Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the incidence and histopathological factors of perirenal fat invasion (pT3a) in cT1a renal cell carcinomas. The implication for postoperative perirenal fat invasion, as a prognostic factor in patients with tumors less than 4cm tumor in size is also discussed.
Materials and Methods
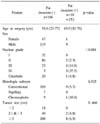
Of 503 patients who underwent an operation for a renal cell carcinoma at our institution, between June 1995 and April 2004, we retrospectively reviewed the records of 176 with T1a renal cell carcinomas. We evaluated the pathological grade, cell type, tumor size, location and incidence of perirenal fat invasion using the Fisher's exact test. The overall survival was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and log-rank test, and the prognostic factors influencing the survival were estimated using the Cox proportional hazard regression model.
Results
In this study, a radical nephrectomy was performed in 128 men and 48 women, with a mean age of 54.6 years, ranging from 23 to 77. The mean follow-up was 31.3 months, ranging from 6 to 106 months. The average size of the renal cell carcinomas was 3.0cm, ranging from 1 to 4cm. The incidence of perirenal fat invasion in the T1a renal cell carcinomas was 5.7% (n=10). The nuclear grade (p<0.001) was a statistically significant factor in the incidence of postoperative perirenal fat invasion.
Conclusions
In the patients with a renal cell carcinoma less than 4cm in size (cT1a), those in the postoperative perirenal fat invasion group had a significantly poorer prognosis. The tumor size and Fuhrman nuclear grade were implicated in the incidence of perirenal fat invasion in the T1a renal cell carcinomas. Therefore, in the case of nephron sparing surgery, more precise preoperative staging of the primary tumor is required.
Figures and Tables
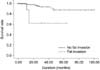
Fig. 1
Survival curves according to the presence of perirenal fat invasion in renal cell carcinomas 4cm or less in size (p<0.004).
References
1. Kim WJ, Chung JI, Hong JH, Kim CS, Jung SI, Yoon DK. Epidemiologic study for urologic cancer in Korea (1998-2002). Korean J Urol. 2004. 45:1081–1088.
2. Jayson M, Sanders H. Increased incidence of serendipitously discovered renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 1998. 51:203–205.
3. Licht MR, Novick AC, Goormastic M. Nephron sparing surgery in incidental versus suspected renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 1994. 152:39–42.
4. Nam JK, Cha CS, Chung MK. The treatment outcomes of a partial nephrectomy in the management of renal cell carcinomas. Korean J Urol. 2004. 45:1100–1105.
5. Fergani AF, Hafez KS, Novick AC. Long-term results of nephron sparing surgery for localized renal cell carcinoma: 10-year followup. J Urol. 2000. 163:442–445.
6. Lee C, Katz J, Shi W, Thaler HT, Reuter VE, Russo P. Surgical management of renal tumors 4cm or less in a contemporary cohort. J Urol. 2000. 163:730–736.
7. Polascik TJ, Pound CR, Meng MV, Partin AW, Marshall FF. Partial nephrectomy: technique, complications and pathological finding. J Urol. 1995. 154:1312–1318.
8. Duque JL, Loughlin KR, O'Leary MP, Kumar S, Richie JP. Partial nephrectomy: alternative treatment for selected patients with renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 1998. 52:584–590.
9. Leibovich BC, Blute ML, Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Weaver AL, Zincke H. Nephron sparing surgery for appropriately selected renal cell carcinoma between 4 and 7cm results in outcome similar to radical nephrectomy. J Urol. 2004. 171:1066–1070.
10. Pantuck AJ, Zisman A, Belldegrun AS. The changing natural history of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2001. 166:1611–1623.
11. Hafez KS, Fergany AF, Novick AC. Nephron sparing surgery for localized renal cell carcinoma: impact of tumor size on patient survival, tumor recurrence and TNM staging. J Urol. 1999. 162:1930–1933.
12. Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz A, Balch CM, Haller DG, et al. AJCC cancer staging manual. 2002. 6th ed. New York: Springer-Verlag;323–328.
13. Roberts WW, Bhayani SB, Allaf ME, Chan TY, Kavoussi LR, Jarrett TW. Pathological stage does not alter the prognosis for renal lesions determined to be stage T1 by computerized tomography. J Urol. 2005. 173:713–715.
14. Lapini A, Serni S, Minervini A, Masieri L, Carini M. Progression and long-term survival after simple enucleation for the elective treatment of renal cell carcinoma: experience in 107 patients. J Urol. 2005. 174:57–60.
15. Allaf ME, Bhayani SB, Rogers C, Varkarakis I, Link RE, Inagaki T, et al. Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: evaluation of long-term oncological outcome. J Urol. 2004. 172:871–873.
16. Puppo P, Introini C, Calvi P, Naselli A. Long term results of excision of small renal cancer surrounded by a minimal layer of grossly normal parenchyma: review of 94 cases. Eur Urol. 2004. 46:477–481.
17. Thomas DH, Verghese A, Kynaston HG, Griffiths DF. Analysis of the prognostic implications of different tumour margin types in renal cell carcinoma. Histopathology. 2003. 43:374–380.
18. Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C. Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1982. 6:655–663.
19. Minardi D, Lucarini G, Mazzucchelli R, Milanese G, Natali D, Galosi AB, et al. Prognostic role of Fuhrman grade and vascular endothelial growth factor in pT1a clear cell carcinoma in partial nephrectomy specimens. J Urol. 2005. 174:1208–1212.
20. Bretheau D, Lechevallier E, de Fromont M, Sault MC, Rampal M, Coulange C. Prognostic value of nuclear grade of renal cell carcinoma. Cancer. 1995. 76:2543–2549.
21. Sandock DS, Seftel AD, Resnick MI. New protocol for the followup of renal cell carcinoma based on pathologic stage. J Urol. 1995. 154:28–31.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download