Abstract
Purpose
We reviewed the operative outcome and the cause of failure for performing subureteral injection of polydimethylsiloxane (PDS, Macroplastique®, Uroplasty Inc. Geleen, The Netherlands), when it is used as a bulking agent for the endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) patients.
Materials and Methods
A total of 29 patients (a total of 37 ureters), with primary grades I to V VUR were treated with a single subureteral injection from 2001 to 2004; these patients were followed for an average of 21.5 months. Each patient underwent preoperative voiding cystourethrography, renal ultrasound, a dimercapto-succinic acid (DMSA) scan and urine culture. With the patient under general anesthesia, the PDS implant was injected transurethrally at the 6 o'clock position of the ureteral opening in the affected renal unit by a modified subureteral transurethral injection (STING) procedure. Renal ultrasound was done at 1 week and voiding cystourethrography was done at 3 months to rule out obstruction at the injection site and/or persistent reflux, respectively. Cure was defined as an absence of VUR on voiding cystourethrography at 3 months after injection. Statistical analyses were performed using the chi-square test.
Results
The grade of reflux was I, II, III, IV and V in 6, 4, 12, 9 and 6 ureteral units respectively. After a single injection, the VUR was cured in 30 ureteral units (81.1%). There were 7 (18.9%) patients who received a second injection after a failed single injection. In these patients, the injected PDS volume was not changed on ultrasound. On the other hand, cystoscopy showed mound displacement in 4 patients, no volcano appearance but rather a broad elevation in 2 patient, and distal ureteral fistula and mound extrusion in 1 patient.
Figures and Tables
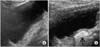 | Fig. 1Urinary bladder sonography. (A) Preoperative bladder sonography shows no specific echogenic shadow at the right ureteral orifice. (B) Postoperative bladder sonography shows an echogenic nodule (arrow) of injected polydimethylsiloxane (PDS). |
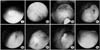 | Fig. 2Cystoscopic findings. (A) Preoperative cystoscopy shows a "golf hole" appearance of the right ureteral orifice in a Gr III vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) patient. (B) Postoperative cystoscopy. (a) Competent ureteral orifice on the top of a "volcano" after the cystoscopic submucosal injection of polydimethylsiloxane (PDS). (b) Competent ureteral orifice on the top of a "volcano" after injection of PDS for Gr II VUR. (c) Incompetent ureteral orifice; a main mound (arrow) is seen above the ureteral orifice. (d) Incompetent ureteral orifice; a mound is still poorly seen around ureteral orifice at 5-7 o'clock. (e) Left ureteral orifice is barely seen at the top of mound due to overcorrection (cystoscopy at 1st operation). (f) Extrusion of PDS is seen due to mucosal necrosis after overcorrection. (g) Ureteral fistula near the Rt. ureteral orifice is seen. It might be the result of complete extrusion of PDS after overcorrection. |
References
1. Smellie JM, Barratt TM, Chantler C, Gordon I, Prescod NP, Ransley PG, et al. Medical versus surgical treatment in children with severe bilateral vesicoureteric reflux and bilateral nephropathy: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001. 357:1329–1333.
2. Jacobson SH, Hansson S, Jakobsson B. Vesico-ureteric reflux: occurrence and long-term risks. Acta Paediatr. 1999. 88:Suppl. 22–30.
3. Cooper CS, Chung BI, Kirsch AJ, Canning DA, Snyder HM 3rd. The outcome of stopping prophylactic antibiotics in older children with vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol. 2000. 163:269–272.
4. Malizia AA Jr, Reiman HM, Myers RP, Sande JR, Barham SS, Benson RC Jr, et al. Migration and granulomatous reaction after periurethral injection of polytef (Teflon). JAMA. 1984. 251:3277–3281.
5. Puri P, O'Donnell B. Correction of experimentally produced vesicoureteric reflux in the piglet by intravesical injection of Teflon. Br Med J(Clin Res Ed). 1984. 289:5–7.
6. Park JW, Kim KS. An experience of endoscopic polydimethylsiloxane injection for the treatment of vesicoureteral reflux in children. Korean J Urol. 2003. 44:150–154.
