REFERENCES
1. Baer AN, Dessypris EN, Goldwasser E, Krantz SB. Blunted erythropoietin response to anaemia in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Haematol. 1987; 66:559–64.

2. Hochberg MC, Arnold CM, Hogans BB, Spivak JL. Serum immunoreactive erythropoietin in rheumatoid arthritis: impaired response to anemia. Arthritis Rheum. 1988; 31:1318–21.

3. Vreugdenhil G, Wognum AW, van Eijk HG, Swaak AJ. Anaemia in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid deficiency, and erythropoietin responsiveness. Ann Rheum Dis. 1990; 49:93–8.

4. Baer AN, Dessypris EN, Krantz SB. The pathogenesis of anemia in rheumatoid arthritis: a clinical and laboratory analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 19:209–23.

5. Means RT Jr, Krantz SB. Progress in understanding the pathogenesis of the anemia of chronic disease. Blood. 1992; 80:1639–47.
6. Park KJ, Jin HM, Cho YN, Kang JH, Jung HJ, Kang JH, et al. Clinical and hematological effects of tocilizumab on serum hepcidin, anemia response and disease activity in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheum Dis. 2016; 23:37–46.

7. Ganz T. Hepcidin, a key regulator of iron metabolism and mediator of anemia of inflammation. Blood. 2003; 102:783–8.

8. Rivera S, Nemeth E, Gabayan V, Lopez MA, Farshidi D, Ganz T. Synthetic hepcidin causes rapid dose-dependent hypoferremia and is concentrated in ferroportin-containing organs. Blood. 2005; 106:2196–9.

9. D'Angelo G. Role of hepcidin in the pathophysiology and diagnosis of anemia. Blood Res. 2013; 48:10–5.
10. Song SN, Tomosugi N, Kawabata H, Ishikawa T, Nishikawa T, Yoshizaki K. Down-regulation of hepcidin resulting from long-term treatment with an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody (tocilizumab) improves anemia of inflammation in multicentric Castleman disease. Blood. 2010; 116:3627–34.

11. Hashizume M, Uchiyama Y, Horai N, Tomosugi N, Mihara M. Tocilizumab, a humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody, improved anemia in monkey arthritis by suppressing IL-6-induced hepcidin production. Rheumatol Int. 2010; 30:917–23.

12. Song SN, Iwahashi M, Tomosugi N, Uno K, Yamana J, Yamana S, et al. Comparative evaluation of the effects of treatment with tocilizumab and TNF-α inhibitors on serum hepcidin, anemia response and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013; 15:R141.

13. Kim HR, Kim KW, Yoon SY, Kim SH, Lee SH. Serum pro-hepcidin could reflect disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:348–52.

14. Demirag MD, Haznedaroglu S, Sancak B, Konca C, Gulbahar O, Ozturk MA, et al. Circulating hepcidin in the crossroads of anemia and inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Intern Med. 2009; 48:421–6.

15. Davis D, Charles PJ, Potter A, Feldmann M, Maini RN, Elliott MJ. Anaemia of chronic disease in rheumatoid arthritis: in vivo effects of tumour necrosis factor alpha blockade. Br J Rheumatol. 1997; 36:950–6.

