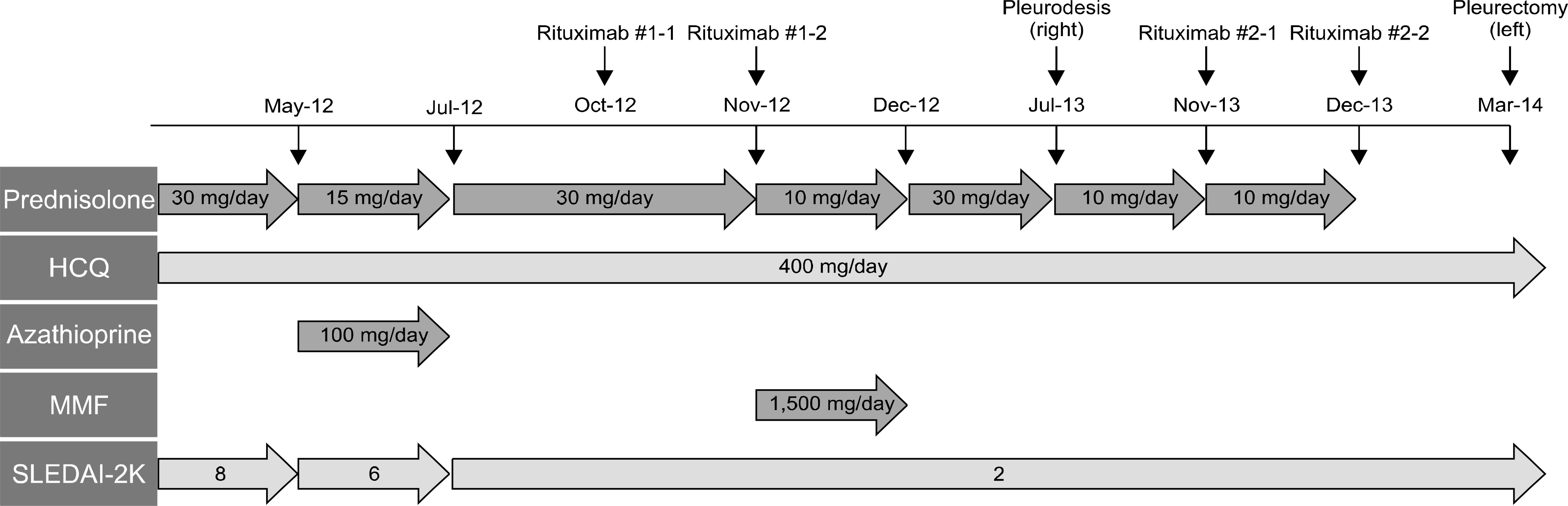
Abstract
Pleural effusion is a common pulmonary manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and often occurs as bilateral exu-dative pleural effusion. The condition usually responds quickly to corticosteroid therapy. However, massive pleural effusion refractory to immunosuppressive drugs has rarely been reported; thus, the proper therapeutic modality is largely decided on a case-by-case basis. In this case, we describe successful treatment with surgical pleurectomy for massive refractory pleural effusion in a patient with SLE.
REFERENCES
1. Keane MP, Lynch JP 3rd. Pleuropulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Thorax. 2000; 55:159–66.
2. Breuer GS, Deeb M, Fisher D, Nesher G. Therapeutic options for refractory massive pleural effusion in systemic lupus erythematosus: a case study and review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 34:744–9.

3. D'Cruz D, Khamashta MA, Hughes G. Pulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. 6th ed.Philadelphia, Lippincott: Williams & Wilkins;2002. p. 663–84.
4. Murin S, Wiedemann HP, Matthay RA. Pulmonary manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Chest Med. 1998; 19:641–65.

5. Sharma S, Smith R, Al-Hameed F. Fibrothorax and severe lung restriction secondary to lupus pleuritis and its successful treatment by pleurectomy. Can Respir J. 2002; 9:335–7.

6. Karim MY, Alba P, Cuadrado MJ, Abbs IC, D'Cruz DP, Khamashta MA, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil for systemic lupus erythematosus refractory to other immunosuppressive agents. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002; 41:876–82.

7. Ginzler EM, Dooley MA, Aranow C, Kim MY, Buyon J, Merrill JT, et al. Mycophenolate mofetil or intravenous cyclophosphamide for lupus nephritis. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:2219–28.

