초록
In adolescents, sleep deprivation problem is getting worse, and increased caffeine consumption is considered to relieve the stress caused by sleep deprivation and academic burden. In this study, immediate neurologic effects of caffeine intake on adolescents were evaluated in three high school students using the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)/creatine ratio on magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). MEGA-PRESS MRS and TE 135 ms single voxel MRS were performed in the anterior cingulate cortex before and after drinking a cup of coffee, which contained 104 mg of caffeine. GABA and creatine were measured on LCModel 6.3, respectively. In all three students, GABA/creatine ratios were decreased after caffeine intake. The GABA/creatine ratios obtained before caffeine intake were decreased after caffeine intake in all the three adolescents. In this preliminary study, caffeine intake caused an immediate decrease in the GABA/creatine ratio in the brain and it may be related to the neurologic effects of caffeine on an adolescent's brain.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Kim MH, Choi JC, Lim HS, et al. Assessment of caffeine intake from foods. Food safety management. Seoul: Ministry of Food and Drug Safety;2014.
2. Shi D, Nikodijevic O, Jacobson KA, Daly JW. Chronic caffeine alters the density of adenosine, adrenergic, cholinergic, GABA, and serotonin receptors and calcium channels in mouse brain. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1993; 13:247–261.

3. Schur RR, Draisma LW, Wijnen JP, et al. Brain GABA levels across psychiatric disorders: A systematic literature review and metaanalysis of (1) H-MRS studies. Hum Brain Mapp. 2016; 37:3337–3352.
4. Bush G, Luu P, Posner MI. Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends Cogn Sci. 2000; 4:215–222.

5. Mullins PG, McGonigle DJ, O'Gorman RL, et al. Current practice in the use of MEGA-PRESS spectroscopy for the detection of GABA. Neuroimage. 2014; 86:43–52.

6. Doelken MT, Hammen T, Bogner W, et al. Alterations of intracerebral gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) levels by titration with levetiracetam in patients with focal epilepsies. Epilepsia. 2010; 51:1477–1482.
7. O'Gorman RL, Michels L, Edden RA, Murdoch JB, Martin E. In vivo detection of GABA and glutamate with MEGA-PRESS: reproducibility and gender effects. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011; 33:1262–1267.
Go to : 
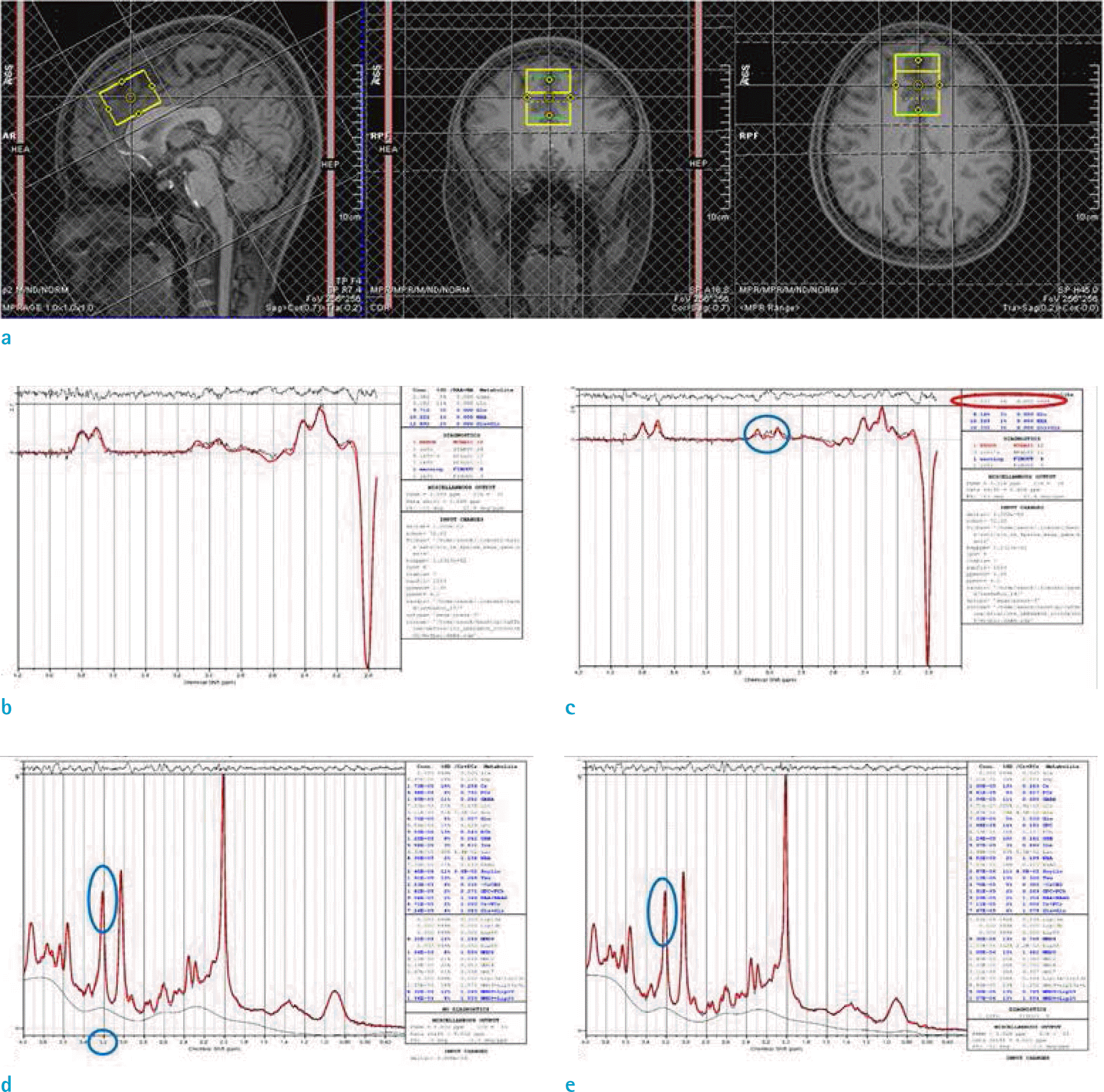 | Fig. 1.Measurement of the GABA/creatine ratio on brain MRS (Subject 1). (a) Brain MRS for measuring GABA at the anterior cingulate cortex. (b) GABA rate before caffeine intake. (c) GABA rate after caffeine intake. (d) Creatine before caffeine intake. (e) Creatine after caffeine intake. |
Table 1.
Changes in Vital Signs in Three Subjects Before and After Caffeine Intake
Table 2.
Changes in the GABA/Creatine Ratio in Three Subjects Before and After Caffeine Intake




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download