Abstract
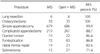
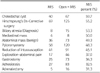
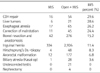
Minimal invasive surgery (MIS) has rapidly gained acceptance for the management of a wide variety of pediatric diseases. A questionnaire was sent to all members of the Korean Association of Pediatric Surgeons. Thirty one members (25.4%) took part in the survey that included data for the year 2012: demographic details, opinion regarding minimal invasive surgery and robotic surgery, spectrum of minimally invasive operations, and quantity of procedures. 48.4% of the respondents had more than 10 years experience, 35.5% less than 10 years experience, and 16.1 % had no experience. The respondents of the recommend MIS and perform MIS for surgical procedures are as follow; inguinal hernia (61.3%), simple appendicitis (87.1%), complicated appendicitis (80.6%), reduction of intussusceptions (83.9%), pyloromyotomy (90.3%), fundoplication (96.8%), biopsy and corrective surgery of Hirschsprung's disease (93.5%/90.3%), imperforate anus (77.4%), congenital diaphragmatic hernia (80.6%), and esophageal atresia (74.2%). The MIS procedures with more than 70% were lung resection (100%), cholecystectomy (100%), appendectomy (96.2%), ovarian torsion (86.7%), fundoplication (86.8%), hiatal hernia repair (82.6%), and splenectomy (71.4%). The MIS procedures with less than 30% were congenial diaphragmatic hernia reapir (29.6%), esophageal atresia (26.2%), correction of malroatation (24.4%), inguinal hernia repair (11.4%), anorectal malformation (6.8%), Kasai operation (3.6%).
Figures and Tables
References
1. Bloom DA, Ayers JW, McGuire EJ. The role of laparoscopy in management of nonpalpable testes. J Urol (Paris). 1988; 94:465–470.
2. Holcomb GW 3rd, Olsen DO, Sharp KW. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the pediatric patient. J Pediatr Surg. 1991; 26:1186–1190.

3. Pier A, Götz F, Bacher C. Laparoscopic appendectomy in 625 cases: from innovation to routine. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1991; 1:8–13.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print










 XML Download
XML Download