Abstract
Objective
Erythropoietin (EPO) has neuroprotective effects in many animal models of brain injury including hypoxic-ischemic (HI) encephalopathy, trauma- and excitotoxicity. Current studies have demonstrated the neuroprotective effects of EPO, but there are limited the same consequences occurring during neonatal periods. Here, we investigated whether recombinant human EPO (rHuEPO) can protect the developing rat brain from HI injury via the modulation of nitric oxide synthase.
Methods
The in vitro model involved culturing embryonic cortical neuronal cells of Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats at 19 days gestation. The cultured cells were divided into five groups: normoxia (N), hypoxia (H), 1, 10 and 100 IU/mL rHuEPO-treated (H+E1, H+E10, and H+E100). In the in vivo model, left carotid artery ligation was performed in 7-day-old SD rat pups. The animals were divided into six groups: normoxia control, normoxia Sham-operated, hypoxia only (H), hypoxia+vehicle, hypoxia+ rHuEPO before a hypoxic insult (HE-B), and hypoxia+rHuEPO after a hypoxic insult (HE-A). Western blotting and real-time polymerase chain reaction using antibodies and primers of inducible NOS (iNOS), endothelial NOS (eNOS) and neuronal NOS (nNOS) were performed.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1). Higuchi Y., Hattori H., Kume T., Tsuji M., Akaike A., Furusho K. Increase in nitric oxide in the hypoxic-ischemic neonatal rat brain and suppression by 7-nitroindazole and aminoguanidine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998. 342:47–9.

2). Ishida A., Trescher WH., Lange MS., Johnston MV. Prolonged suppression of brain nitric oxide synthase activity by 7-nitroindazole protects against cerebral hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal rat. Brain Dev. 2001. 23:349–54.

3). Kumral A., Baskin H., Gokmen N., Yilmaz O., Genc K., Genc S, et al. Selective inhibition of nitric oxide in hypoxic-ischemic brain model in newborn rats: is it an explanation for the protective role of erythropoietin? Biol Neonate. 2004. 85:51–4.

4). Niwa M., Inao S., Takayasu M., Kawai T., Kajita Y., Nihashi T, et al. Time course of expression of three nitric oxide synthase isoforms after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2001. 41:63–72. discussion 72-3.

5). Zhang ZG., Chopp M., Zaloga C., Pollock JS., Förstermann U. Cerebral endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 1993. 24:2016–21. discussion 2021-2.

6). Samdani AF., Dawson TM., Dawson VL. Nitric oxide synthase in models of focal ischemia. Stroke. 1997. 28:1283–8.

7). Ishida A., Ishiwa S., Trescher WH., Nakajima W., Lange MS., Blue ME, et al. Delayed increase in neuronal nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in thalamus and other brain regions after hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal rats. Exp Neurol. 2001. 168:323–33.

8). Garcia-Bonilla L., Moore JM., Racchumi G., Zhou P., Butler JM., Iadecola C, et al. Inducible nitric oxide synthase in neutrophils and endothelium contributes to ischemic brain injury in mice. J Immunol. 2014. 193:2531–7.

9). Voituron N., Jeton F., Cholley Y., Hasnaoui-Saadani RE., Marchant D., Quidu P, et al. Catalyzing role of erythropoietin on the nitric oxide central pathway during the ventilatory responses to hypoxia. Physiol Rep. 2014. 2:e00223.

10). Calapai G., Marciano MC., Corica F., Allegra A., Parisi A., Frisina N, et al. Erythropoietin protects against brain ischemic injury by inhibition of nitric oxide formation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000. 401:349–56.

11). Lombardero M., Kovacs K., Scheithauer BW. Erythropoietin: a hormone with multiple functions. Pathobiology. 2011. 78:41–53.

12). Rangarajan V., Juul SE. Erythropoietin: emerging role of erythropoietin in neonatal neuroprotection. Pediatr Neurol. 2014. 51:481–8.

13). Sakanaka M., Wen TC., Matsuda S., Masuda S., Morishita E., Nagao M, et al. In vivo evidence that erythropoietin protects neurons from ischemic damage. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A. 1998. 95:4635–40.

14). Gonzalez FF., Larpthaveesarp A., McQuillen P., Derugin N., Wendland M., Spadafora R, et al. Erythropoietin increases neurogenesis and oligoden-drogliosis of subventricular zone precursor cells after neonatal stroke. Stroke. 2013. 44:753–8.

15). Iwai M., Cao G., Yin W., Stetler RA., Liu J., Chen J. Erythropoietin promotes neuronal replacement through revascularization and neurogenesis after neonatal hypoxia/ischemia in rats. Stroke. 2007. 38:2795–803.