7. Smith DP, Kaplan WE, Oyasu R. Evaluation of polydimethylsiloxane as an alternative in the endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol. 1994. 152:1221–1224.
8. Herz D, Hafez A, Bagli D, Capolicchio G, McLorie G, Khoury A. Efficacy of endoscopic subureteral polydimethylsiloxane injection for treatment of vesicoureteral reflux in children: a North American clinical report. J Urol. 2001. 166:1880–1886.
9. Sternberg A, Lackgren G. A new bioimplant for the endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux: experimental and short-term clinical results. J Urol. 1995. 154:800–803.
10. Oswald J, Riccabona M, Lusuardi L, Bartsch G, Radmayr C. Prospective comparison and 1-year follow-up of a single endoscopic subureteral polydimethylsiloxane versus dextranomer/hyaluronic acid copolymer injection for treatment of vesicoureteral reflux in children. Urology. 2002. 60:894–897.
11. Puri P, Granata C. Multicenter survey of endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux using polytetrafluoroethylene. J Urol. 1998. 160:1007–1011.
12. Ozyavuz R, Ozgur GK, Yuzuncu AK. Subureteric polydimethylsiloxane injection in the treatment of vesico-ureteric reflux. Int Urol Nephrol. 1998. 30:123–126.
13. Cho KS, Yun JM, Jeong H, Jung JY, Kim KM. Ureteral submucosal macroplastique injection in the treatment of vesicoureteral reflux. J Korean Continence Soc. 1999. 3:51–59.
14. Chertin B, De Caluwe D, Puri P. Endoscopic treatment of primary grades IV and V vesicoureteral reflux in children with subureteral injection of polytetrafluoroethylene. J Urol. 2003. 169:1847–1849.
15. Frankenschmidt A, Katzenwadel A, Zimmerhackl LB, Sommerkamp H. Endoscopic treatment of reflux by subureteric collagen injection: critical review of 5 years' experience. J Endourol. 1997. 11:343–348.
16. Leonard MP, Decter A, Mix LW, Johnson HW, Coleman GU. Endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux with collagen: preliminary report and cost analysis. J Urol. 1996. 155:1716–1720.
17. Diamond DA, Caldamone AA, Bauer SB, Retik AB. Mechanisms of failure of endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux based on endoscopic anatomy. J Urol. 2003. 170:1556–1558.
18. Vereecken RL, Proesmans W. Results of endoscopic treatment of vesico-ureteral reflux. Eur Urol. 1995. 27:76–79.
19. Dewan PA, Higgs MJ. Correlation of the endoscopic appearance with clinical outcome for submucous Polytef paste injection in vesico-ureteric reflux. Aust N Z J Surg. 1995. 65:642–644.
20. Kirsch AJ, Perez-Brayfield M, Smith EA, Scherz HC. The modified sting procedure to correct vesicoureteral reflux: improved results with submucosal implantation within the intramural ureter. J Urol. 2004. 171:2413–2416.
21. Aboutaleb H, Bolduc S, Upadhyay J, Farhat W, Bagli DJ, Khoury AE. Subureteral polydimethylsiloxane injection versus extravesical reimplantation for primary low grade vesicoureteral reflux in children: a comparative study. J Urol. 2003. 169:313–316.
22. Aboutaleb H, Bolduc S, Khoury AE, Upadhyay J, Bagli DJ, Farhat W. Polydimethylsiloxane injection versus open surgery for the treatment of vesicoureteral reflux in complete duplex systems. J Urol. 2003. 170:1563–1565.
23. Perez-Brayfield M, Kirsch AJ, Hensle TW, Koyle MA, Furness P, Scherz HC. Endoscopic treatment with dextranomer/ hyaluronic acid for complex cases of vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol. 2004. 172:1614–1616.
24. Ji YH, Kim HS, Choo MS. Effect of subureteral injection of polydimethylsiloxane in women with vesicoureteral reflux. Korean J Urol. 2002. 43:1014–1018.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download