Abstract
Objective
Assessing the disease activity is a key part of clinical decision-making in rheumatology. In particular, a high disease activity, which is represented by a disease activity score-28 (DAS28) score >5.1, is used as a cutoff value for the use of biologics in many countries, including Korea. This study compared the DAS28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and DAS28-C-re-active protein (CRP) to determine if these indices can be used interchangeably in patients with high disease activity.
Methods
This cross-sectional study enrolled 1,117 patients with rheumatoid arthritis and examined the initial registration data from the Korean Biologics Registry.
Results
In general, DAS28-CRP showed an excellent correlation with DAS28-ESR (r2=0.889, p <0.001). On the other hand, DAS28-CRP tended to underestimate the disease activity in those with moderate-to-high disease activity. The best agreement between DAS28-ESR and DAS28-CRP for defining a high disease activity was achieved using a cutoff value of 4.5 for the latter (kappa, 0.68; sensitivity, 85.9%; specificity, 88.1%).
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr, Akl EA, Bannuru RR, Sullivan MC, et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68:1–26.

2. Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC, Buch M, Burmester G, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 73:492–509.
3. Smolen JS, Breedveld FC, Burmester GR, Bykerk V, Dougados M, Emery P, et al. Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: 2014 update of the recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis. 2016; 75:3–15.

4. Felson DT, Smolen JS, Wells G, Zhang B, van Tuyl LH, Funovits J, et al. American College of Rheumatology/ European League Against Rheumatism provisional definition of remission in rheumatoid arthritis for clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63:573–86.
5. Emery P, Breedveld FC, Hall S, Durez P, Chang DJ, Robertson D, et al. Comparison of methotrexate monotherapy with a combination of methotrexate and etanercept in active, early, moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (COMET): a randomised, double-blind, parallel treatment trial. Lancet. 2008; 372:375–82.

6. Kim HY, Hsu PN, Barba M, Sulaiman W, Robertson D, Vlahos B, et al. Randomized comparison of etanercept with usual therapy in an Asian population with active rheumatoid arthritis: the APPEAL trial. Int J Rheum Dis. 2012; 15:188–96.

7. Prevoo ML, van't Hof MA, Kuper HH, van Leeuwen MA, van de Putte LB, van Riel PL. Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995; 38:44–8.

9. Inoue E, Yamanaka H, Hara M, Tomatsu T, Kamatani N. Comparison of disease activity score (DAS)28-erythrocyte sedimentation rate and DAS28-C-reactive protein threshold values. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; 66:407–9.
10. Castrejón I, Ortiz AM, García-Vicuña R, Lopez-Bote JP, Humbría A, Carmona L, et al. Are the C-reactive protein values and erythrocyte sedimentation rate equivalent when estimating the 28-joint disease activity score in rheumatoid arthritis? Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008; 26:769–75.
11. Crowson CS, Rahman MU, Matteson EL. Which measure of inflammation to use? A comparison of erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein measurements from randomized clinical trials of golimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2009; 36:1606–10.

12. Nielung L, Christensen R, Danneskiold-Samsøe B, Bliddal H, Holm CC, Ellegaard K, et al. Validity and agreement between the 28-joint disease activity score based on C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis. 2015; 2015; 401690.
13. Stucki G, Liang MH, Stucki S, Brühlmann P, Michel BA. A self-administered rheumatoid arthritis disease activity index (RADAI) for epidemiologic research. Psychometric properties and correlation with parameters of disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 1995; 38:795–8.
14. Anderson J, Caplan L, Yazdany J, Robbins ML, Neogi T, Michaud K, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis disease activity measures: American College of Rheumatology recommendations for use in clinical practice. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:640–7.

15. Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977; 33:159–74.

16. Won S, Sung YK, Cho SK, Choi CB, Koh EM, Kim SK, et al. Prediction for TNF inhibitor users in RA patients according to reimbursement criteria based on DAS28. J Rheum Dis. 2014; 21:64–73.

17. Son KM, Kim SY, Lee SH, Yang CM, Seo YI, Kim HA. Comparison of the disease activity score using the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein levels in Koreans with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016; 19:1278–83.

