Abstract
Intracranial angiolipoma is extremely rare. We report the radiologic findings of angiolipoma in the right middle cranial fossa, extending medially into the suprasellar and cavernous sinus region, in a 63-year-ola woman. The lesion was a relatively well marginated extra-axial tumor that showed low density on precontrast CT and marked enhancement after contrast infusion. MR imaging showed heterogeneous low signal on T1W1 mixed with hyperintense foci on T2W1, and marked enhancement after gadolinium infusion. On cerebral angiography, displacement of the right internal carotid artery by the tumor was seen. On an arteriogram of the right external carotid artery, the mass showed persistent capillary blush.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1.Bowen JT. Multiple subcutaneous haemangiomas together with multiple lipomas, occurring in enormous numbers in an otherwise healthy, muscular subject. Am J Med Sci. 1912. 144:189–192.
4.Wilkins PR., Hoddinott C., Hourhan MD, et al. Intracranial Angilipoma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987. 50:10571059.
5.Shuangshoti S., Vajragupta L. Angiolipoma of thalamus presenting with abrupt onset suggestive of cerebrovascular disease. Clin Neuropathol. 1995. 14:82–85.
6.Prabu SS., O'Donovan DG., Gurusinghe NT. Intracranial Angiolipoma: report of two cases. Br J Neurosurg. 1995. 9:793–797.

7.Lin J J., Lin F. Two entities in angiolipoma. Cancer. 1974. 34:720–727.
Go to : 
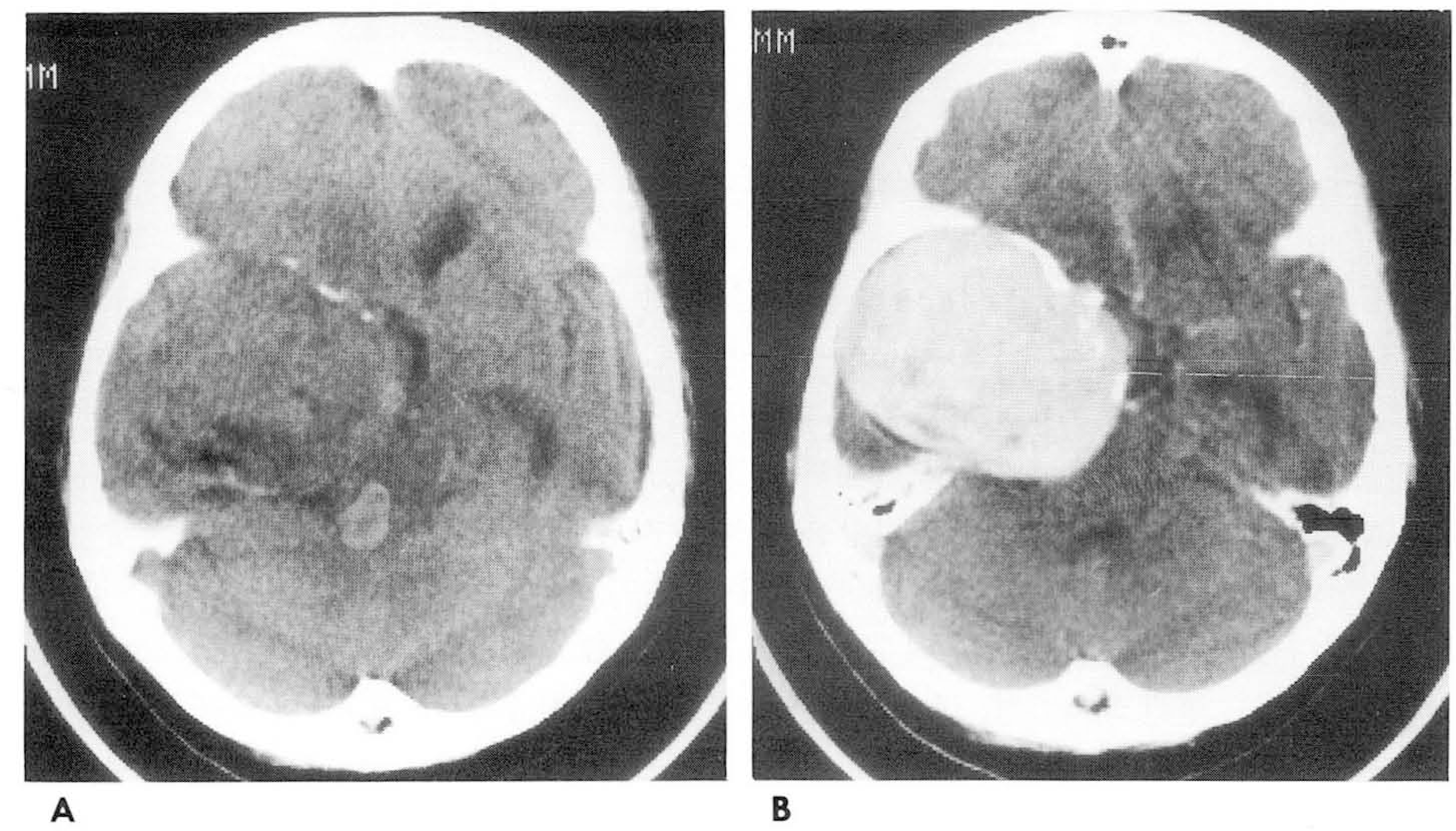 | Fig. 1.CT scan without (A) and with (B) intravenous contrast infusion. A. There is a relatively well demarcated heterogeneous low density mass in the right miaale cranial fossa. B. Intense and homogeneous enhancement is evident after contrast infusion. |
 | Fig. 2.MR imaging of the brain A. Tl-weighted image shows an extra-axial mass with mostly iso-intense signal and several hyperintense foci. B. T2-weighted image shows hyperintense signal. C. Gadolinium enhanced coronal Tl-weighted image shows homogeneous intense enhancement. |
1998亼䰼 䴀⪤䏗㽔㻠㢨⪧⥴ 㛯㥬⩷㽔 㢄㟫 㪸佌 (Π)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download