16). Elmahdy H., El-Mashad AR., El-Bahrawy H., El-Gohary T., El-Barbary A., Aly H. Human recombinant erythropoietin in asphyxia neonatorum: pilot trial. Pediatrics. 2010. 125:e1135–42.

17). Wu YW., Bauer LA., Ballard RA., Ferriero DM., Glidden DV., Mayock DE, et al. Erythropoietin for neuroprotection in neonatal encephalopathy: safety and pharmacokinetics. Pediatrics. 2012. 130:683–91.

18). Fan X., van Bel F., van der Kooij MA., Heijnen CJ., Groenendaal F. Hypothermia and erythropoietin for neuroprotection after neonatal brain damage. Pediatr Res. 2013. 73:18–23.

19). Maiese K., Chong ZZ., Hou J., Shang YC. Erythropoietin and oxidative stress. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2008. 5:125–42.

20). Brewer GJ. Isolation and culture of adult rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Methods. 1997. 71:143–55.

21). Genc K., Genc S., Baskin H., Semin I. Erythropoietin decreases cytotoxicity and nitric oxide formation induced by inflammatory stimuli in rat oligo-dendrocytes. Physiol Res. 2006. 55:33–8.

22). Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983. 65:55–63.

23). Rice JE 3rd., Vannucci RC., Brierley JB. The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol. 1981. 9:131–41.

24). Kumral A., Ozer E., Yilmaz O., Akhisaroglu M., Gokmen N., Duman N, et al. Neuroprotective effect of erythropoietin on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Biol Neonate. 2003. 83:224–8.

25). Digicaylioglu M., Lipton SA. Erythropoietin-mediated neuroprotection involves cross-talk between Jak2 and NF-kappaB signalling cascades. Nature. 2001. 412:641–7.
26). Ioroi T., Yonetani M., Nakamura H. Effects of hypoxia and reoxygenation on nitric oxide production and cerebral blood flow in developing rat striatum. Pediatr Res. 1998. 43:733–7.

27). Zhang ZG., Chopp M., Gautam S., Zaloga C., Zhang RL., Schmidt HH, et al. Upregulation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase and mRNA, and selective sparing of nitric oxide synthase-containing neurons after focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Brain Res. 1994. 654:85–95.
29). De Pascali F., Hemann C., Samons K., Chen CA., Zweier JL. Hypoxia and reoxygenation induce endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling in endothelial cells through tetrahydrobiopterin depletion and S-gluta-thionylation. Biochemistry. 2014. 53:3679–88.

30). Ferriero DM., Holtzman DM., Black SM., Sheldon RA. Neonatal mice lacking neuronal nitric oxide synthase are less vulnerable to hypoxic-ischemic injury. Neurobiol Dis. 1996. 3:64–71.

31). Iadecola C., Zhang F., Xu S., Casey R., Ross ME. Inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in brain following cerebral ischemia. JCereb Blood Flow Metab. 1995. 15:378–84.

32). Morishita E., Masuda S., Nagao M., Yasuda Y., Sasaki R. Erythropoietin receptor is expressed in rat hippocampal and cerebral cortical neurons, and erythropoietin prevents in vitro glutamate-induced neuronal death. Neuroscience. 1997. 76:105–16.

33). Yu X., Shacka JJ., Eells JB., Suarez-Quian C., Przygodzki RM., Beleslin-Cokic B, et al. Erythropoietin receptor signalling is required for normal brain development. Development. 2002. 129:505–16.

34). Reitmeir R., Kilic E., Kilic U., Bacigaluppi M., ElAli A., Salani G, et al. Post-acute delivery of erythropoietin induces stroke recovery by promoting perilesional tissue remodelling and contralesional pyramidal tract plasticity. Brain. 2011. 134(Pt 1):84–99.

35). Xiong Y., Mahmood A., Qu C., Kazmi H., Zhang ZG., Noguchi CT, et al. Erythropoietin improves histological and functional outcomes after traumatic brain injury in mice in the absence of the neural erythropoietin receptor. J Neurotrauma. 2010. 27:205–15.

36). Iwai M., Stetler RA., Xing J., Hu X., Gao Y., Zhang W, et al. Enhanced oligo-dendrogenesis and recovery of neurological function by erythropoietin after neonatal hypoxic/ischemic brain injury. Stroke. 2010. 41:1032–7.

37). Zhu C., Kang W., Xu F., Cheng X., Zhang Z., Jia L, et al. Erythropoietin improved neurologic outcomes in newborns with hypoxic-ischemic en-cephalopathy. Pediatrics. 2009. 124:e218–26.