18. Song GG, Lee YH. Comparison of disease activity score 28 using C-reactive protein and disease activity score 28 using erythrocyte sedimentation rate in assessing activity and treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. J Rheum Dis. 2016; 23:241–9.

Go to : 
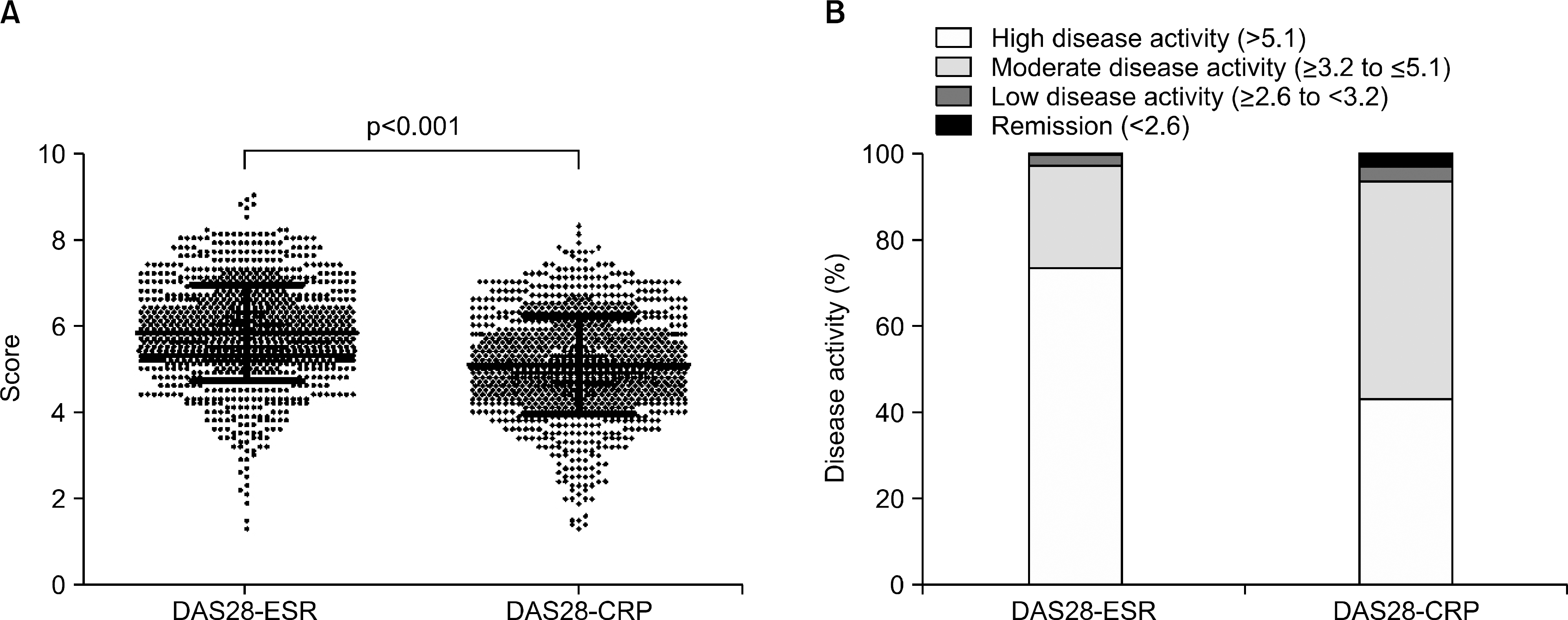 | Figure 1.(A) Scatter plot showing the DAS28-ESR and DAS28-CRP scores in this population. Each dot represents the score for a single patient. Bars represent the mean±standard deviation, which is 5.7±1.1 for DAS28-ESR and 5.0±1.1 for DAS28-CRP. (B) Distribution of disease activity as defined by the DAS28-ESR and DAS28-CRP. DAS28-ESR: 73.8% of patients had high disease activity, 24.4% had moderate disease activity, 1.5% had low disease activity, and 0.8% were in remission. DAS28-CRP: 43.0% of patients had high disease activity, 51.1% had moderate disease activity, 2.9% had low disease activity, and 3.0% were in remission. DAS: disease activity score, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, CRP: C-reactive protein. |
