Abstract
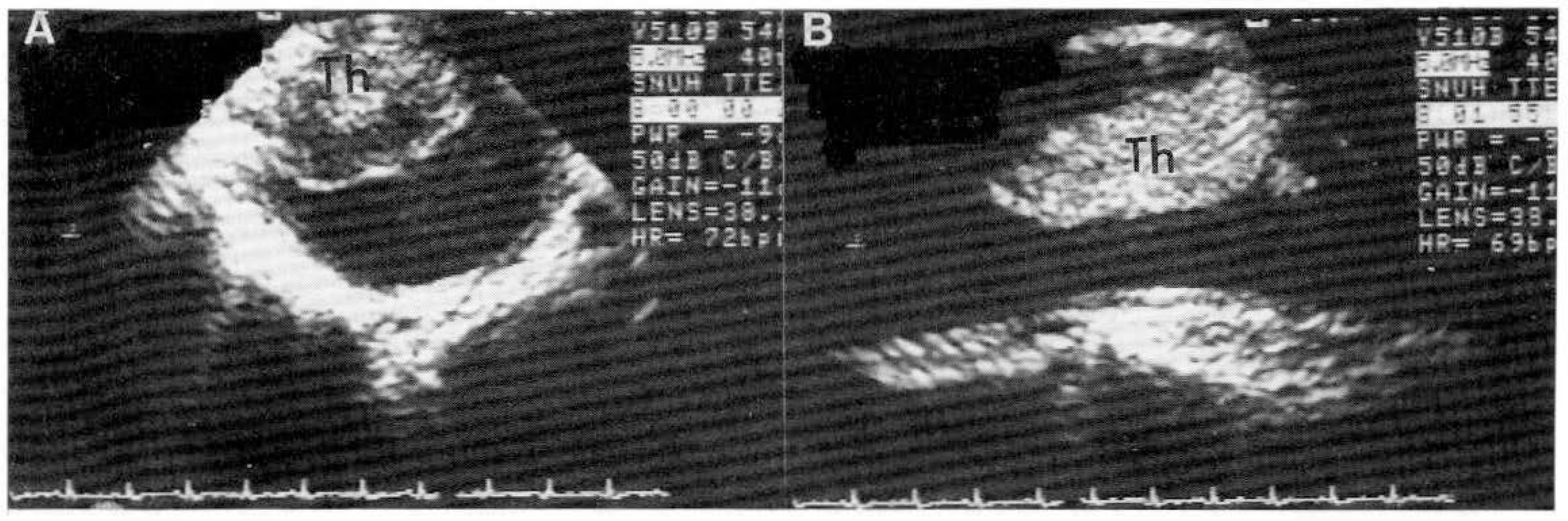
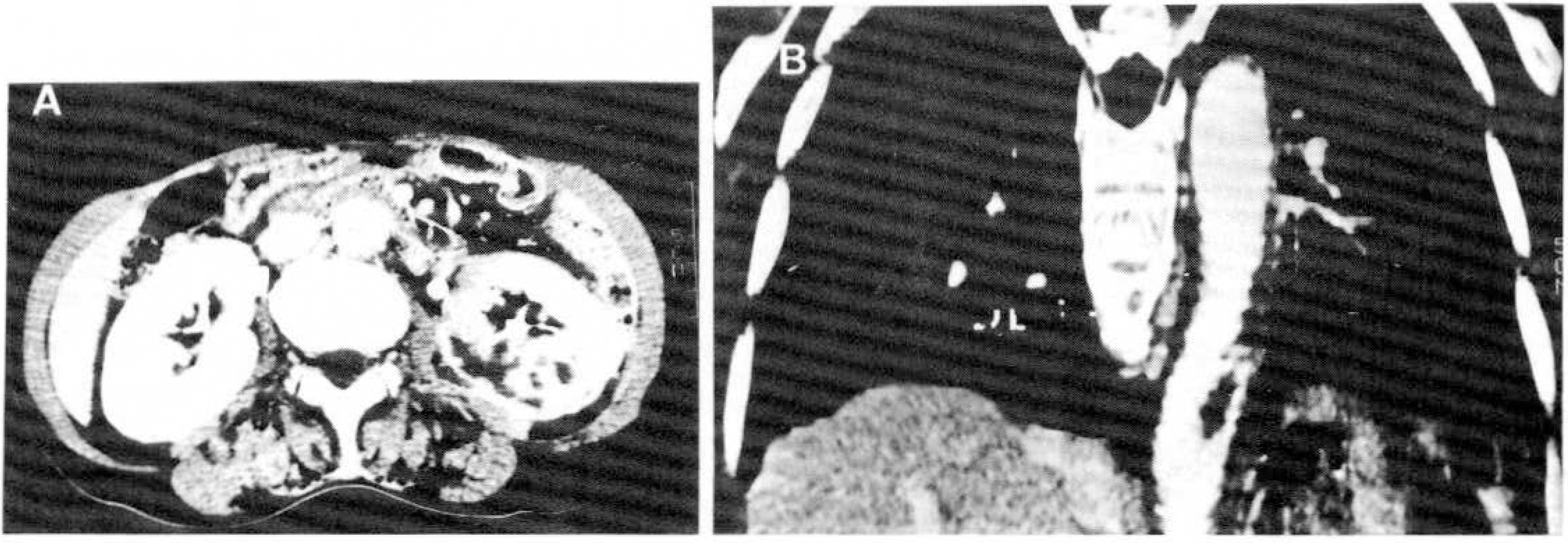
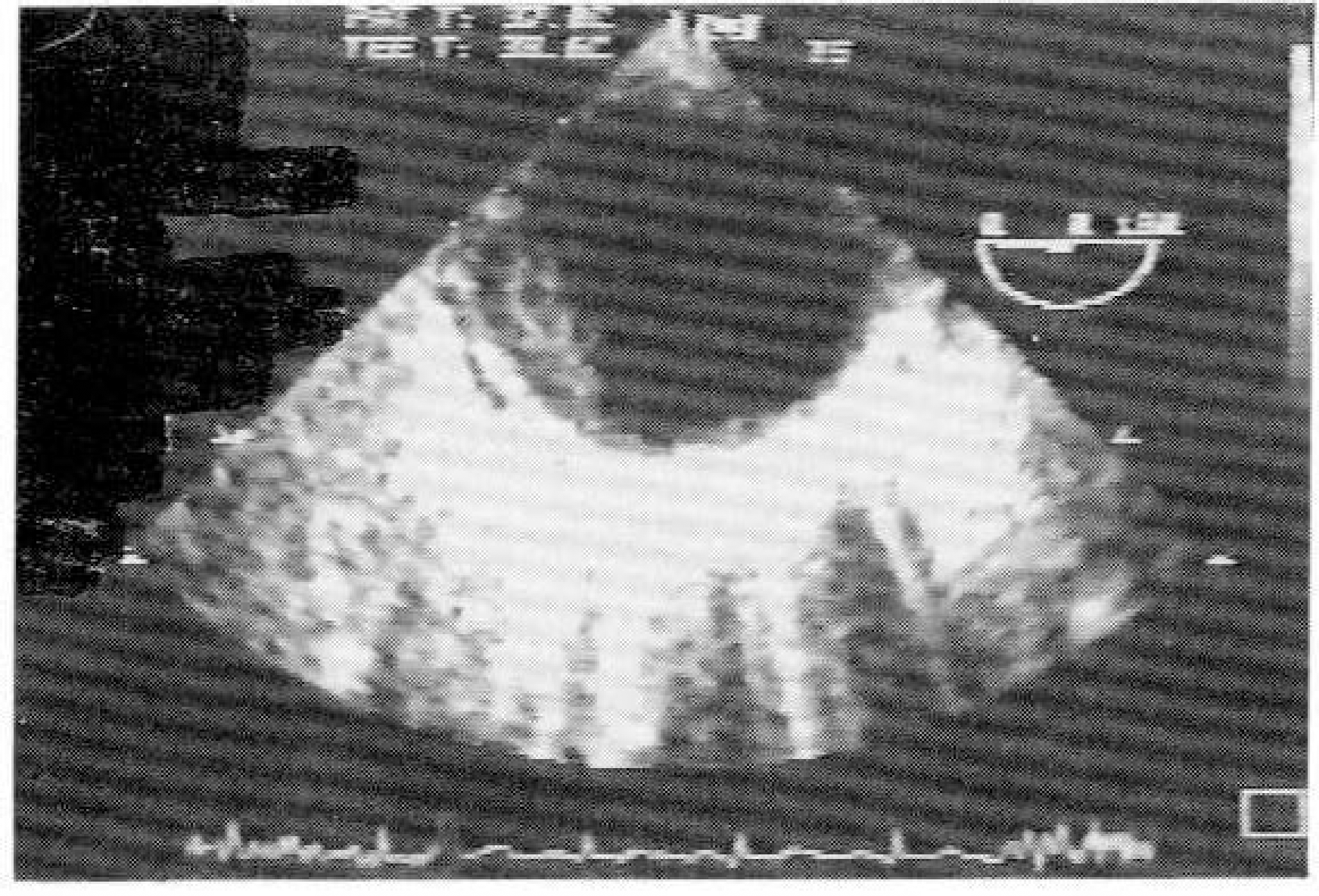
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome is characterized by recurrent fetal loss, neurologic dysfunction. arterial and venous thrombosis, and systemic and pulmonary hypertension associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. We observed a large visible thrombus in the descending aorta leading to multiple systemic embolism in a patient with antiphospholipid antibody without other risk factors for thrombosis. We assume that this thrombus is associated with antiphospholipid antibody syndrome.
References
1). Mitusch R, Stierle U, Tepe C, Kummer P, Kessler C, Seikhzadeh A. Systemic embolism in aortic arch atheromatosis. Eur Heart J. 15(10):1373–80. 1994.