38). Dawson DA. Nitric oxide and focal cerebral ischemia: multiplicity of actions and diverse outcome. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1994. 6:299–324.
Go to : 
 | Fig. 1High magnification (×200) photomicrographs of brain cortical cell culture from a pregnant 19 days Sprague-Dawley rat were revealed. The recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rHuEPO) was administered at 1, 10, and 100 IU/mL. (A) Normoxia group (N), (B) hypoxia group (H), (C) hypoxia+1 IU/mL rHuEPO treated group (H+E1), (D) hypoxia+10 IU/mL rHuEPO treated group (H+E10), (E) hypoxia+100 IU/mL rHuEPO treated group (H+E100). |
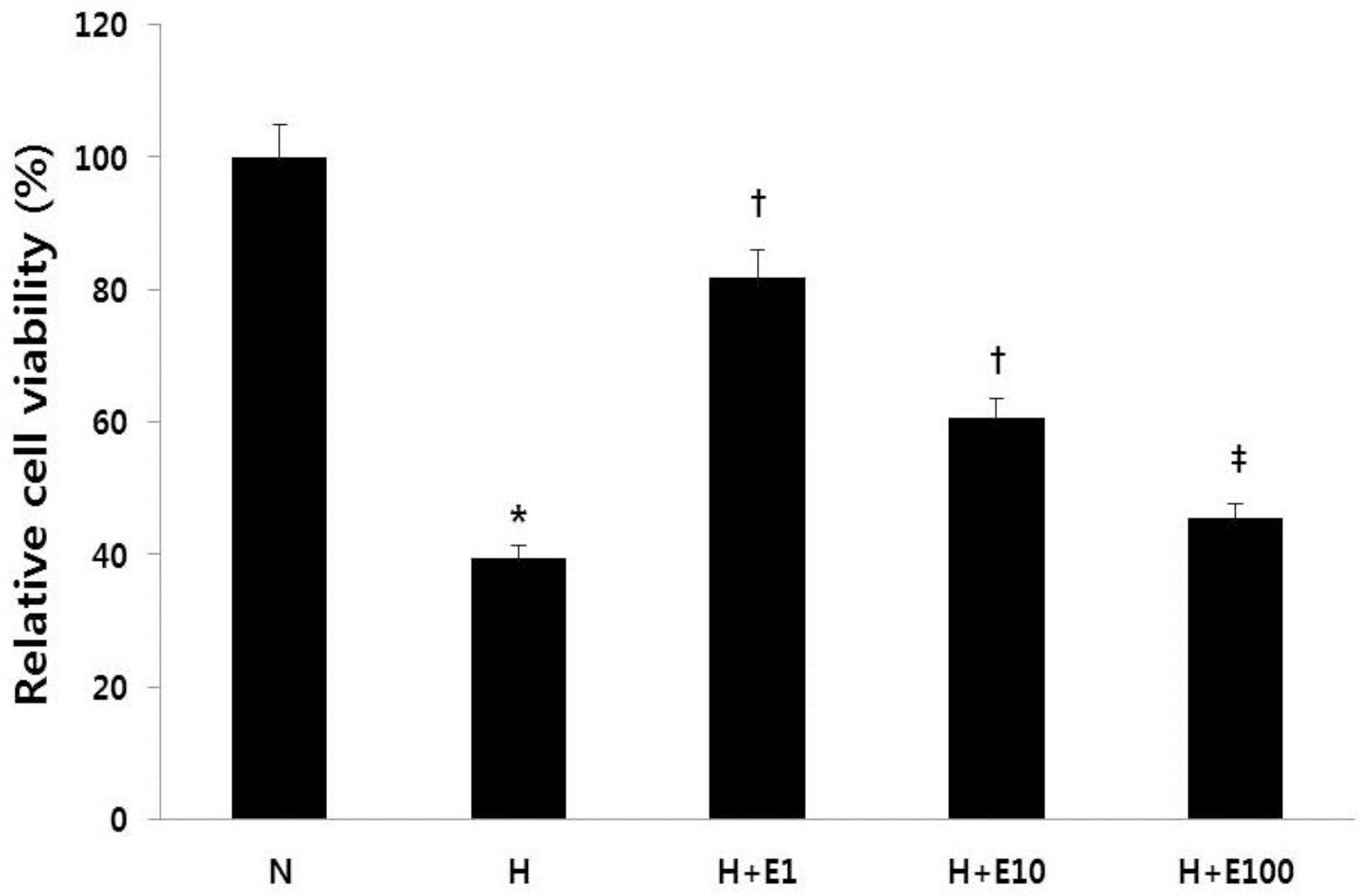 | Fig. 2The recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rHuEPO) attenuates hypoxic injury of rat brain. Cultured