16. Charles P, Elliott MJ, Davis D, Potter A, Kalden JR, Antoni C, et al. Regulation of cytokines, cytokine inhibitors, and acute-phase proteins following anti-TNF-alpha therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1999; 163:1521–8.
17. Constante M, Wang D, Raymond VA, Bilodeau M, Santos MM. Repression of repulsive guidance molecule C during inflammation is independent of Hfe and involves tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Am J Pathol. 2007; 170:497–504.
Go to : 
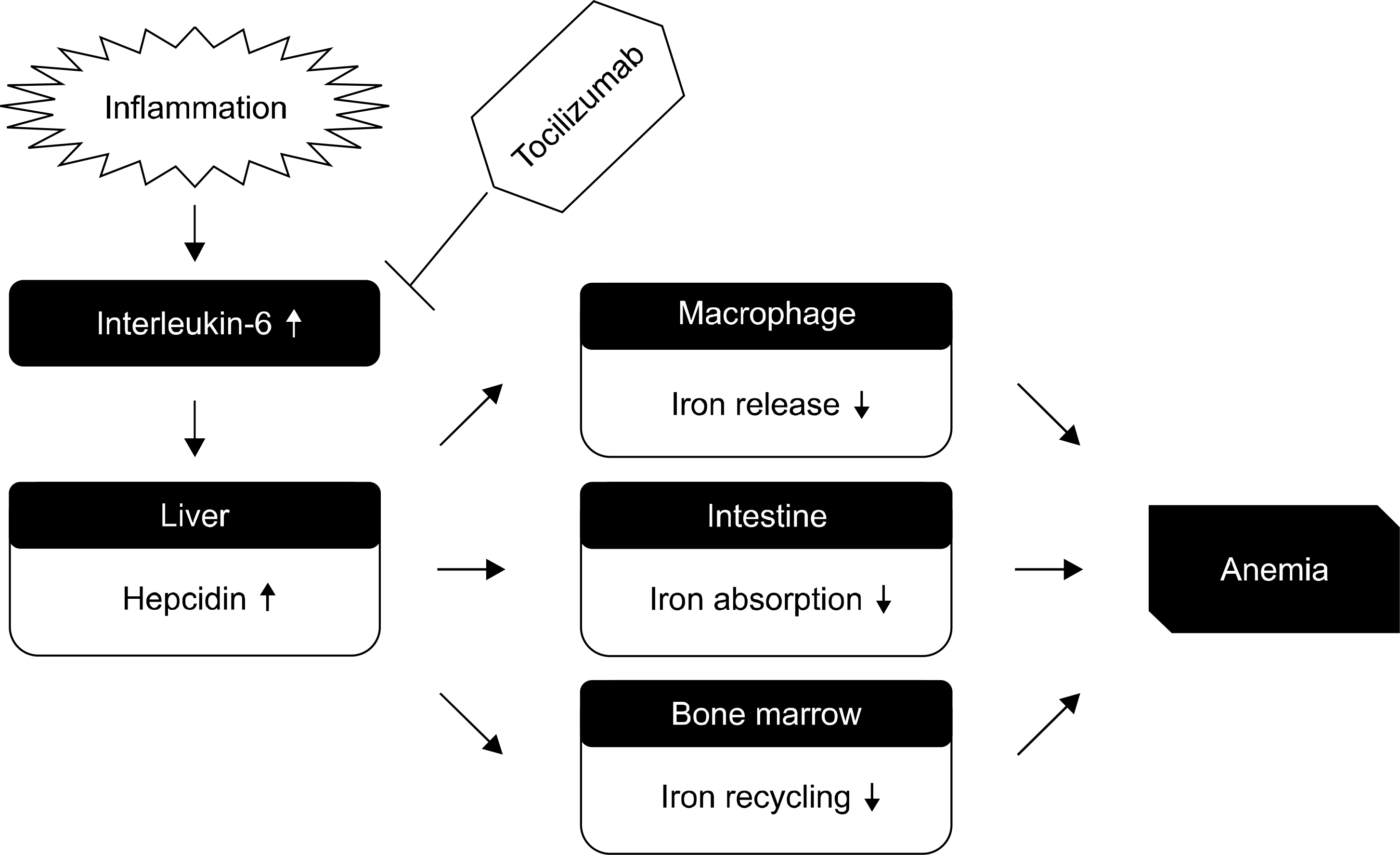 | Figure 1.Hepcidin and anemia of chronic disease. Inflammation increases interleukin-6 production. The increase in hepcidin decreases macrophage iron release, intestinal iron absorption, and iron recycling in the bone marrow. Administering tocilizumab in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis has significant therapeutic implications regarding ameliorating anemia, inflammation, and abnormal iron metabolism. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download