Abstract
Objective
A substantial portion of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) patients present with localized disease limited to the upper respiratory tract, however; disease spectrum and prognosis of these patients are unclear. The aim of this study is to describe the clinical characteristics and outcome of patients with localized GPA.
Methods
This was a retrospective descriptive case series of patients with a biopsy proven localized GPA presenting to a single tertiary rheumatology service between January 1995 and September 2015.
Results
A total of 5 patients, median age 56 years (range 48 to 59 years) at diagnosis and 80% female, were identified. The median follow-up period was 42 months (range 15 to 62 months). Diagnosis was delayed with median time to diagnosis of 12 months (range 3 to 36 months), and patients underwent 1-3 ear, nose, and throat surgeries during the period of diagnostic delay. Sinusitis was the most frequent symptom in all patients, followed by otomastoiditis with cranial nerve palsies (n=2) and orbital mass (n=1). Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) was positive initially in 2/5 patients (40%). Two patients with otomastoiditis and cranial nerve palsies progressed to systemic disease with ANCA positive conversion. These two cases along with a case with orbital mass were refractory to standard treatment of cyclophosphamide with glucocorticoids requiring rituximab treatment.
REFERENCES
1. Reinhold-Keller E, Beuge N, Latza U, de Groot K, Rudert H, Nölle B, et al. An interdisciplinary approach to the care of patients with Wegener's granulomatosis: long-term outcome in 155 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43:1021–32.

2. Reinhold-Keller E, De Groot K, Rudert H, Nölle B, Heller M, Gross WL. Response to trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole in Wegener's granulomatosis depends on the phase of disease. QJM. 1996; 89:15–23.

3. Holle JU, Gross WL, Holl-Ulrich K, Ambrosch P, Noelle B, Both M, et al. Prospective long-term follow-up of patients with localised Wegener's granulomatosis: does it occur as persistent disease stage? Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69:1934–9.

4. Hellmich B, Flossmann O, Gross WL, Bacon P, Cohen-Tervaert JW, Guillevin L, et al. EULAR recommendations for conducting clinical studies and/or clinical trials in systemic vasculitis: focus on anti-neutrophil cytoplasm anti-body-associated vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; 66:605–17.

5. Carrington CB, Liebow A. Limited forms of angiitis and granulomatosis of Wegener's type. Am J Med. 1966; 41:497–527.

6. Fienberg R. The protracted superficial phenomenon in pa-thergic (Wegener's) granulomatosis. Hum Pathol. 1981; 12:458–67.

7. Knoch DW, Lucarelli MJ, Dortzbach RK, Smith ME. Limited Wegener granulomatosis with 40 years of follow-up. Arch Ophthalmol. 2003; 121:1640–2.

8. Ahmad I, Lee WC, Nagendran V, Wilson F, Shortridge RT. Localised Wegener's granulomatosis in otolaryngology: a review of six cases. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2000; 62:149–55.

9. Langford CA, Sneller MC, Hallahan CW, Hoffman GS, Kammerer WA, Talar-Williams C, et al. Clinical features and therapeutic management of subglottic stenosis in patients with Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996; 39:1754–60.

10. Boudes P. Purely granulomatous Wegener's granulomatosis: a new concept for an old disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 19:365–70.

11. Borner U, Landis BN, Banz Y, Villiger P, Ballinari P, Caversaccio M, et al. Diagnostic value of biopsies in identifying cytoplasmic antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-negative localized Wegener's granulomatosis presenting primarily with sinonasal disease. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2012; 26:475–80.

12. Rao JK, Weinberger M, Oddone EZ, Allen NB, Landsman P, Feussner JR. The role of antineutrophil cytoplasmic anti-body (c-ANCA) testing in the diagnosis of Wegener granulomatosis. A literature review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1995; 123:925–32.

13. Tsuzuki K, Fukazawa K, Takebayashi H, Hashimoto K, Sakagami M. Difficulty of diagnosing Wegener's granulomatosis in the head and neck region. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2009; 36:64–70.