embryonic cortical neuronal cells were prepared with rHuEPO for 30 min before a hypoxic insult. Cell viability was measured by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. N, normoxia group; H, hypoxia group; H+E1, hypoxia+1 IU/mL rHuEPO-treated group; H+ E10, hypoxia+10 IU/mL rHuEPO-treated group; H+E100, hypoxia +100 IU/mL rHuEPO-treated group. ∗P<0.01 for the H group compared to the N group. †P<0.01 for the H+E1 and H+E10 groups compared to the H group. ‡P<0.05 for the H+E100 group compared to the H group. |
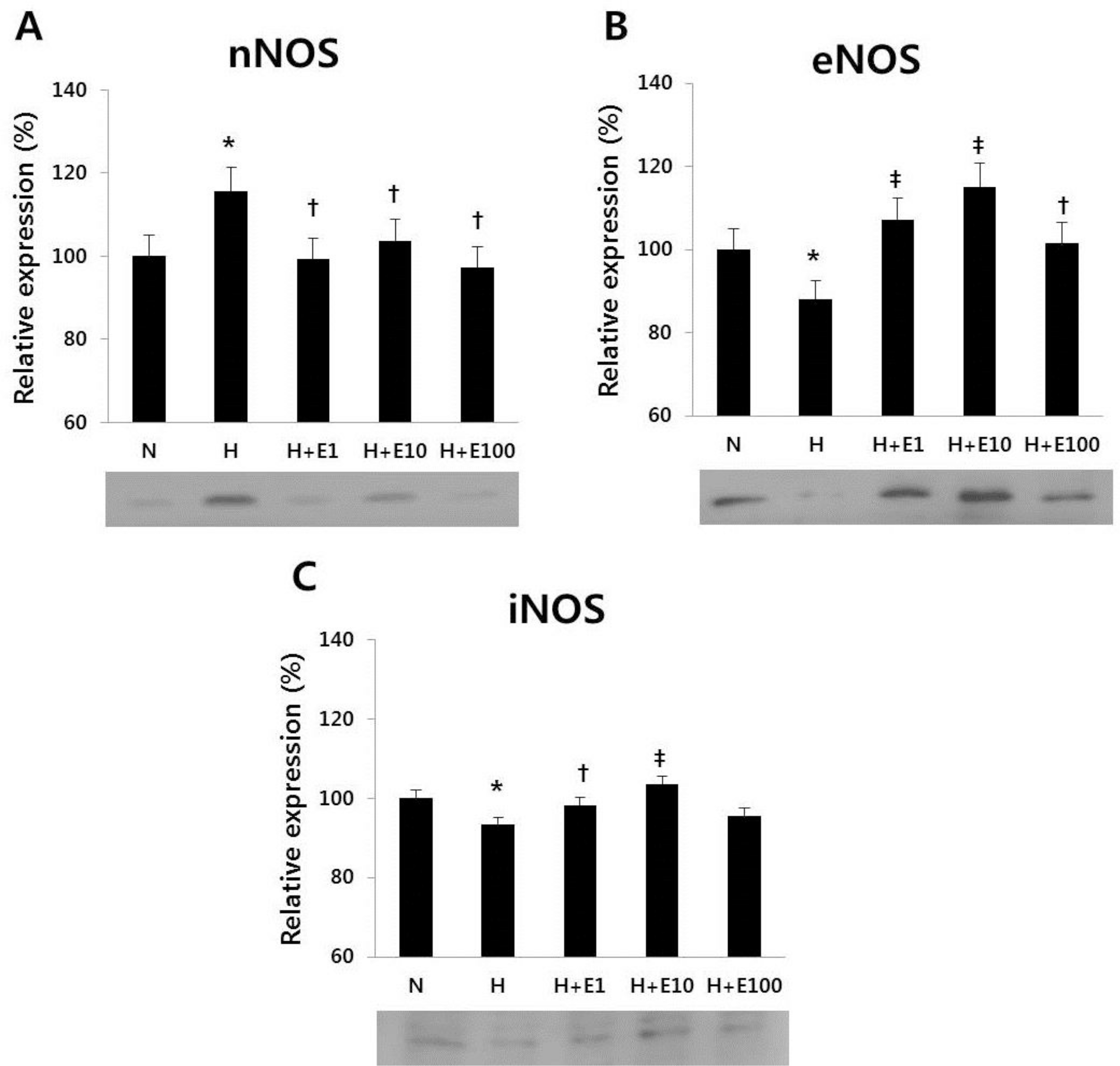 | Fig. 3Western blotting of (A) nNOS, (B) eNOS, and (C) iNOS in cultured cortical neuronal cells from 19-day-old rat embryos was revealed. The recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rHuEPO) was administered at 1, 10, 100 