. Cerebral malaria in Indian adults: a prospective study of 441 patients from Bikaner, north-west India. J Assoc Physicians India. 2002. 50:234–241.
10. Grote CL, Pierre-Louis SJ, Durward WF. Deficits in delayed memory following cerebral malaria: a case study. Cortex. 1997. 33:385–388.

11. Mishra SK, Newton CR. Diagnosis and management of the neurological complications of falciparum malaria. Nat Rev Neurol. 2009. 5:189–198.

12. Patankar TF, Karnad DR, Shetty PG, Desai AP, Prasad SR. Adult cerebral malaria: prognostic importance of imaging findings and correlation with postmortem findings. Radiology. 2002. 224:811–816.

13. Ozen M, Gungor S, Atambay M, Daldal N. Cerebral malaria owing to Plasmaodim vivax: case report. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2006. 26:141–144.
15. Tilluckdharry CC, Chadee DD, Doon R, Nehall J. A case of vivax malaria presenting with psychosis. West Indian Med J. 1996. 45:39–40.
16. Udomsanpetch R, Thanikkul K, Pukrittayakamee S, White NJ. Rosette formation by Plasmodium vivax. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1995. 89:635–637.
17. Sugiyama M, Ikeda E, Kawai S, Higuchi T, Zhang H, Khan N, Tomiyoshi K, Inoue T, Yamaguchi H, Katakura K, Endo K, Suzuki M. Cerebral metabolic reduction in severe malaria: fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography imaging in a primate model of severe human malaria with cerebral involvement. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004. 71:542–545.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download