Abstract
Purpose
Since Rho-Rho kinase calcium sensitizing pathway is being regarded as a potential target not only for the treatment of erectile dysfunction but also atherosclerosis, we designed a study to prevent vasculogenic erectile dysfunction in an atherosclerotic rat model by chronic administration of fasudil, oral Rho kinase inhibitor.
Materials and Methods
Rats (3 months old) were divided into 3 groups (n=10 in each group): control (group 1), atherosclerosis (group 2), and fasudil-treated (group 3). The group 2, 3 received atherosclerosis-prone treatment but group 3 was concurrently treated by fasudil (30mg/kg/day) for 6 weeks. Following the treatment, the erectile function and the amount of pelvic atherosclerosis amount were determined. Cavernosal tissues were prepared for Western blot and malondialdehyde (MDA) assay.
Results
Compared to group 2, the progression of atherosclerosis in iliac and pudendal arteries was significantly suppressed by the chronic administration of fasudil. Also the treatment lowered the level of malondialdehyde in the cavernosal tissue. The results of Western blot revealed that systemically administered fasudil could ameliorate cavernosal molecular environment characterized by the decreased expression of Rho A, transforming growth factor-beta 1 and overexpression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. As a result, erectile function was maintained by the treatment.
Conclusions
These results indicate that Rho/Rho kinase pathway is substantially involved in the development of penile erection and pelvic atherosclerosis, both of which could be prevented by chronic treatment of fasudil. Thus, Rho-kinase might be considered as a novel target for prevention of vasculogenic erectile dysfunction.
Figures and Tables
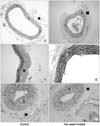 | Fig. 1Photomicrographs of representative cross sections of the arteries of the rats in the pilot study. (A) No intimal lesion in the control group. The internal iliac artery (H&E, ×200). (B) Well preserved elastic lamella in the control group. The internal iliac artery (EVG, ×1,000). (C) Normal cellularity and a well preserved internal elastic lamella are observed in the control group. The internal pudendal artery (H&E, ×400). (D) Asymmetrical intimal irregularity and focal thickening of the intima are observed in the 2 week treated rats. The internal iliac artery (H&E, ×200). (E) Widening of the interlamellar spaces and the gradual loss of elastic fiber are observed after a 2 week treatment. The internal iliac artery EVG, ×1,000). (F) No significant intimal change is observed after a 2 week treatment (H&E, ×400). H&E: hematoxylin and eosin, EVG: Elastic van Gieson staining, I: intima; M: media. |
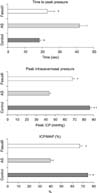 | Fig. 2Results of cavernous nerve electrostimulation. Treatment with fasudil effectively ameliorates the deterioration of erectile function. *denotes statistical difference versus atherosclerosis (AS). †denotes statistical difference versus fasudil. |
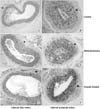 | Fig. 3Photomicrographs of representative cross sections of rat internal iliac (left sided panel) and internal pudendal (right side panel) arteries. The progression of atherosclerosis is substantially attenuated by the fasudil treatment (H&E, ×200 (internal iliac artery) and ×400 (internal pudendal artery)). |
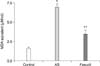 | Fig. 4The results of malondialdehyde assay show that fasudil significantly reduces oxidative stress compared to the atherosclerosis (AS) group. *statistically significant differences from control, †statistically significant differences from AS. |
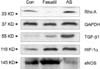 | Fig. 5The protein expression of our experimental groups is analysed by Western blotting. TGF-β1: transforming growth factor β1, HIF-1α: hypoxia induced factor 1α, eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase, AS: atherosclerosis. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) served as a control for the loading. |
References
1. Son HC, Byun SS, Park EC, Cho KS, Jo MK, Kim SW, et al. Prevalence of sexual dysfunction in men older than 40 living in Seoul: epidemiologic survey using questionnaire. Korean J Urol. 2002. 43:52–61.
2. Kim TH, Chung TG, Ahn TY. Relation between lower urinary tract symptoms and erectile dysunction: epidemiologic study in Jeong-Eup, Korea. Korean J Androl. 1998. 16:87–91.
3. Kubin M, Wagner G, Fugl-Meyer AR. Epidemiology of erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 2003. 15:63–71.
