Abstract
Thiemann's disease is a form of idiopathic avascular necrosis of the immature epiphyses of the phalanges of the fingers and toes. Few cases of Thiemann's disease have been reported because the disease is rare and difficult to diagnose. To the best of our knowledge, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings of Thiemann's disease have not been reported. Here, we report a case of Thiemann's disease diagnosed by typical clinical symptoms and characteristic MRI findings before radiologic bony abnormalities were apparent.
References
1. Thiemann H. Juvenile epiphysenstörungen. Fortschr Röntgenstr. 1909; 14:79–87.
2. Shaw EW. Avascular necrosis of the phalanges of the hands (Thiemann's disease). J Am Med Assoc. 1954; 156:711–713.

3. Allison AC, Blumberg BS. Familial osteoarthropathy of the fingers. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1958; 40-B:538–545.

4. Cullen JC. Thiemann's disease. Osteochondrosis juvenilis of the basal epiphyses of the phalanges of the hand. Report of two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970; 52:532–534.
5. Seckin U, Ozoran K, Polat N, Ucan H, Tutkak H. Thiemann's disease: a case report. Rheumatol Int. 1999; 18:157–158.
6. Dessecker C. Zur epiphysenekrose der mittelphalangen beider Häinde. Dtsch Z Chir. 1930; 229:327–336.
7. van der Laan JG, Thijn CJ. Ivory and dense epiphyses of the hand: Thiemann disease in three sisters. Skeletal Radiol. 1986; 15:117–122.

