Abstract
The Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is an inherited connective tissue disorder with special characteristics such as joint hypermobility, tissue fragility and skin abnormalities. The recently classification divide six subtypes. Dermatosparaxis types of these are recessively inherited connective tissue disorders and caused by a deficient function of procollagen I N-proteinase (ADAMTS2). In this report, craniofacial features were found such as micrognathia, narrow forehead covered with dense hair, broad nasal root and narrow upper lip. Clenched fists and rocker bottom feet were found which are typically shown at patients of Edwards syndrome. We report a first case of a newborn with EDS of Dermatosparaxis type confirmed by microarray test in Korea.
REFERENCES
1). Klaassens M., Reinstein E., Hilhorst-Hofstee Y., Schrander JJ., Malfait F., Staal H, et al. Ehlers-Danlos arthrochalasia type (VIIA-B)—expanding the phenotype: from prenatal life through adulthood. Clin Genet. 2012. 82:121–30.
2). Yen JL., Lin SP., Chen MR., Niu DM. Clinical features of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. J Formos Med Assoc. 2006. 105:475–80.

3). Giunta C., Superti-Furga A., Spranger S., Cole WG., Steinmann B. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII: clinical features and molecular defects. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999. 81:225–38.
4). Byers PH., Duvic M., Atkinson M., Robinow M., Smith LT., Krane SM, et al. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIIA and VIIB result from splice-junction mutations or genomic deletions that involve exon 6 in the COL1A1 and COL1A2 genes of type I collagen. Am J Med Genet. 1997. 72:94–105.
5). De Paepe A., Malfait F. The Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, a disorder with many faces. Clin Genet. 2012. 82:1–11.

6). Beighton P., De Paepe A., Steinmann B., Tsipouras P., Wenstrup RJ. Ehlers-Danlos syndromes: revised nosology, Villefranche, 1997. Ehlers-Danlos National Foundation (USA) and Ehlers-Danlos Support Group (UK). Am J Med Genet. 1998. 77:31–7.
7). Wang WM., Lee S., Steiglitz BM., Scott IC., Lebares CC., Allen ML, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta induces secretion of activated ADAMTS-2. A procollagen III N-proteinase. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:19549–57.
8). Malfait F., De Coster P., Hausser I., van Essen AJ., Franck P., Colige A, et al. The natural history, including orofacial features of three patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, dermatosparaxis type (EDS type VIIC). Am J Med Genet A. 2004. 131:18–28.

9). Colige A., Sieron AL., Li SW., Schwarze U., Petty E., Wertelecki W, et al. Human Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII C and bovine dermatosparaxis are caused by mutations in the procollagen I N-proteinase gene. Am J Hum Genet. 1999. 65:308–17.

10). Colige A., Nuytinck L., Hausser I., van Essen AJ., Thiry M., Herens C, et al. Novel types of mutation responsible for the dermatosparactic type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (Type VIIC) and common polymorphisms in the ADAMTS2 gene. J Invest Dermatol. 2004. 123:656–63.

11). Gage JP., Shaw RM., Moloney FB. Collagen type in dysfunctional temporomandibular joint disks. J Prosthet Dent. 1995. 74:517–20.

12). Fujimoto A., Wilcox WR., Cohn DH. Clinical, morphological, and biochemical phenotype of a new case of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIIC. Am J Med Genet. 1997. 68:25–8.

13). Melis D., Cappuccio G., Ginocchio VM., Minopoli G., Valli M., Corradi M, et al. Cardiac valve disease: an unreported feature in Ehlers Danlos syndrome arthrocalasia type? Ital J Pediatr. 2012. 38:65.

14). Byers PH., Murray ML. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: a showcase of conditions that lead to understanding matrix biology. Matrix Biol. 2014. 33:10–5.

15). Lee SY., Park SH., Choi HJ., Yun SK., Kim HU., Ihm CW. Type II and classical type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: report of 3 cases & review of Korean cases. Korean J Dermatol. 2006. 44:834–8.
16). Kim HS., Choi CH., Lee TH., Kim SP. Fusiform aneurysm presenting with cervical radiculopathy in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010. 48:528–31.

