Abstract
Vascular Ehlers-Danlos sydrome (vEDS) is a life-threatening autosomal dominant inherited disorder of connective tissue characterized by arterial aneurysm, dissection and rupture, bowel rupture, and rupture of the gravid uterus. vEDS results from mutation of COL3A1, which encodes the chains of type III collagen, a major protein in vessel walls and hollow organs. A 32-year-old primigravida had aneurysmal rupture in right posterior popliteal artery 9 days after induced vaginal delivery. The reason of labor induction was preterm premature rupture of membrane. She was diagnosed with vEDS by sequence analysis of COL3A1 mutation. A multidisciplinary team is required to provide tailored counseling and education about vEDS. Also, a long term follow up is need for individuals with vEDS.
REFERENCES
2). Beridze N., Frishman WH. Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and prevention and treatment of its complications. Cardiol Rev. 2012. 20:4–7.
4). Park JK. Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome type IV and the management of its vascular complication. Korean J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011. 27:47–51.

5). Beighton P., de Paepe A., Danks D., Finidori G., Gedde-Dahl T., Goodman R, et al. International nosology of heritable disorders of connective tissue, Berlin, 1986. Am J Med Genet. 1988. 29:581–94.

6). Beighton P., De Paepe A., Steinmann B., Tsipouras P., Wenstrup RJ. Ehlers-Danlos syndromes: revised nosology, Villefranche, 1997. Ehlers-Danlos National Foundation (USA) and Ehlers-Danlos Support Group (UK). Am J Med Genet. 1998. 77:31–7.
7). Malfait F., Francomano C., Byers P., Belmont J., Berglund B., Black J, et al. The 2017 international classification of the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2017. 175:8–26.
8). Frank M., Albuisson J., Ranque B., Golmard L., Mazzella JM., Bal-Theoleyre L, et al. The type of variants at the COL3A1 gene associates with the phenotype and severity of vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015. 23:1657–64.

9). Pepin MG., Schwarze U., Rice KM., Liu M., Leistritz D., Byers PH. Survival is affected by mutation type and molecular mechanism in vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS type IV). Genet Med. 2014. 16:881–8.

10). Yoon YM., Kim DC., Kang MJ. A case of vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with novel mutation c. 2931+2dupT in COL3A1 gene. J Korean Soc Inher Metab Dis. 2014. 14:168–73.
11). Byers PH., Belmont J., Black J., De Backer J., Frank M., Jeunemaitre X, et al. Diagnosis, natural history, and management in vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2017. 175:40–7.

12). Murray ML., Pepin M., Peterson S., Byers PH. Pregnancy-related deaths and complications in women with vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Genet Med. 2014. 16:874–80.

13). Volkov N., Nisenblat V., Ohel G., Gonen R. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: insights on obstetric aspects. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2007. 62:51–7.

14). Lind J., Wallenburg HC. Pregnancy and the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: a retrospective study in a Dutch population. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2002. 81:293–300.

15). Hurst BS., Lange SS., Kullstam SM., Usadi RS., Matthews ML., Marshburn PB, et al. Obstetric and gynecologic challenges in women with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. 2014. 123:506–13.

16). Erez Y., Ezra Y., Rojansky N. Ehlers-Danlos type IV in pregnancy. A case report and a literature review. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2008. 23:7–9.
17). Weinbaum PJ., Cassidy SB., Campbell WA., Rickles FR., Vintzileos AM., No-chimson DJ, et al. Pregnancy management and successful outcome of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV. Am J Perinatol. 1987. 4:134–7.

18). Palmquist M., Pappas JG., Petrikovsky B., Blakemore K., Roshan D. Successful pregnancy outcome in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, vascular type. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009. 22:924–7.