8. Rubinstein HM. Thiemann's disease. A brief reminder. Arthritis Rheum. 1975; 18:357–360.
Fig. 1.
Simple radiograph of right fifth finger shows no fracture line or other abnormal bone lesion.
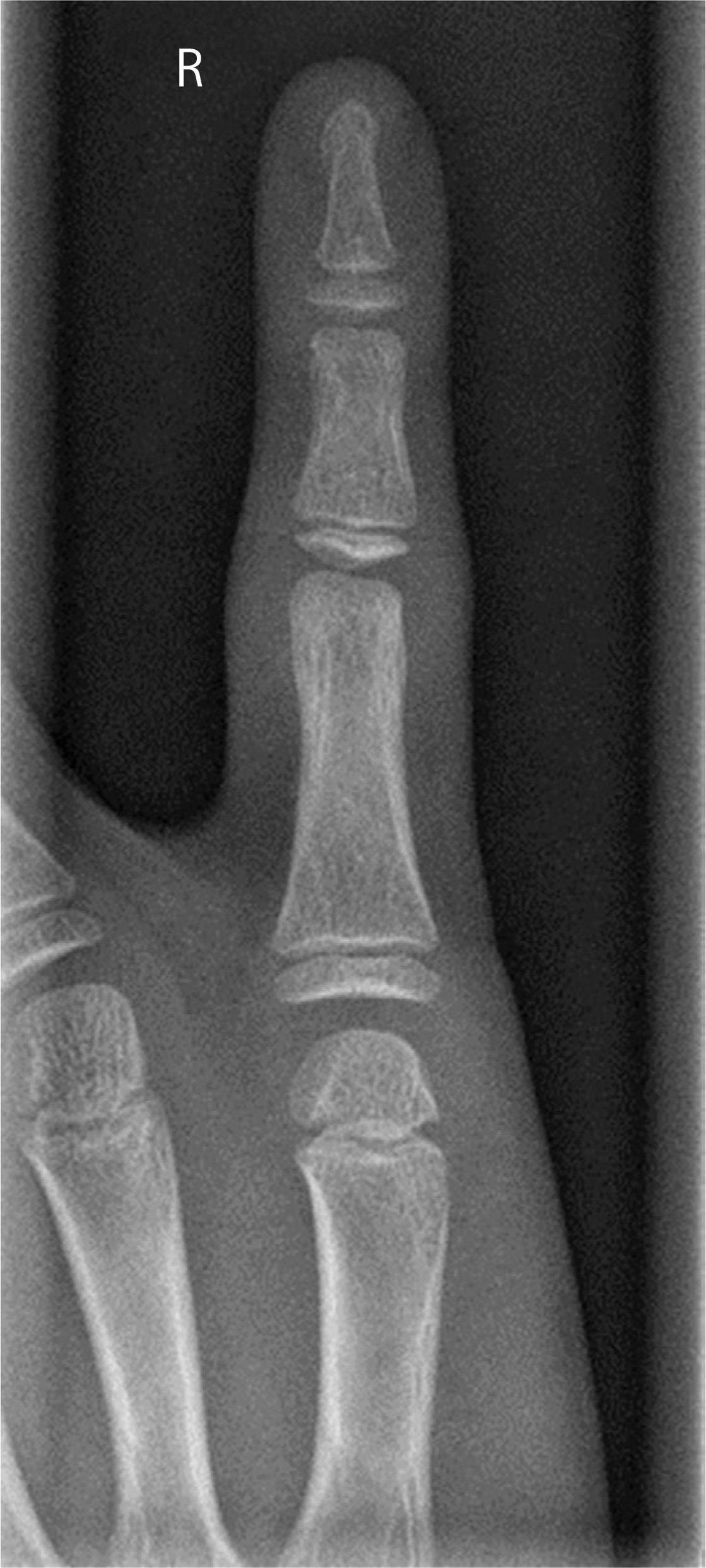
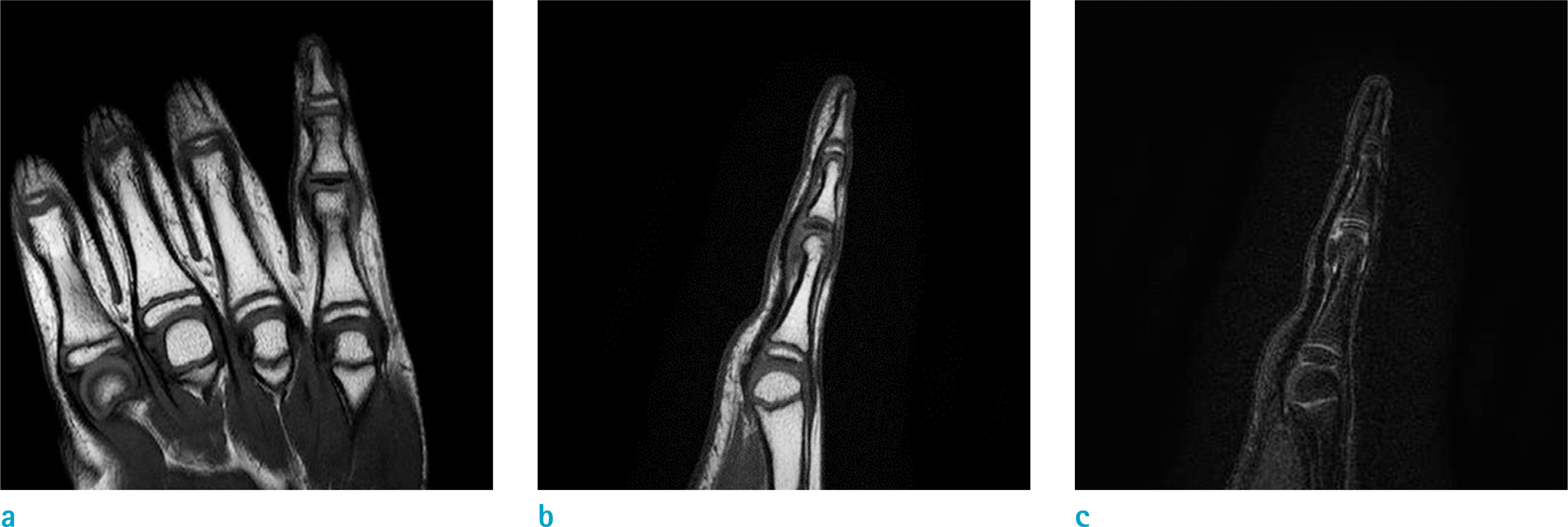
Fig. 2.
MRI of right hand (a) on coronal T1-weighted image shows diffuse low-signal intensity lesion with loss of normal fat marrow signal confined to the proximal epiphysis of the right fifth middle phalanx. There was no definite fracture line. (b) The sagittal T1-weighted image also shows diffuse dark signal intensity lesion in same region. (c) The sagittal fat-suppressed (c) The sagittal fat-suppressed T2-weighted image shows abnormal linear high-signal intensity lesion in proximal epiphysis of the right fifth middle phalanx. There was no significant joint effusion in proximal interphalangeal and distal interphalangeal joints of right fifth finger.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download