Abstract
Purpose
There is a high prevalence of erectile dysfunction (ED) after electric injuries, but our medical understanding of ED after electric injuries is scanty at best. Thus, the authors attempted to investigate nocturnal penile tumescence (NPT), bulbocavernosus reflex latency (BCRL) and penile duplex Doppler ultrasonography (PDDU) for the patients who suffer from ED after electric injuries.
Materials and Methods
Of the patients who visited our Burn Care Center between January 2005 and February 2006, ten male patients (aged 20 or older) who complaining of ED after electric injuries underwent NPT, BCRL and PDDU.
Results
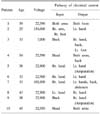
The patients' mean age was 38.1 years (age range: 25-54), and the numbers of patients exposed to whole body, upper-lower extremity and upper-upper extremity pathways of the electrical current were 1, 2 and 7, respectively. For the patient exposed to the whole body pathway, abnormal findings were observed on all the tests. For one patient who experienced two upper-lower extremity pathways, normal findings were seen on all the tests, while the other patient showed an abnormal NPT, an normal BCRL and an arteriogenic ED. Three of the patients who experienced the upper-upper extremity pathway showed normal findings on all the tests. The other two in the group showed an abnormal NPT, a normal BCRL and arteriogenic ED; the other one showed a normal vascular function, a abnormal NPT and no reaction to BCRL; the other one showed an abnormal NPT, a delayed BCRL and an arteriogenic ED.
References
1. Kim HJ, Kim JM, Kang IM, Choi NG. Erectile dysfunction in patients with eletrical injury. Korean J Urol. 2005. 46:737–740.
2. Korean Andrology Society. Textbook of andrology. 2003. 1st ed. Seoul: Koonja Publishing Inc;277–300.
3. Koumbourlis AC. Electrical injuries. Crit Care Med. 2002. 30:11 Suppl. S424–S430.
4. Jain S, Bandi V. Electrical and lightning injuries. Crit Care Clin. 1999. 15:319–331.
5. Cooper MA. Emergent care of lightning and electrical injuries. Semin Neurol. 1995. 15:268–278.
6. Varghese G, Mani MM, Redford JB. Spinal cord injuries following electrical accidents. Paraplegia. 1986. 24:159–166.
7. Hunt JL, McManus WF, Haney WP, Pruitt BA Jr. Vascular lesions in acute electric injuries. J Trauma. 1974. 14:461–473.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download