Fig. 1
Computed tomography venography revealed aneurysmal rupture of right posterior tibial artery (arrow) with hematoma formation (arrowheads) without deep vein thrombosis.
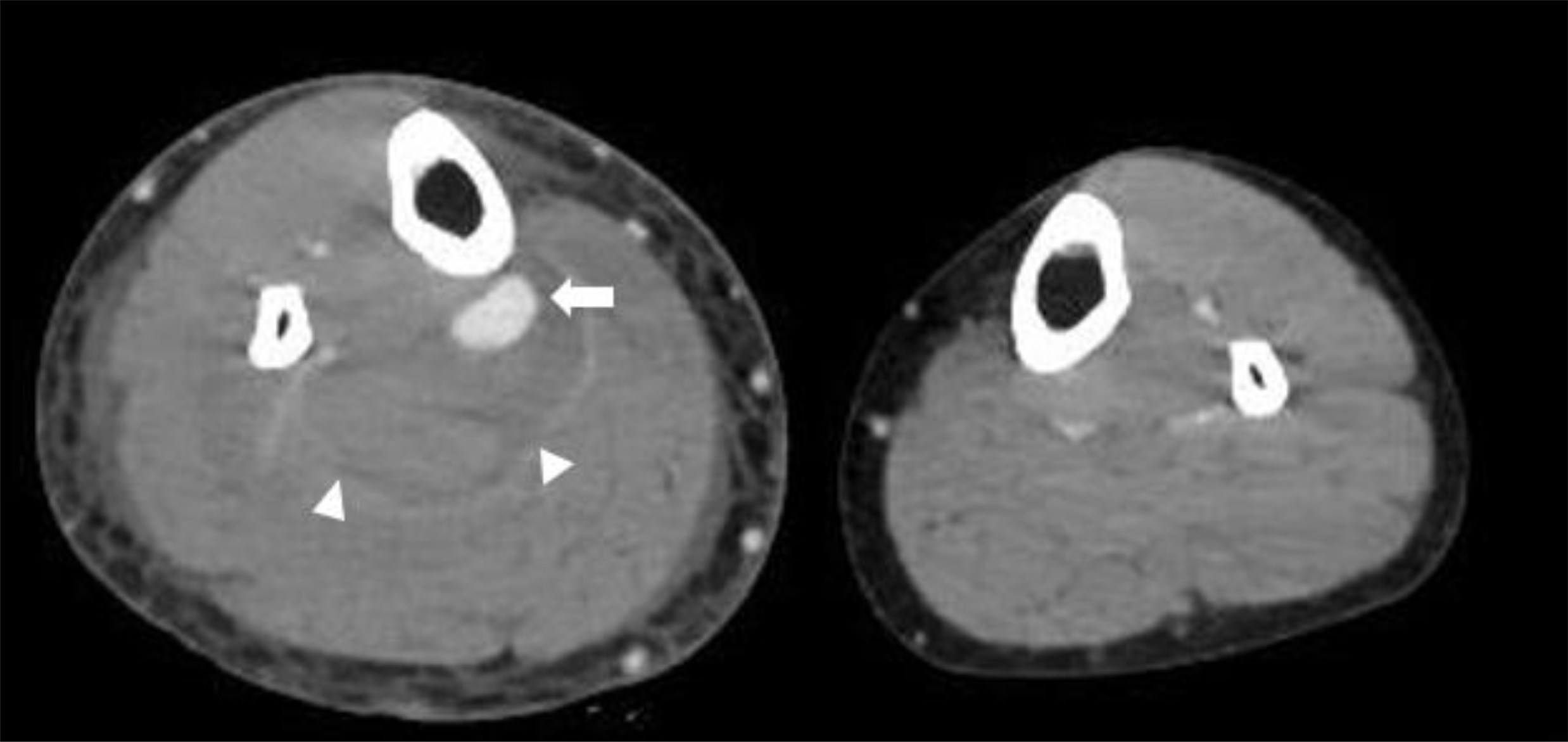
Fig. 2
Axial scan of contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) angiography (A) showed aneurysmal dilatation of right proximal posterior