Abstract
Sinus pericranii is a rare vascular anomaly consisting of abnormal venous communication between intra- and extracranial circulation. We report one case, confirmed by surgery, and describe the radiological findings of Doppler ultrasonography, CT and MR imaging.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Sadler LR., Tarr RW., Jungreis CA., Sekhar L. Sinus pericranii: CT and MR findings. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990. 14(1):124–127.
Go to : 
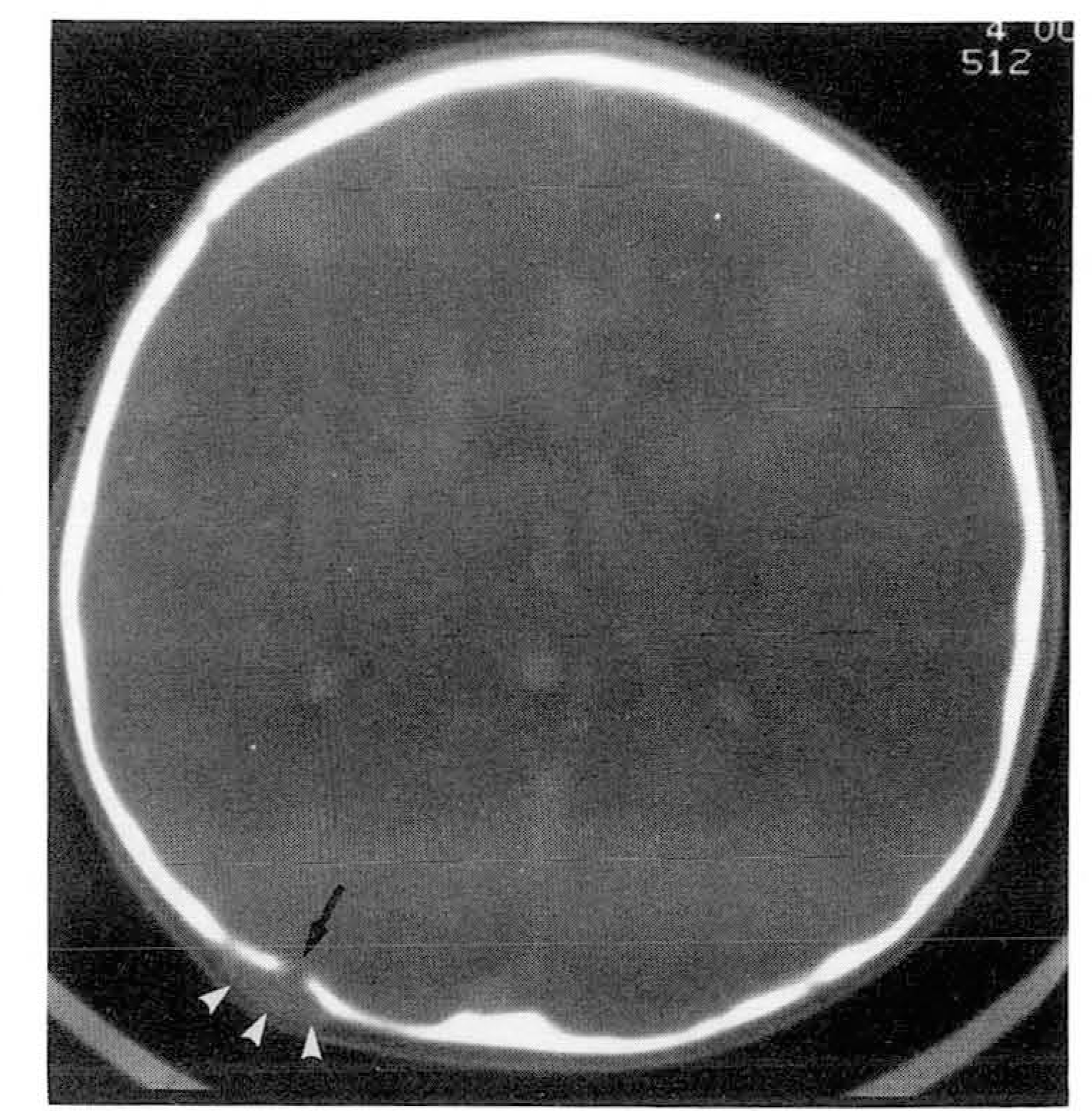 | Fig. 1.Postcontrast CT with bone window setting shows soft tissue mass (arrowheads) beneath the scalp. Underlying bone erosion with small bone defect (arrow) is also noted. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download