Abstract
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is categorized as vasculitis of the large and medium-sized vessels. Visual loss is one potential consequence of cranial arteritis. Temporal artery biopsies are performed frequently to demonstrate the involvement of arteritis. On the other hand, cerebral artery involvement with pathological findings is not well documented in patients with GCA. We report a rare case of GCA with cerebral vessel involvement in a 76-year-old woman.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Huston KA, Hunder GG. Giant cell (cranial) arteritis: a clinical review. Am Heart J. 1980; 100:99–105.

2. Lie JT. Illustrated histopathologic classification criteria for selected vasculitis syndromes. American College of Rheumatology Subcommittee on Classification of Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33:1074–87.
3. Guida A, Tufano A, Perna P, Moscato P, De Donato MT, Finelli R, et al. The thromboembolic risk in giant cell arteritis: a critical review of the literature. Int J Rheumatol. 2014; 2014; 806402.

4. Mahr AD, Jover JA, Spiera RF, Hernández-García C, Fernández-Gutiérrez B, Lavalley MP, et al. Adjunctive methotrexate for treatment of giant cell arteritis: an individual patient data metaanalysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 56:2789–97.

5. Salvarani C, Cantini F, Hunder GG. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant-cell arteritis. Lancet. 2008; 372:234–45.

6. Kobayashi S, Yano T, Matsumoto Y, Numano F, Nakajima N, Yasuda K, et al. Clinical and epidemiologic analysis of giant cell (temporal) arteritis from a nationwide survey in 1998 in Japan: the first government-supported nationwide survey. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 49:594–8.

7. Cha DM, Lee T, Choe G, Yang HK, Hwang JM. Silent giant cell arteritis in an elderly Korean woman. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2013; 27:224–7.

8. Kwon H, Han Y, Son DH, Cho YP, Kwon TW. Abdominal aortic aneurysm in giant cell arteritis. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2015; 89:224–7.

9. Salvarani C, Cantini F, Boiardi L, Hunder GG. Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant-cell arteritis. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:261–71.

10. ter Borg EJ, Haanen HC, Seldenrijk CA. Relationship between histological subtypes and clinical characteristics at presentation and outcome in biopsy-proven temporal arteritis. Identification of a relatively benign subgroup. Clin Rheumatol. 2007; 26:529–32.
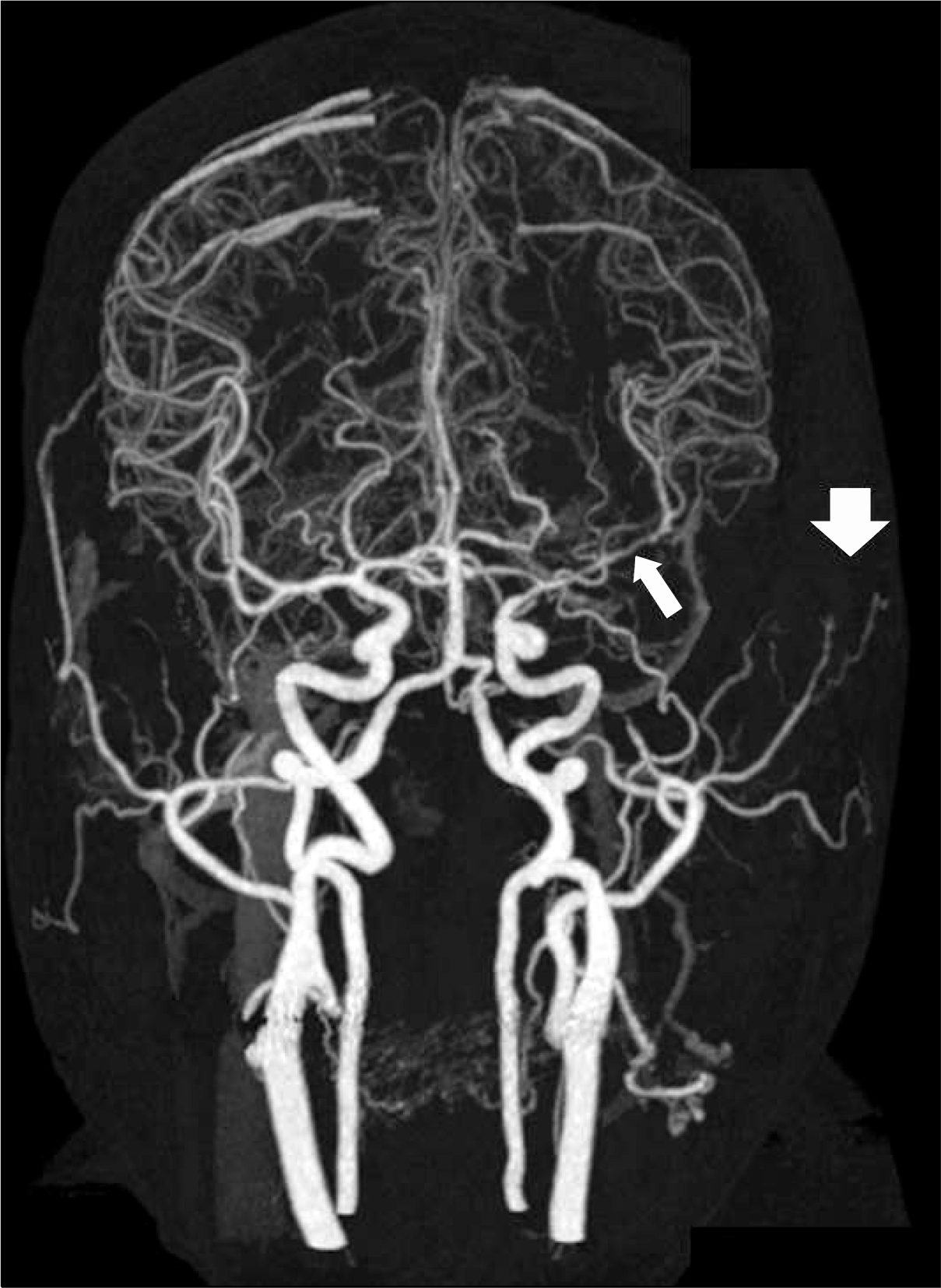
11. Morinobu A, Tsuji G, Kasagi S, Saegusa J, Hayashi H, Nakazawa T, et al. Role of imaging studies in the diagnosis and evaluation of giant cell arteritis in Japanese: report of eight cases. Mod Rheumatol. 2011; 21:391–6.