14. Devaney KO, Travis WD, Hoffman G, Leavitt R, Lebovics R, Fauci AS. Interpretation of head and neck biopsies in Wegener's granulomatosis. A pathologic study of 126 biopsies in 70 patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990; 14:555–64.
Figure 1.
Case 1 in 2012. Computed tomography of paranasal sinus image showed mass extends to the intraorbital portin of the left oribt (arrow). Soft tiss densities along the both maxillary and frontoethmoidal sinuses.
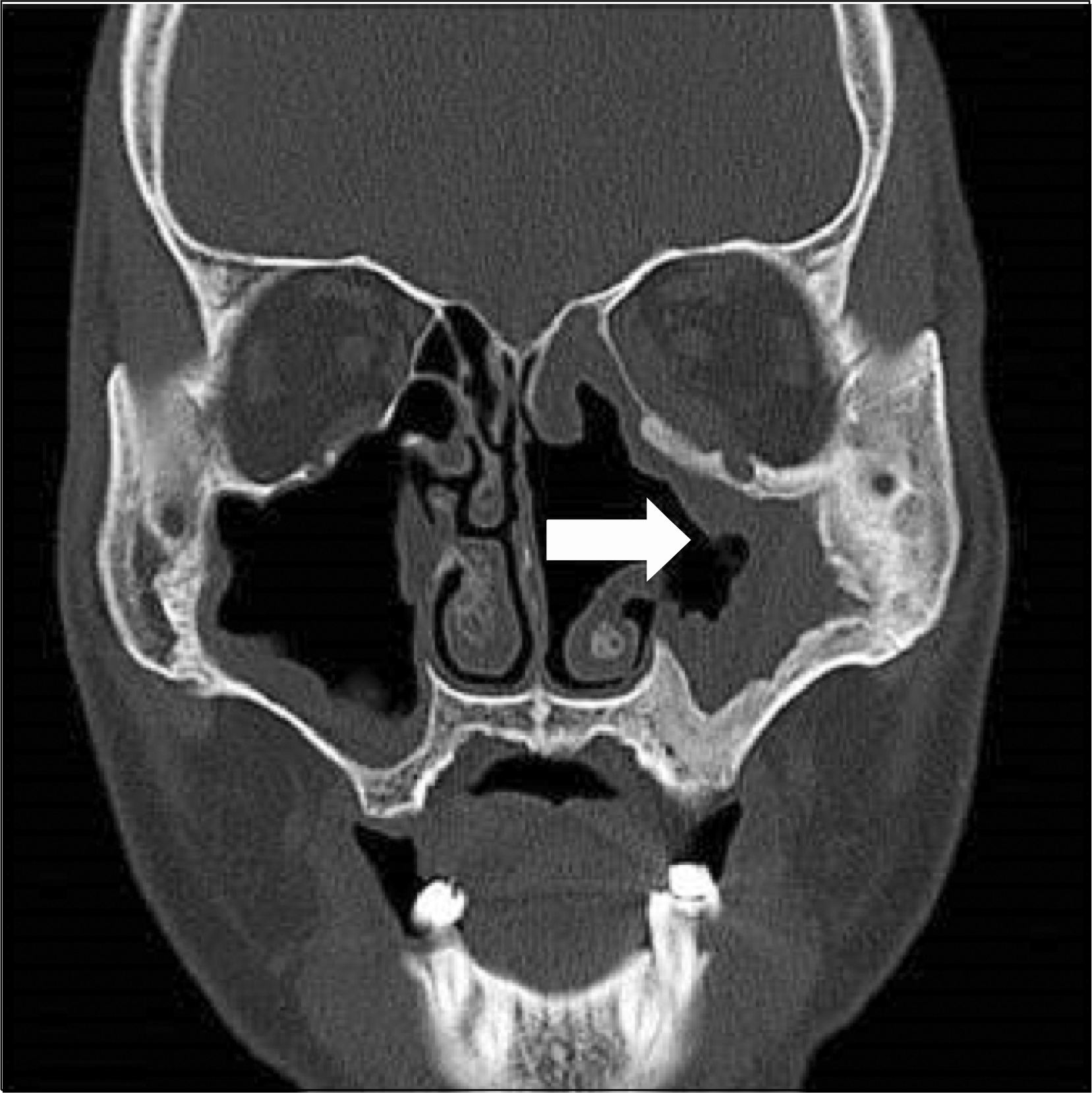
Figure 2.
Case 1 in 2013. Naso-pharyngeal biopsy revealing granulomatous inflammation with palisading necrosis (A), and vasculitis (B) (H&E, ×200).
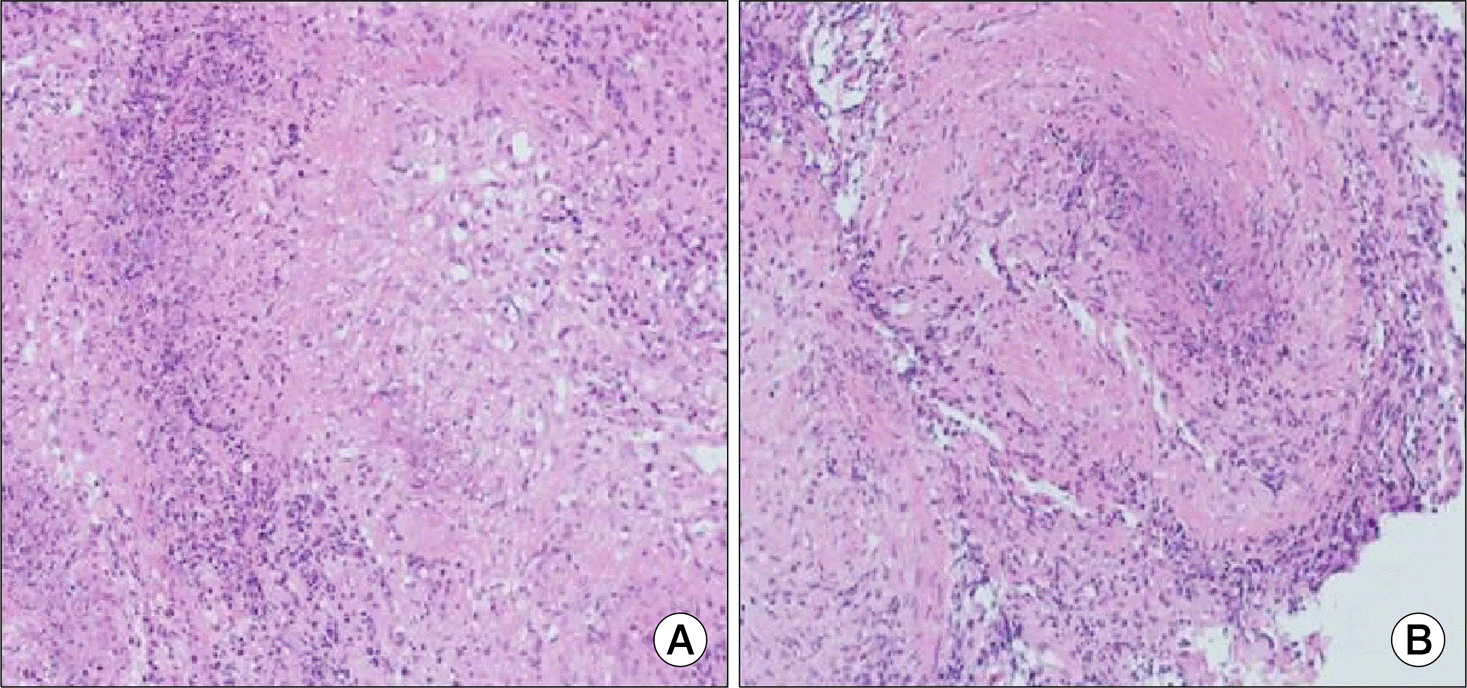
Figure 3.
Case 3 in 2014. Gadolinium enhanced T1-weighted sagittal magnetic resonance image showed diffuse enlargement of pituitary gland (11.5 mm in height) with thickened enhanced pituitary stalk (arrow).
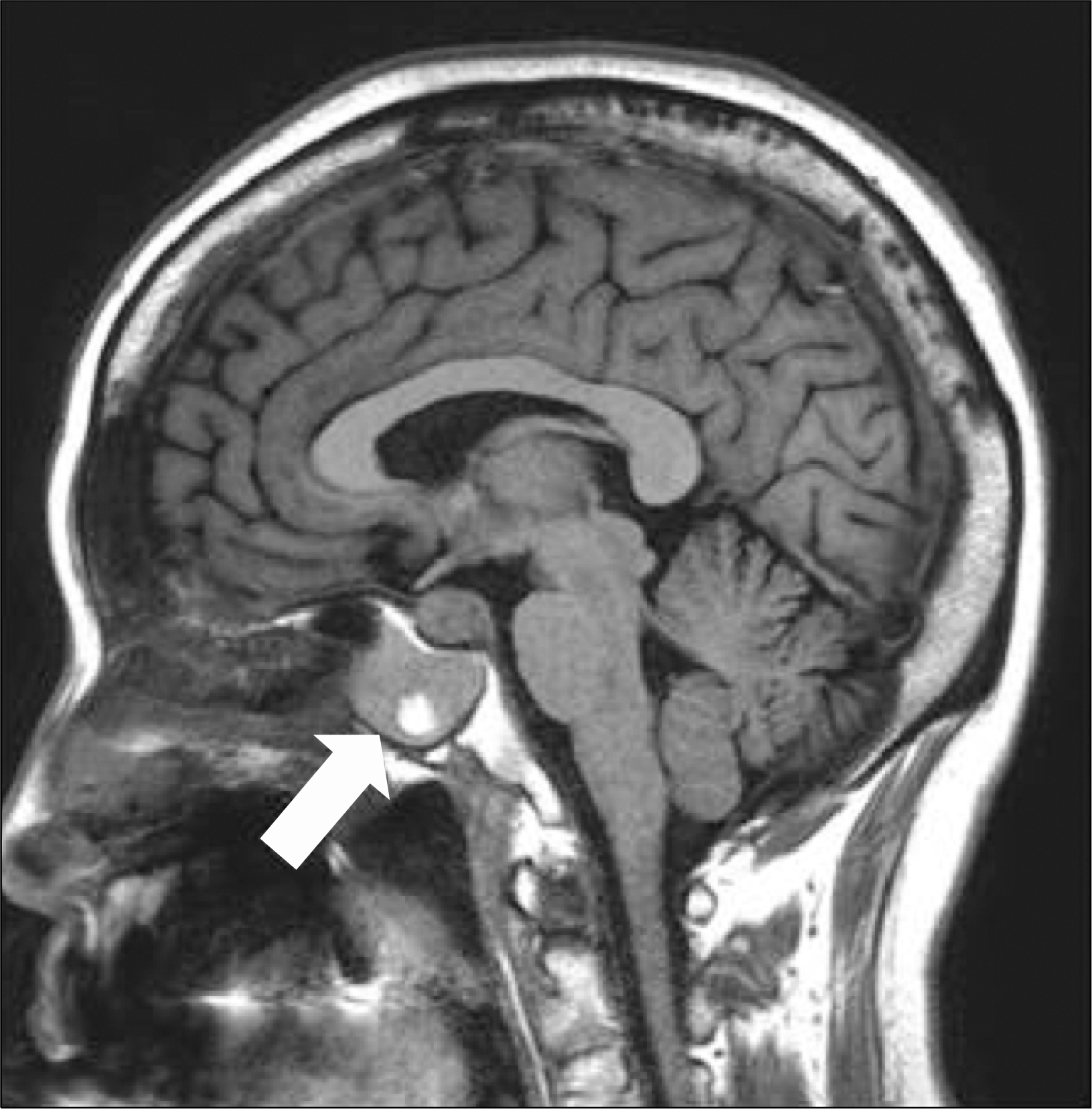
Table 1.