IU/mL. N, normoxia group; H, hypoxia group; H+E1, hypoxia+1 IU/mL rHuEPO treated group; H+E10, hypoxia+10 IU/mL rHuEPO treated group; H+E100, hypoxia+100 IU/mL rHuEPO treated group. nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase. ∗P<0.05 for the H group compared to the N group. †P<0.05, ‡P<0.05 for the H+E1, H+E10, and H+E100 groups compared to the H group. |
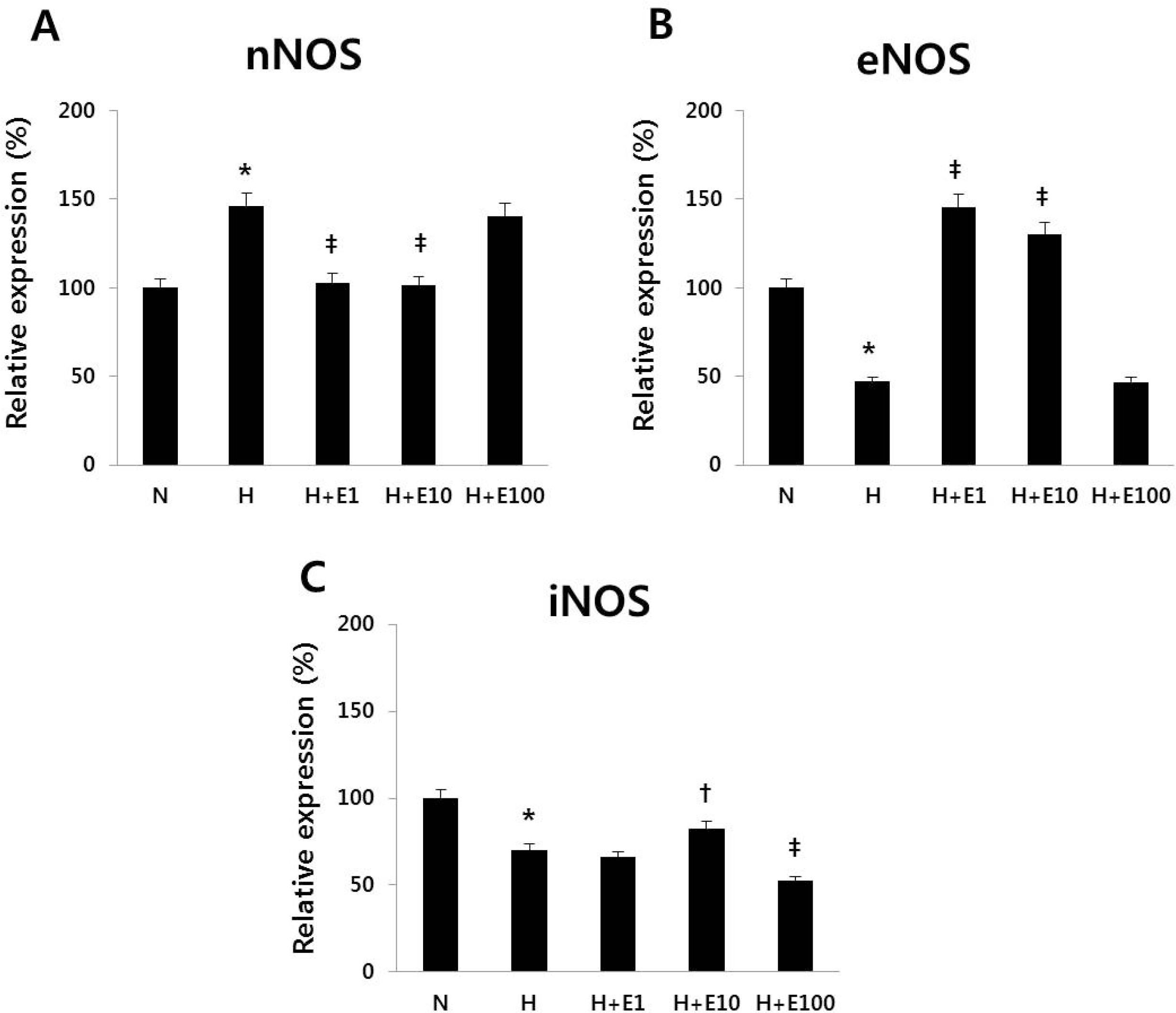 | Fig. 4Real-time PCR of (A) nNOS, (B) eNOS, and (C) iNOS in cultured cortical neuronal cells from 19-day-old rat embryos was revealed. The recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rHuEPO) was administered at 1, 10, 100 IU/mL. N, normoxia group; H, hypoxia group; H+ E1, hypoxia+1 IU/mL rHuEPO treated group; H+E10, hypoxia+10 IU/mL rHuEPO treated group; H+E100, hypoxia+100 IU/mL