4. Chen KK, Chiang HS, Jiann BP, Lin JS, Liu WJ, Wu CJ, et al. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction and impacts on sexual activity and self-reported intercourse satisfaction in men older than 40 years in Taiwan. Int J Impot Res. 2004. 16:249–255.
5. Padma-nathan H, Eardley I, Kloner RA, Laties AM, Montorsi F. A 4-year update on the safety of sildenafil citrate (Viagra). Urology. 2002. 60:2 Suppl 2. 67–90.
6. Son H, Park K, Kim SW, Paick JS. Reasons for discontinuation of sildenafil citrate after successful restoration of erectile function. Asian J Androl. 2004. 6:117–120.
7. Fink HA, Mac Donald R, Rutks IR, Nelson DB, Wilt TJ. Sildenafil for male erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2002. 162:1349–1360.
8. Shimokawa H. Rho-kinase as a novel therapeutic target in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2002. 39:319–327.
9. Kataoka C, Egashira K, Inoue S, Takemoto M, Ni W, Koyanagi M, et al. Important role of Rho-kinase in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular inflammation and remodeling induced by long-term blockade of nitric oxide synthesis in rats. Hypertension. 2002. 39:245–250.
10. Chitaley K, Wingard CJ, Clinton Webb R, Branam H, Stopper VS, Lewis RW, et al. Antagonism of Rho-kinase stimulates rat penile erection via a nitric oxide-independent pathway. Nat Med. 2001. 7:119–122.
11. Park K, Son H, Kim SW, Paick JS. Initial validation of a novel rat model of vasculogenic erectile dysfunction with generalized atherosclerosis. Int J Impot Res. 2005. 17:424–430.
12. Tomita H, Egashira K, Kubo-Inoue M, Usui M, Koyanagi M, Shimokawa H, et al. Inhibition of NO synthesis induces inflammatory changes and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in rat hearts and vessels. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1998. 18:1456–1464.
13. Eto Y, Shimokawa H, Hiroki J, Morishige K, Kandabashi T, Matsumoto Y, et al. Gene transfer of dominant negative Rho kinase suppresses neointimal formation after balloon injury in pigs. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2000. 278:H1744–H1750.
14. Ikegaki I, Hattori T, Yamaguchi T, Sasaki Y, Satoh SI, Asano T, et al. Involvement of Rho-kinase in vascular remodeling caused by long-term inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. 427:69–75.
15. Chitaley K, Bivalacqua TJ, Champion HC, Usta MF, Hellstrom WJ, Mills TM, et al. Adeno-associated viral gene transfer of dominant negative RhoA enhances erectile function in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. 298:427–432.
16. Sauzeau V, Le Jeune H, Cario-Toumaniantz C, Smolenski A, Lohmann SM, Bertoglio J, et al. Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase signaling pathway inhibits RhoA-induced Ca2+ sensitization of contraction in vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:21722–21729.
17. Eto M, Barandier C, Rathgeb L, Kozai T, Joch H, Yang Z, et al. Thrombin suppresses endothelial nitric oxide synthase and upregulates endothelin-converting enzyme-1 expression by distinct pathways: role of Rho/ROCK and mitogen-activated protein kinase. Circ Res. 2001. 89:583–590.
18. Moreland RB, Albadawi H, Bratton C, Patton G, Goldstein I, Traish A, et al. O2-dependent prostanoid synthesis activates functional PGE receptors on corpus cavernosum smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2001. 281:H552–H558.
19. Ming XF, Viswambharan H, Barandier C, Ruffieux J, Kaibuchi K, Rusconi S, et al. Rho GTPase/Rho kinase negatively regulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation through the inhibition of protein kinase B/Akt in human endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. 22:8467–8477.
20. Sullivan ME, Keoghane SR, Miller MA. Vascular risk factors and erectile dysfunction. BJU Int. 2001. 87:838–845.
21. Shatrov VA, Sumbayev VV, Zhou J, Brune B. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) triggers hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) accumulation via redox-dependent mechanisms. Blood. 2003. 101:4847–4849.
22. Chun YS, Kim MS, Park JW. Oxygen-dependent and -inde pendent regulation of HIF-1alpha. J Korean Med Sci. 2002. 17:581–588.
23. Shimokawa H, Hiramori K, Iinuma H, Hosoda S, Kishida H, Osada H, et al. Anti-anginal effect of fasudil, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, in patients with stable effort angina: a multicenter study. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2002. 40:751–761.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download