17). Im JS., Lim YH., Park JS., Lee SS., Kim KM. Rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm after spine surgery in the patient with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome-a case report. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2010. 58:555–9.
18). Kim UK., Nam HM., Park K., Park SD. Classic type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with cutis laxa-like histopathologic findings. Korean J Dermatol. 2011. 49:524–8.
19). Yoon YM., Kim DC., Kang MJ. A case of vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with novel mutation c.2931+2dupT in COL3A1 gene. J Korean Soc Inherit Metab Dis. 2014. 14:168–73.
Fig. 1
(A) Patient had a generalized edema with hypotonia state and orofacial features included short forehead with hypertrichosis, flat supraorbital ridges, a broad nasal root, wide nares, a smooth philtrum, and micrognathia. (B) Both hands were clenched into fists with his index finger overlapping his other fingers. (C) Both feet showed a form of rocker bottom.
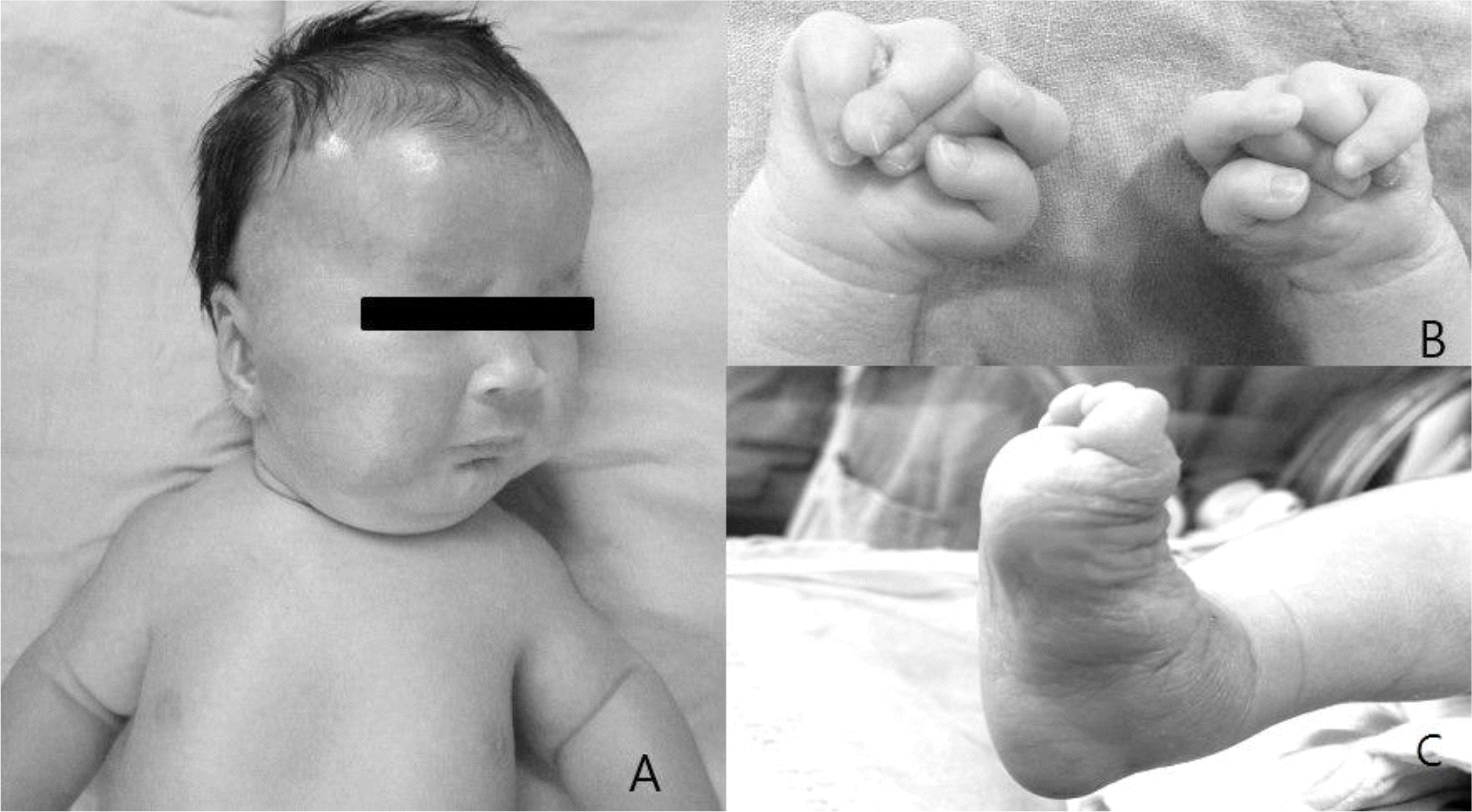
Fig. 2
