Abstract
Objective
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease, mainly involving joints and bones. Sauchinone is an anti-inflammatory agent isolated from Saururus chinensis, which was used in oriental medicine. The aim of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic effect of sauchinone on inflammatory arthritis and underlying mechanism of anti-arthritic effect.
Methods
Mice with collagen induced arthritis (CIA) was intraperitoneally injected with sauchinone (20 mg/kg) or vehicle. The clinical and histological evaluations were performed with arthritis scoring and hematoxylin-eosin staining, respectively. CD4+ interleukin (IL) 17+ T cells were determined under Th17 skewing condition treated with sauchinone. To evaluate the effect of sauchinone on osteoclastogenesis, mice bone marrow macrophages (BMMs) and human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were cultured with macrophage-colony stimulating factor and receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand in the absence or presence of sauchinone.
Results
Sauchinone significantly attenuated the inflammatory arthritis in CIA mice both clinically and histologically. The proportion of Th17 cells were decreased with treatment with sauchinone in vivo and in vitro. The expressions of Th17 cell markers (IL-17 and retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor gamma t) and B cell markers (activation-induced cytidine deaminase) were downregulated in the presence of sauchinone. Sauchinone also suppressed the formation of tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase positive cells from mice BMMs and human PBMCs, and the expression of osteoclastogenic markers.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2. Miossec P, Korn T, Kuchroo VK. Interleukin-17 and type 17 helper T cells. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:888–98.

3. Smolen JS, Landewé R, Breedveld FC, Buch M, Burmester G, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 73:492–509.
4. Singh JA, Furst DE, Bharat A, Curtis JR, Kavanaugh AF, Kremer JM, et al. 2012 update of the 2008 American College of Rheumatology recommendations for the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologic agents in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2012; 64:625–39.

5. Kim YW, Kim YM, Yang YM, Kim TH, Hwang SJ, Lee JR, et al. Inhibition of SREBP-1c-mediated hepatic steatosis and oxidative stress by sauchinone, an AMPK-activating lignan in Saururus chinensis. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010; 48:567–78.

6. Kim YW, Lee SM, Shin SM, Hwang SJ, Brooks JS, Kang HE, et al. Efficacy of sauchinone as a novel AMPK-activating lignan for preventing iron-induced oxidative stress and liver injury. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009; 47:1082–92.

7. Han HJ, Li M, Son JK, Seo CS, Song SW, Kwak SH, et al. Sauchinone, a lignan from Saururus chinensis, attenuates neutrophil proinflammatory activity and acute lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013; 17:471–7.

8. Song SY, Jung YY, Hwang CJ, Lee HP, Sok CH, Kim JH, et al. Inhibitory effect of ent-Sauchinone on amyloidogenesis via inhibition of STAT3-mediated NF-κ B activation in cultured astrocytes and microglial BV-2 cells. J Neuroinflammation. 2014; 11:118.
9. Camps M, Rückle T, Ji H, Ardissone V, Rintelen F, Shaw J, et al. Blockade of PI3Kgamma suppresses joint inflammation and damage in mouse models of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 2005; 11:936–43.
10. Kay HY, Kim YW, Ryu da H, Sung SH, Hwang SJ, Kim SG. Nrf2-mediated liver protection by sauchinone, an anti-oxidant lignan, from acetaminophen toxicity through the PKCδ-GSK3β pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 2011; 163:1653–65.

11. Seo CS, Lee YK, Kim YJ, Jung JS, Jahng Y, Chang HW, et al. Protective effect of lignans against sepsis from the roots of Saururus chinensis. Biol Pharm Bull. 2008; 31:523–6.
12. Scott DL, Kingsley GH. Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:704–12.

13. Bae HB, Li M, Son JK, Seo CS, Chung SH, Kim SJ, et al. Sauchinone, a lignan from Saururus chinensis, reduces tumor necrosis factor-alpha production through the inhibition of c-raf/MEK1/2/ERK 1/2 pathway activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2010; 10:1022–8.
14. Jang EY, Yang CH, Han MH, Choi YH, Hwang M. Sauchinone suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through Akt signaling in BV2 cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2012; 14:188–94.

15. Lee AK, Sung SH, Kim YC, Kim SG. Inhibition of lip-opolysaccharide-inducible nitric oxide synthase, TNF-alpha and COX-2 expression by sauchinone effects on I-kappaBalpha phosphorylation, C/EBP and AP-1 activation. Br J Pharmacol. 2003; 139:11–20.
16. Yang XO, Panopoulos AD, Nurieva R, Chang SH, Wang D, Watowich SS, et al. STAT3 regulates cytokinemediated generation of inflammatory helper T cells. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:9358–63.

17. Yang XO, Pappu BP, Nurieva R, Akimzhanov A, Kang HS, Chung Y, et al. T helper 17 lineage differentiation is programmed by orphan nuclear receptors ROR alpha and ROR gamma. Immunity. 2008; 28:29–39.
18. Zhang F, Meng G, Strober W. Interactions among the transcription factors Runx1, RORgammat and Foxp3 regulate the differentiation of interleukin 17-producing T cells. Nat Immunol. 2008; 9:1297–306.
19. Lee CS, Won C, Yoo H, Yi EH, Cho Y, Maeng JW, et al. Inhibition of double-stranded RNA-induced inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by fraxinellone and sauchinone in murine microglia. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009; 32:1870–4.

20. Jeong GS, Lee DS, Park BH, Kwon KB, Kim YC. Sauchinone protects pancreatic β cells against cytokinemediated toxicity. Toxicol In Vitro. 2011; 25:505–12.