tibial artery (arrow) with adjacent hematoma (arrowheads). CT angiography with three-dimensional reconstruction scan (B) also revealed aneurysmal dilatation of right proximal posterior tibial artery (arrow).
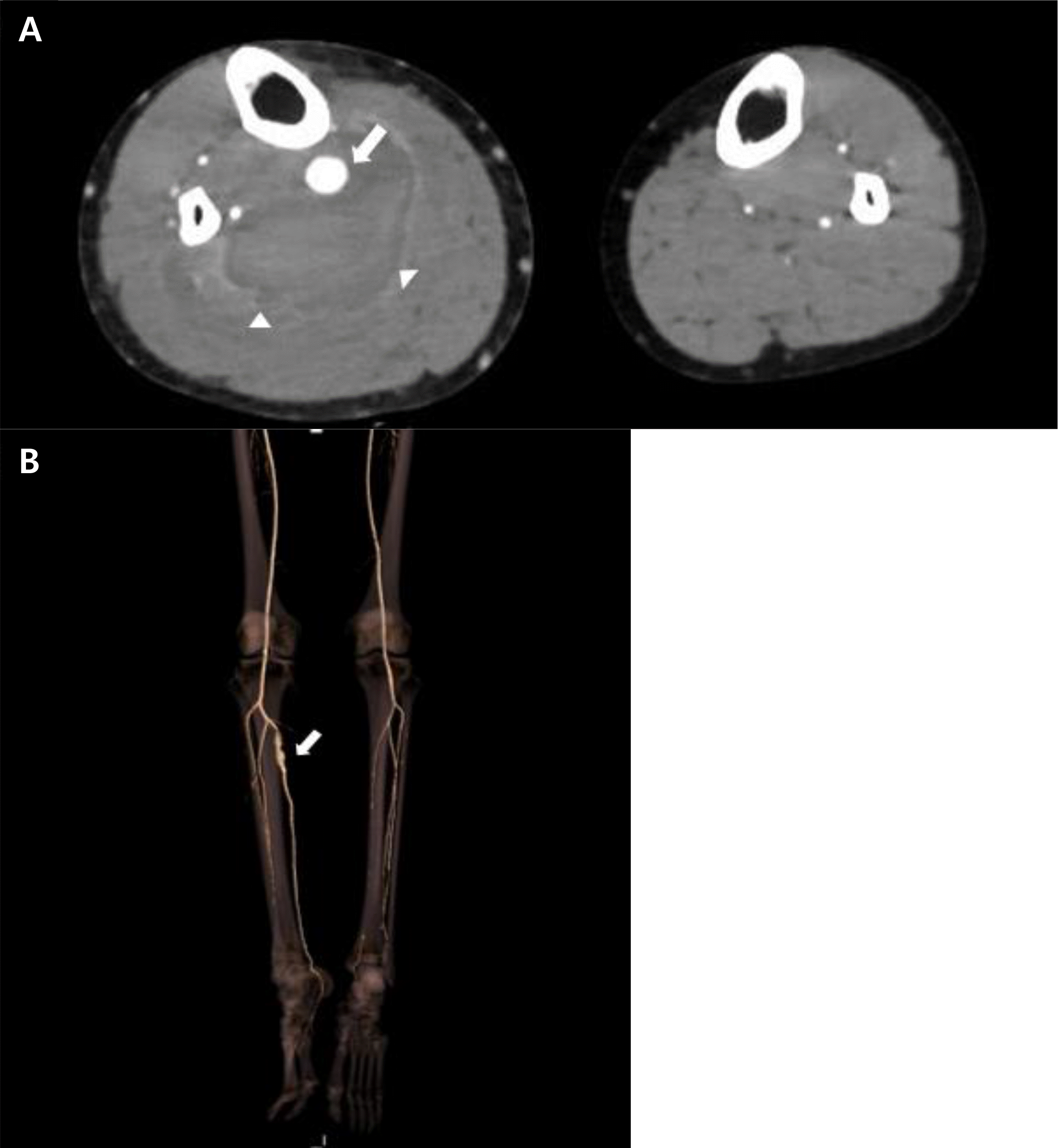
Fig. 3
Computed tomography (CT) angiography with three-dimensional reconstruction scan (A) showed luminal irregularity in