(A) On kidney ultrasonography, left renal pelvis was mildly dilated (6 mm), suggesting pyelectasia. On echocardiography, it showed 3.3 mm-sized peri-membranous ventricular septal defect (B) and 2.4 mm-sized secundum atrial septal defect (C).
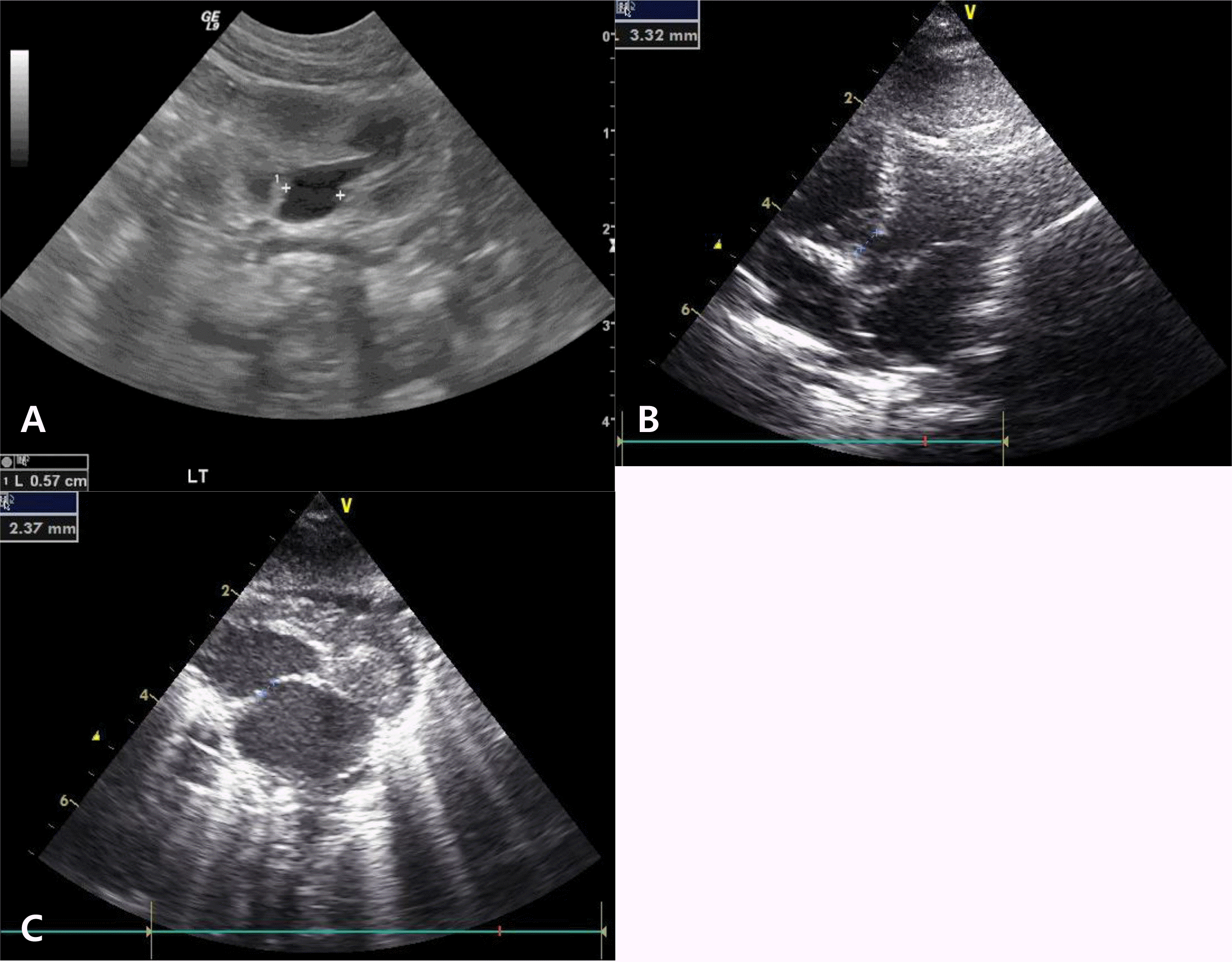
Fig. 3
On enhanced chest computed tomogram image of the patient on 6th day after birth, it showed pneumonia and congenital emphysema. (A) In transverse view, it showed an air space consolidation and a ground glass opacity in dependent portion of both lower lobes (black arrows). (B) In coronal view, it showed a multiseptated wall cystic emphysematous lesion in posterior segment of right upper lobe (black arrowhead).
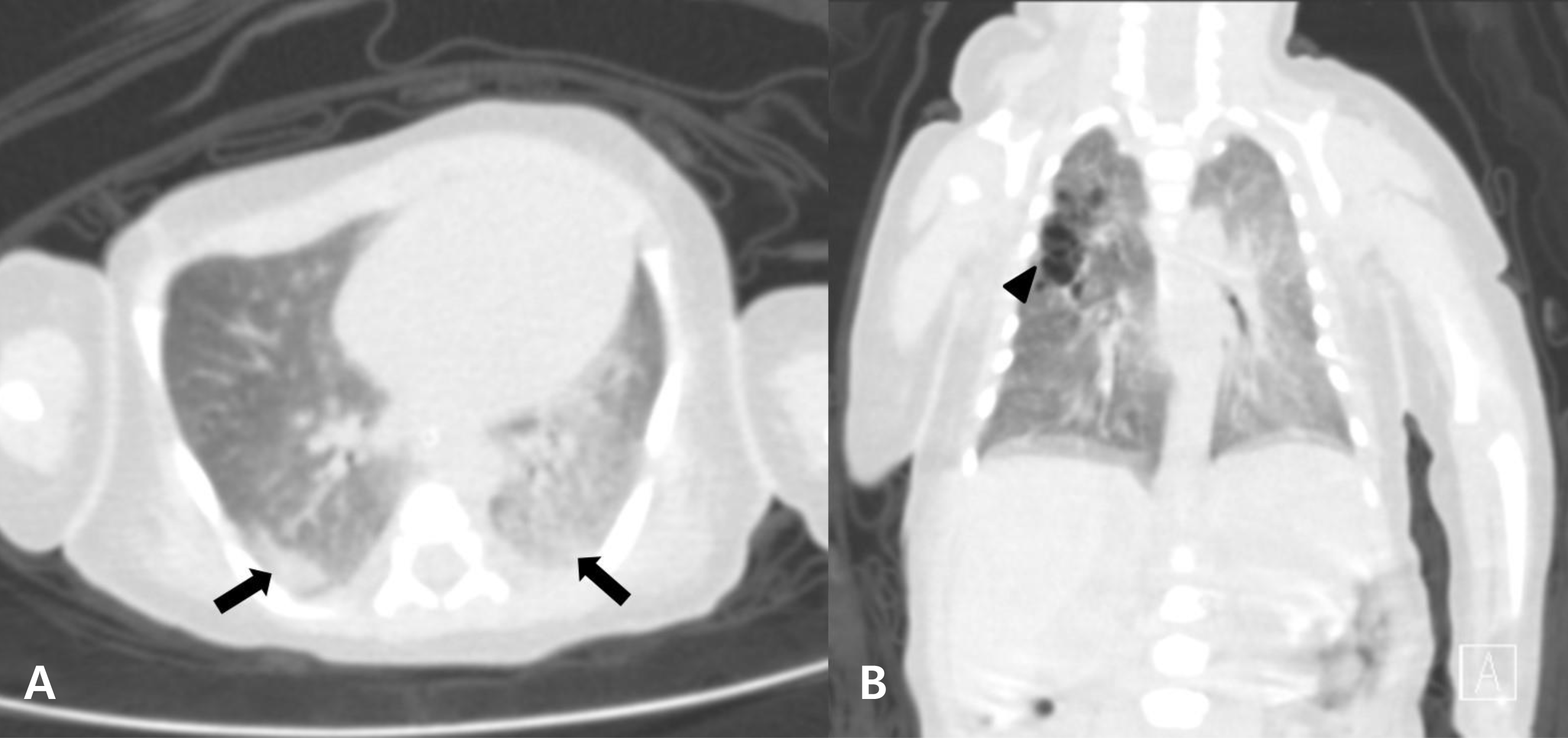
Table 1.
Classification of EDS6
Table 2.
Summary of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome Cases Reported in Korea under 20-Year Old Age15
| Study | Sex | Age (years) | Type | Past history & major complication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Park et al. (1970)∗ | F | 1 | Arthrochalasia (VII) | Skin hyper extensiblity |
| F | 8 | Arthrochalasia (VII) | Joint hypermobility | |
| Congenital hip dislocation | ||||