rHuEPO treated group. nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase. ∗P<0.01 for the H group compared to the N group. ‡P<0.05, †P<0.01 for the H+E1, H+E10, and H+E100 groups compared to the H group. |
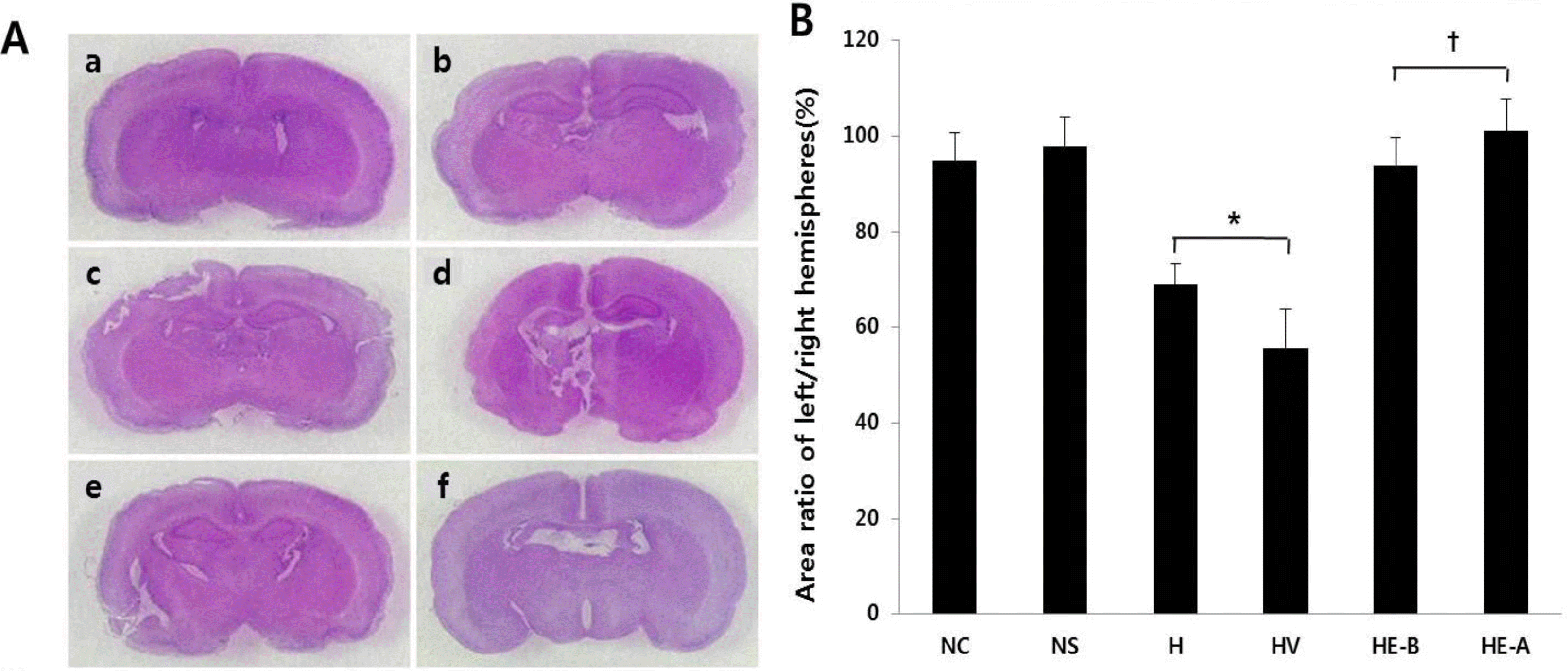 | Fig. 5(A) H&E staining. (a) normoxia control group, (b) normoxia sham-operated group, (c) hypoxia group, (d) hypoxia+vehicle group, (e) hypoxia+recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rHuEPO)-treated group before a hypoxic insult, (f) hypoxia+rHuEPO-treated group after a hypoxic insult (n=5 in each group). (B) Area ratio of left/right hemispheres. NC, normoxia control group; NS, normoxia sham-operated group; H, hypoxia group; HV, hypoxia+vehicle group; HE-B, hypoxia+rHuEPO group treated before a hypoxic insult; HE-A, hypoxia+rHuEPO