common iliac artery, external iliac artery (arrowheads). Axial scan of contrast-enhanced CT angiography (B) also showed luminal irregularity of celiac trunk (arrow).
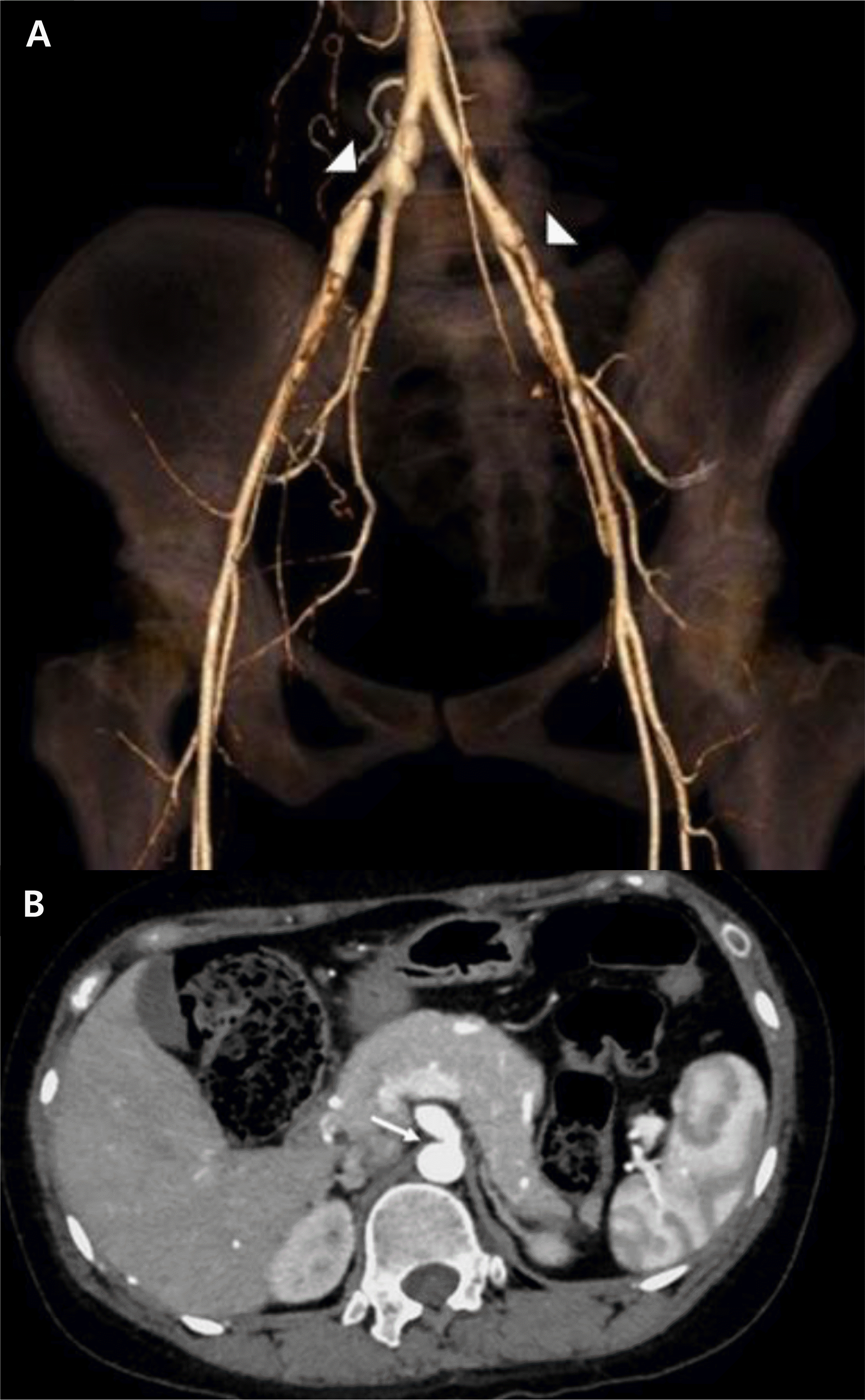
Table 1.
Diagnostic Criteria for Vascular Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (vEDS)7




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download