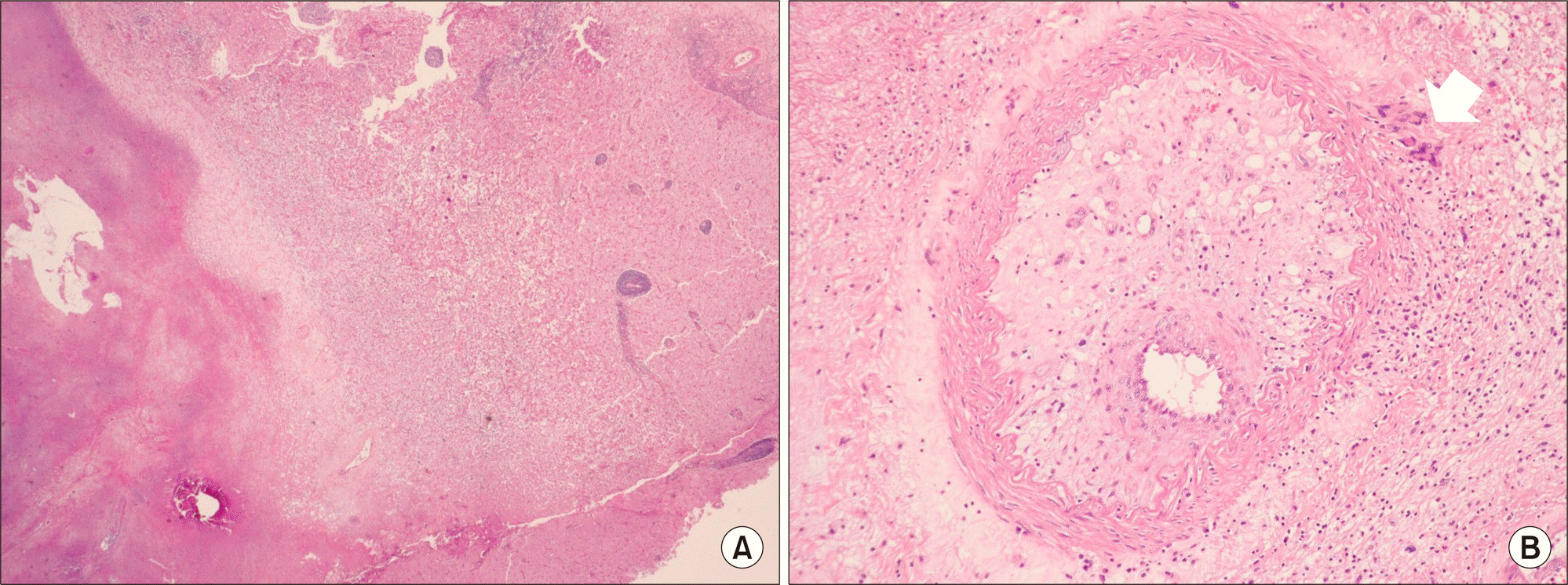
12. Salvarani C, Giannini C, Miller DV, Hunder G. Giant cell arteritis: Involvement of intracranial arteries. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 55:985–9.

13. Larivière D, Sacre K, Klein I, Hyafil F, Choudat L, Chauveheid MP, et al. Extra- and intracranial cerebral vasculitis in giant cell arteritis: an observational study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2014; 93:e265.
14. Salvarani C, Brown RD Jr, Calamia KT, Christianson TJ, Weigand SD, Miller DV, et al. Primary central nervous system vasculitis: analysis of 101 patients. Ann Neurol. 2007; 62:442–51.

15. García-Cabo C, Benavente L, Calleja S. Infrequent presentation of giant cell arteritis. BMJ Case Rep. 2016; DOI: DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2015-213973.

Go to : 
 | Figure 1.Brain magnetic resonance T1-weighted contrastenhanced and T2-weighted images demonstrate a mass with vasogenic edema in the left frontal and temporal lobes. (A∼D) T2-weighted sequence images; (E∼H) T1-weighted contrastenhanced sequence images. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download