group treated after a hypoxic insult. ∗P<0.01 for the H, HV groups compared to the NC, NS groups. †P<0.01 for the HE-B, HE-A groups compared to the H, HV groups. |
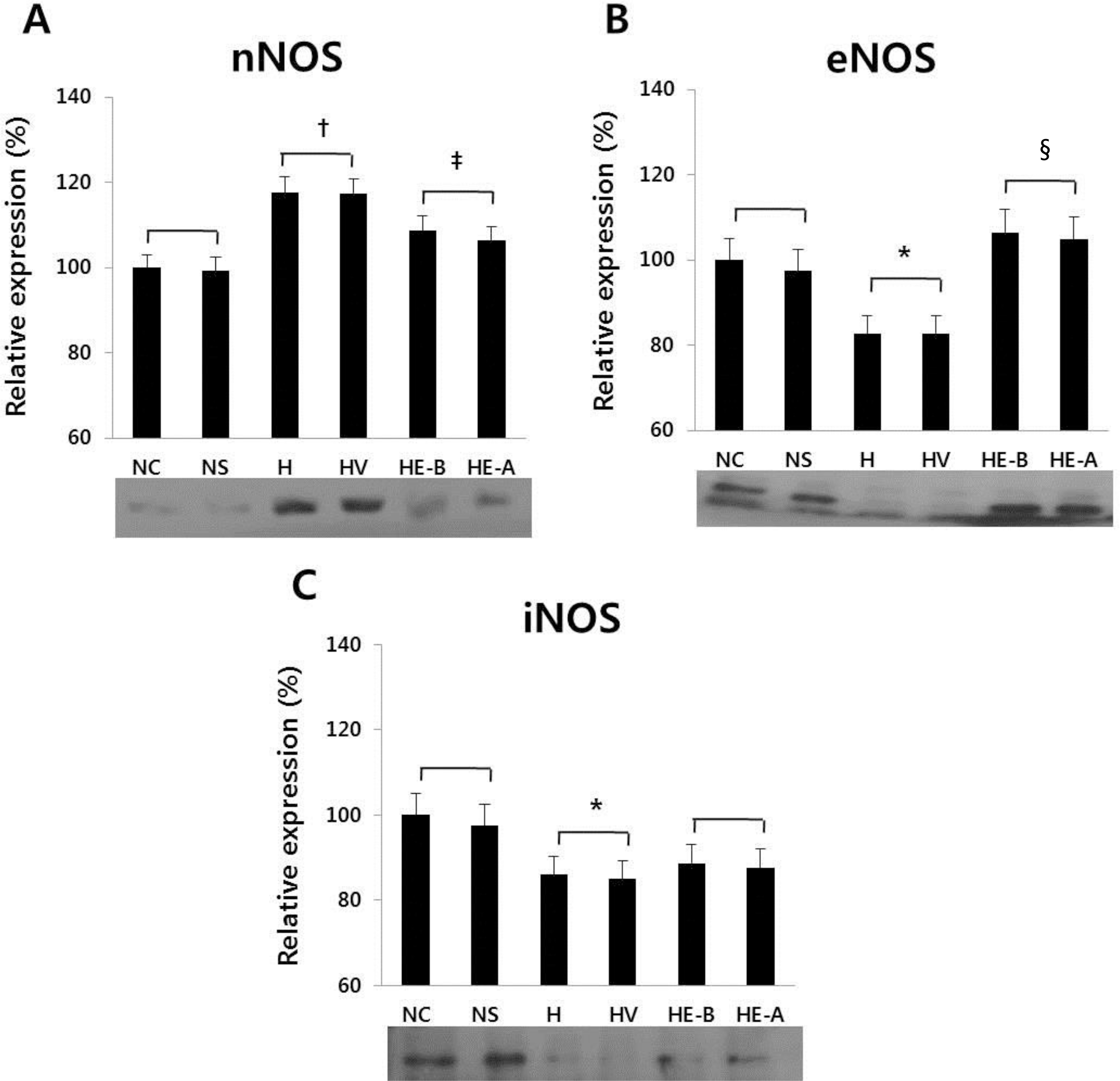 | Fig. 6Western blotting of (A) nNOS, (B) eNOS, and (C) iNOS at 7 days after a hypoxic injury was revealed. The recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rHuEPO) was administered at 1,000 IU/kg. nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase. NC, normoxia control group; NS, normoxia sham-operated group; H, hypoxia group; HV, hypoxia+vehicle group; HE-B, hypoxia+rHuEPO group treated before a hypoxic insult; HE-A, hypoxia+rHuEPO group treated after a hypoxic insult. ∗P<0.05, †P<0.01 for the H, HV groups compared to the NC, NS groups; ‡P <0.05, §P<0.01 for the HE-B, HE-A groups compared to the H, HV groups. |