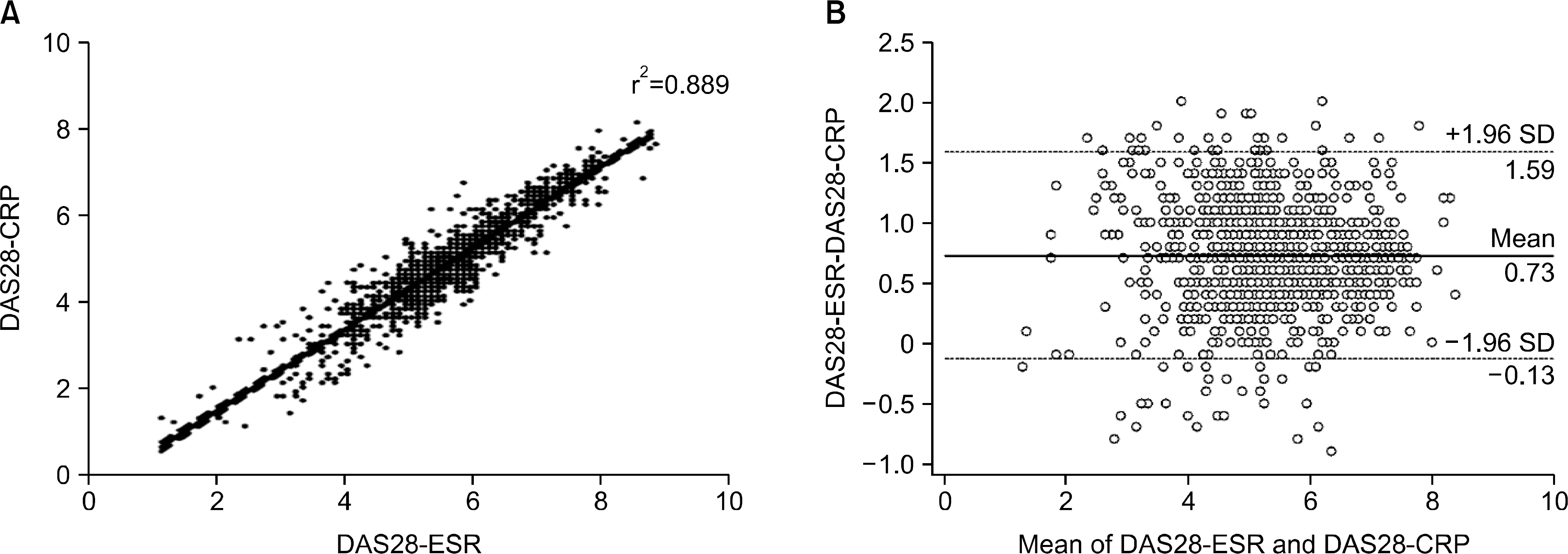 | Figure 2.(A) Scatter plot showing DAS28-ESR (x axis) versus DAS28-CRP (y axis) values along with a regression line. The slope and inter-cept of the regression line were 0.9427 and −0.4004, respectively. Each point represents a single patient, and the scatter lines indicate the 95% confidence interval. (B) Bland-Altman plot of DAS28-ESR and DAS28-CRP. The difference between DAS28-CRP and DAS28-ESR scores (y axis) versus the mean value for DAS28-CRP and DAS28-ESR (x axis) is shown. The mean difference is represented by the central line, and the upper and lower dashed lines represent ±1.96 standard deviation (SD) from the mean. The mean DAS28-ESR minus DAS28-CRP was 0.73, suggesting that the DAS28-CRP underestimates the overall disease activity in those with moderate-to-high disease activity. DAS: disease activity score, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, CRP: C‐reactive protein. |
Table 1.
Demographics and disease characteristics of the 1,117 patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Table 2.
Comparison of DAS28-ESR and DAS28-CRP: sensitivity, specificity, and kappa coefficient values according to the cutoffs used to define high disease activity




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download