2). Aldrich HR, Girardi L, Bush HL, Dedevereux RB, Rosengart TK. Recurrent systemic embolization caused by aortic thrombi, Ann Thorac Surg. 57:466–8. 1994.
3). Sharifi M, Sorkln R. Lakier J, Chaitra S. Thoracic aortic thrombosis as a cause of bowel ischemia: A case report, Angiology. 45(11):973–7. 1994.
4). Josephson GD, Tiefenbrun J, Harvey J. Thrombosis of the descending thoracic aorta: A case report. Surgery. 114:598–600. 1993.
5). Machleder HI, Takiff H, Lois JF, Holburt E. Aortic mural thrombus: An occult source of arterial thromboembolism, J Vasc Surg. 4:473–8. 1986.
6). Tunick PA, Perez JC, Kronzon I. Protruding atheromas in the thoracic aorta and systemic embolization. Ann Intern Med. 115:423–7. 1991.

7). Karalis DG, Chandrasekaran K, and Victor MF Ross JJ, Mintz GS. Recognition and embolic potential of intraaortic atherosclerotic debris. J Am Coll Cardiol. 17:73–8. 1991.

8). Wasserinann A. Neissr A, Bruck C. Eine serodiagnostische reaktion bei syphilis. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 32:745–46. 1906.

9). Conley CL, Hartmann RC. A hemorrhagic disorder caused by circulating anticoagulant in patients with disseminated lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 31:621–22. 1952.
10). Meyer O, Cyna L, Bourgeois P, Kahn MF, Ryckewaert A. Profile and cross reactivities of antiphospholipid antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus and syphilis. Clin Rheumatol. 6:369–77. 1987.
11). Meyer O, Piette JC, Bourgeois P. Antiphospholipid antibodies: A disease marker in 25 patients with autoimmune antibody negative SLE. J Rheumatol. 14:502–06. 1987.
12). Manoussakis MN, Gharavi AE, Drosos AA, Kitridou RC, Moutsopoulous HM. Anticardiolipin antibodies in unselected autoimmune rheumatic disease patients. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 44:297–307. 1987.

13). McGee GS, Pearce WH, Sharma L, Green D, Yao JS. Antiphospholipid antibodies and arterial thrombosis: Case reports and a review of the literature. Arch Surg. 127:342–6. 1992.
14). Ordi RJ, Perez PP, Monasterio J. Clinical and therapeutic aspects associated to phospholipid binding antibodies. Haemostasis. 24(3):165–74. 1994.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download