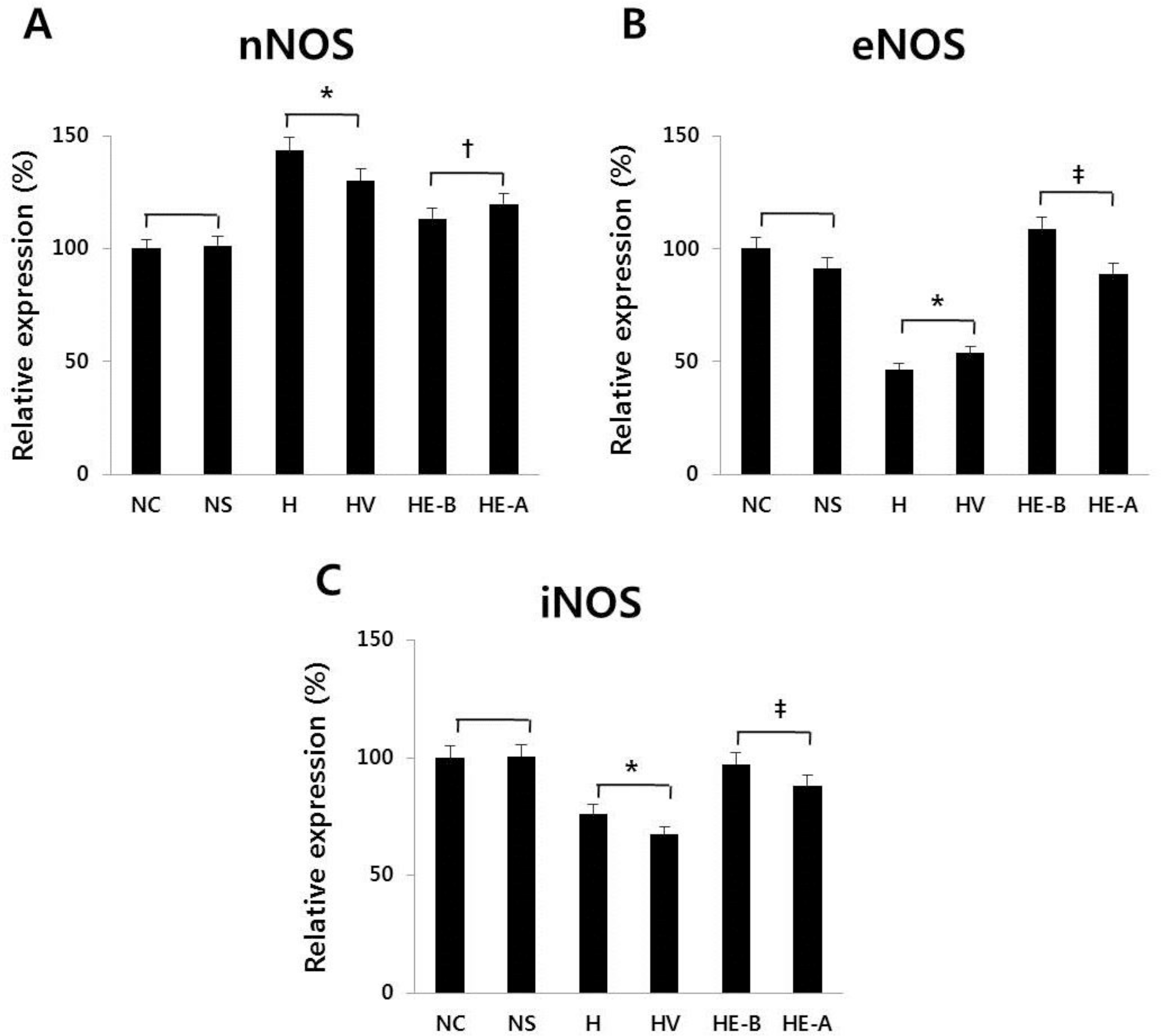 | Fig. 7Real-time PCR of (A) nNOS, (B) eNOS, and (C) iNOS at 7 days after a hypoxic injury was revealed. The recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rHuEPO) was administered at 1,000 IU/kg. nNOS, neuronal nitric oxide synthase; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; NC, normoxia control group; NS, normoxia sham-operated group; H, hypoxia group; HV, hypoxia+vehicle group; HE-B, hypoxia+rHuEPO group treated before a hypoxic insult; HE-A, hypoxia+rHuEPO group treated after a hypoxic insult. ∗P< 0.01 for the H, HV groups compared to the NC, NS groups. †P<0.05. ‡P<0.01 for the HE-B, HE-A groups compared to the H, HV groups. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download