Initial clinical and histologic characteristics of patients with localized GPA
| Variable | Case | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Sex | Female | Male | Female | Female | Female |
| Age at diagnosis (yr) | 48 | 56 | 58 | 59 | 56 |
| Time to diagnosis (mo) | 9 | 36 | 15 | 3 | 12 |
| Initial symptoms | Sinusitis, otitis, mastoiditis, and bilateral facial nerve palsy | Sinusitis, and orbital mass | Sinusitis, otitis, mastoiditis, and multiple lower cranial nerve palsies | Sinusitis | Sinusitis |
| Number (type) of surgery performed | 1 (Bilateral mastoidectomy) | 3 (FESS, uncinectomy, ethmoidectomy) | 1 (FESS) | 0 | 1 (Infundibulectomy) |
| Histologic features | Granuloma, necrosis, vasculitis* | Granuloma, necrosis, vasculitis | Granuloma, necrosis, vasculitis | Granuloma | Granuloma, microabscess |
| Local bone destruction | Nasal bone, septum, and sphenoid bone | Intraorbital portion of the left orbit wall | Bilateral orbit | No | No |
| ANCA positivity | Negative | PR-3 | Negative | MPO | Negative |
Table 2.
Outcome and treatment of patients with localized granulomatosis with polyangiitis
| Variable | Case | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Median follow up duration (mo) | 32 | 42 | 48 | 62 | 15 |
| Development of systemic disease | Yes | No | Yes | No | No |
| Time to diagnosis* (mo) | Diagnosis made at onset of systemic disease | NA | 36 | NA | NA |
| Symptoms† | Fever, weight loss, lymphadenopathy, and acute nasal swelling | NA | involvement (diabetes insipidus) Pituitary gland | NA | NA |
| ANCA positivity‡ | Yes (MPO) | NA | Yes (PR-3) | NA | NA |
| Refractory disease | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Treatment | CS, CY, MTX, RTX | CS, CY, RTX | CS, CY, RTX | CS, CY, MTX | CS, MTX |
| Current status of follow up | Out-patient | Out-patient | Out-patient | Out-patient | Out-patient |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download