| Lee et al. (1980)∗ | F | 3 | Unknown | Velvety skin, Skin hyperextensibility |
| Lee et al. (1985)∗ | M | 5 | Hypermobility (III) | Hypermobility of the joints, asymmetry of the thorax |
| F | 3 | Hypermobility (III) | Waddling gait | |
| Kim et al. (1994)∗ | F | 5 | Kyphoscoliosis (VI) | Oscillopsia, corneal opacity, blue sclera |
| Ha et al. (2000)∗ | M | 19 | Classical (II) | Soft & velvety skin with marked hyperextensibility and hypermobile finger joint |
| Lee et al. (2006)∗ | M | 19 | Classical (II) | Hyperextensibility of skin at the forearm, Hyperpigmented atrophic scars |
| Kim et al. (2010)16 | M | 18 | Vascular (IV) | Tingling sensation in the neck and left shoulder, left upper extremity weakness |
| C4/5 radiculopathy | ||||
| Fusiform aneurysm | ||||
| Im et al. (2010)17 | F | 15 | Kyphoscoloisis (VI) | Congenital scoliosis |
| Kim et al. (2011)18 | M | 6 | Classical (II) | Hyperextensible skin, Cutis laxa |
| M | 18 | Classical (II) | Hyperextensible skin, Cutis laxa | |
| Yoon et al. (2014)19 | M | 16 | Vascular (IV) | Spontaneous colon perforation |
| Rt. Thigh hematoma |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download