8. Ng KP, Leandro MJ, Edwards JC, Ehrenstein MR, Cambridge G, Isenberg DA. Repeated B cell depletion in treatment of refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006; 65:942–5.
9. Glazer M, Berkman N, Lafair JS, Kramer MR. Successful talc slurry pleurodesis in patients with nonmalignant pleural effusion. Chest. 2000; 117:1404–9.

11. Ukale V, Agrenius V, Hillerdal G, Mohlkert D, Widström O. Pleurodesis in recurrent pleural effusions: a randomized comparison of a classical and a currently popular drug. Lung Cancer. 2004; 43:323–8.

12. Weissberg D, Ben-Zeev I. Talc pleurodesis. Experience with 360 patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1993; 106:689–95.
13. Elborn JS, Conn P, Roberts SD. Refractory massive pleural effusion in systemic lupus erythematosus treated by pleurectomy. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987; 46:77–80.

14. Sherer Y, Langevitz P, Levy Y, Fabrizzi F, Shoenfeld Y. Treatment of chronic bilateral pleural effusions with intravenous immunoglobulin and cyclosporin. Lupus. 1999; 8:324–7.

15. Passero FC, Myers AR. Hemopneumothorax in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 1980; 7:183–6.
Figure 2.
Chest X-ray showing persistent bilateral pleural effusion after pleurodesis of right pleura and rituximab administration.
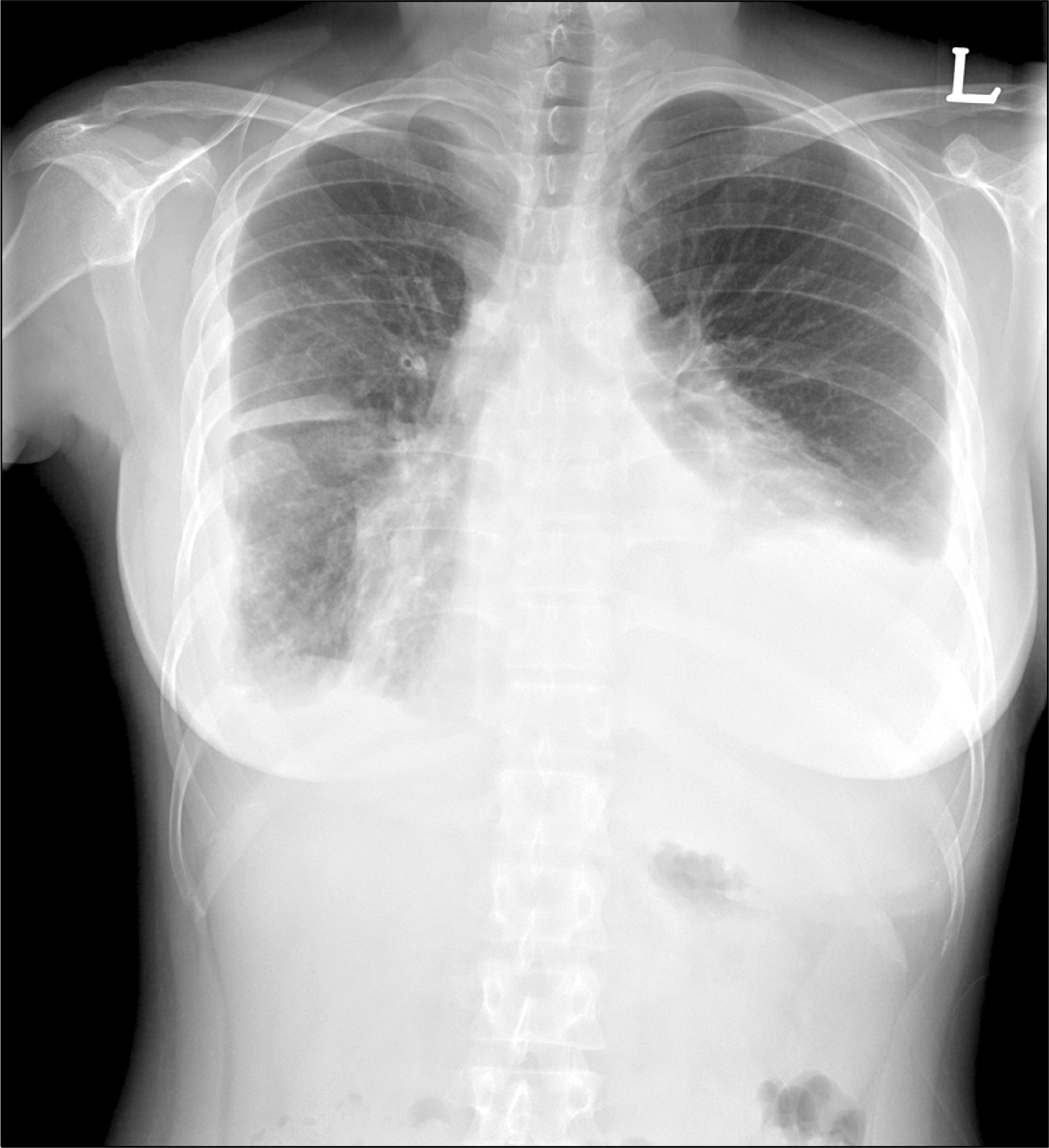
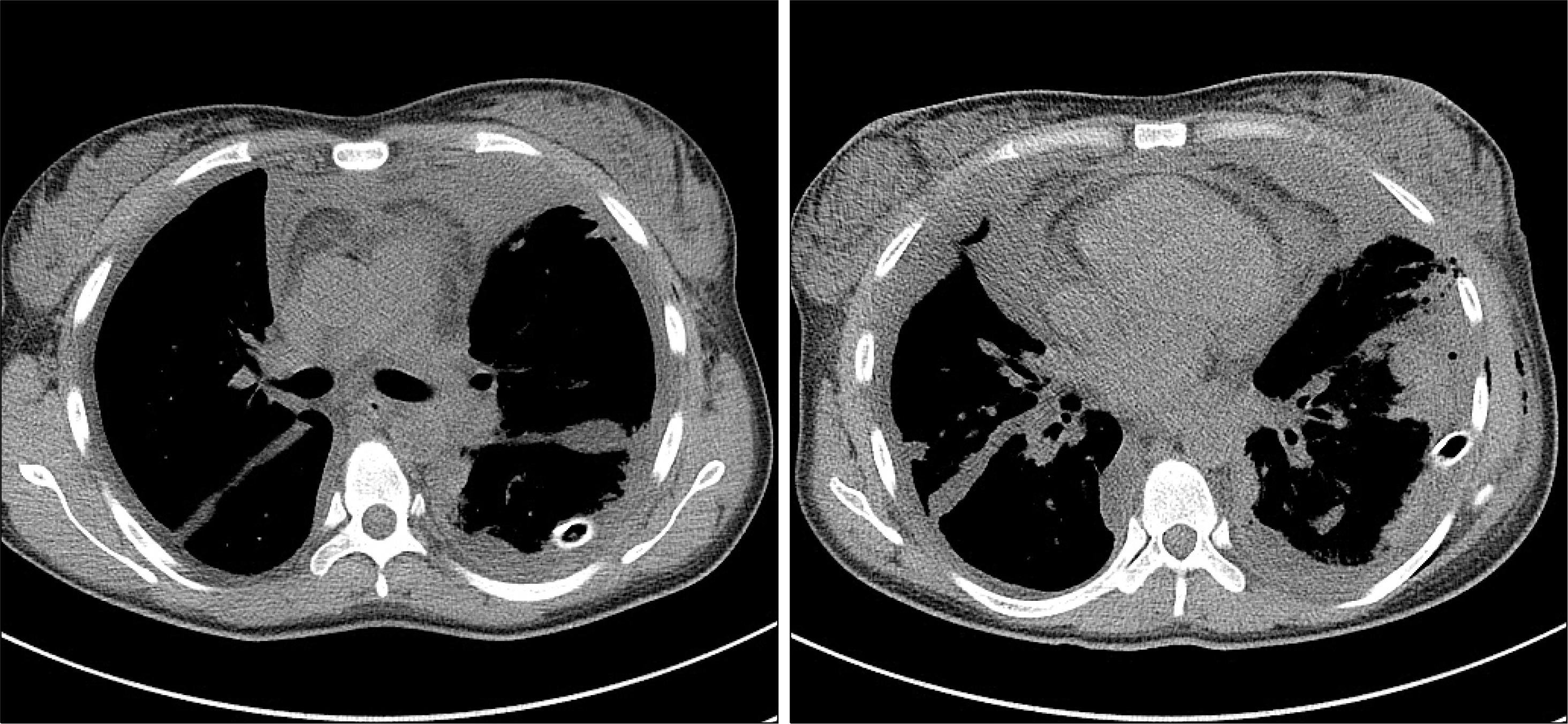
Figure 3.
Chest computed tomography showing bilateral pleural effusion with multilo-culated effusion in both hemi-thoraces.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download