21. Bax M, Huizinga TW, Toes RE. The pathogenic potential of autoreactive antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 2014; 36:313–25.

22. Nakken B, Munthe LA, Konttinen YT, Sandberg AK, Szekanecz Z, Alex P, et al. B-cells and their targeting in rheumatoid arthritis–current concepts and future perspectives. Autoimmun Rev. 2011; 11:28–34.
Go to : 
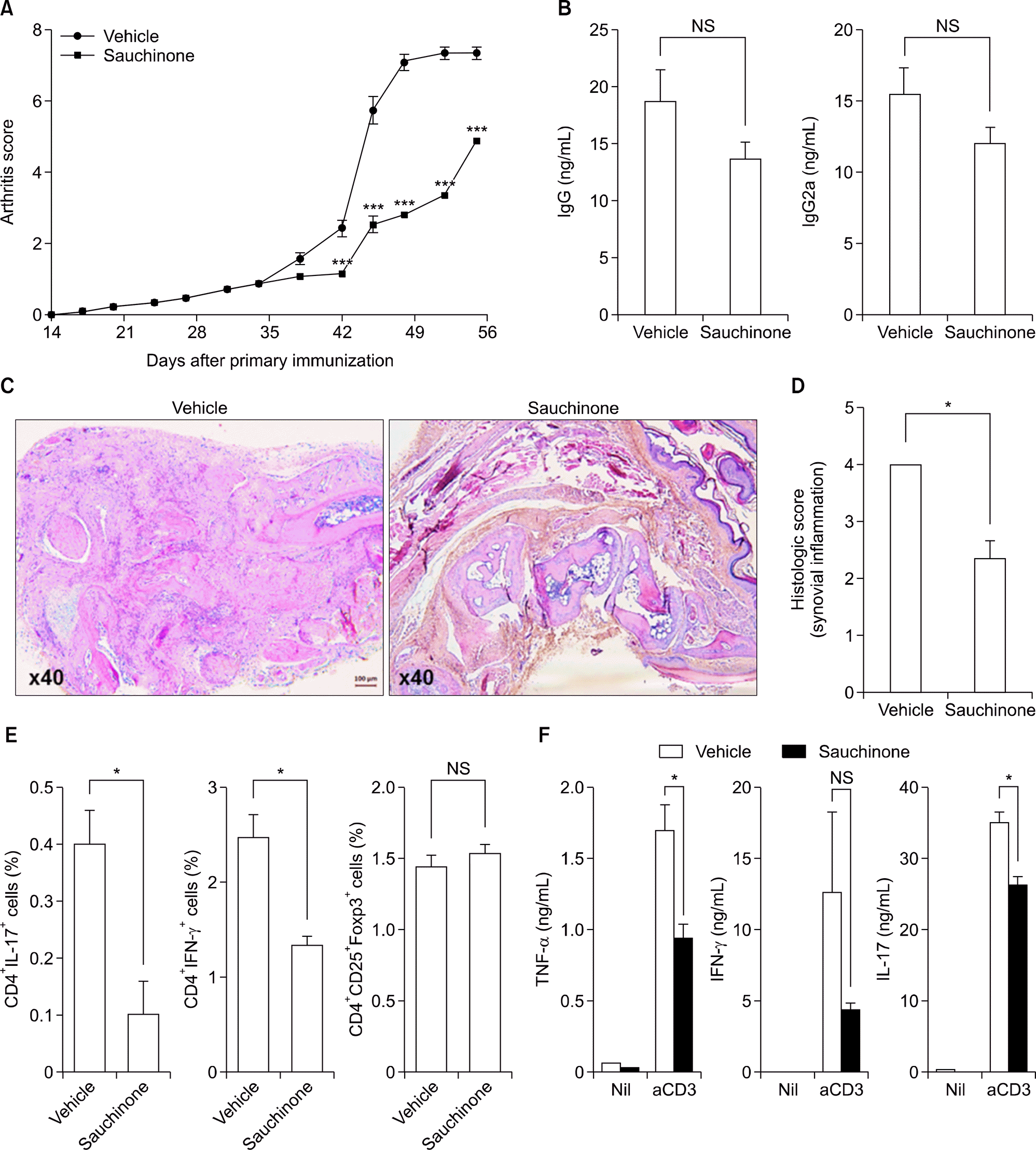 | Figure 1.Sauchinone alleviates the inflammatory arthritis in mice. Mice with collagen induced arthritis were intraperitoneally injected with sauchinone (20 mg/kg) or vehicle for six weeks immediately after second immunization. (A) Inflammatory arthritis was assessed with clinical scoring by three independent examiners. (B) The serum level of IgG and IgG2a was measured with ELISA. (C) Histological analysis was performed with hematoxylin-eosin staining of mice paws. Bar in the left corner of figure indicates 100 μ m. (D) Histologic score for synovial inflammation of mice paws was determined by three independent examiners. (E) The composition of mice splenocytes were determined by flowcytometry. The percentages of CD4+ IL-17+ T cells, CD4+ IFN-γ+ T cells, and CD4+ CD25+ FOXP3+ T cells were compared between two groups. (F) The production of TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-17 from mice splenocytes was evaluated with ELISA of culture supernatant after stimulation with anti-CD3 antibodies. Values are presented as three independent experiments±standard error of mean. aCD3: stimulation with anti-CD3 antibodies, ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, IFN: interferon, Ig: immunoglobulin, IL: interleukin, Nil: no stimulation, NS: not significant, TNF: tumor necrosis factor. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001. |
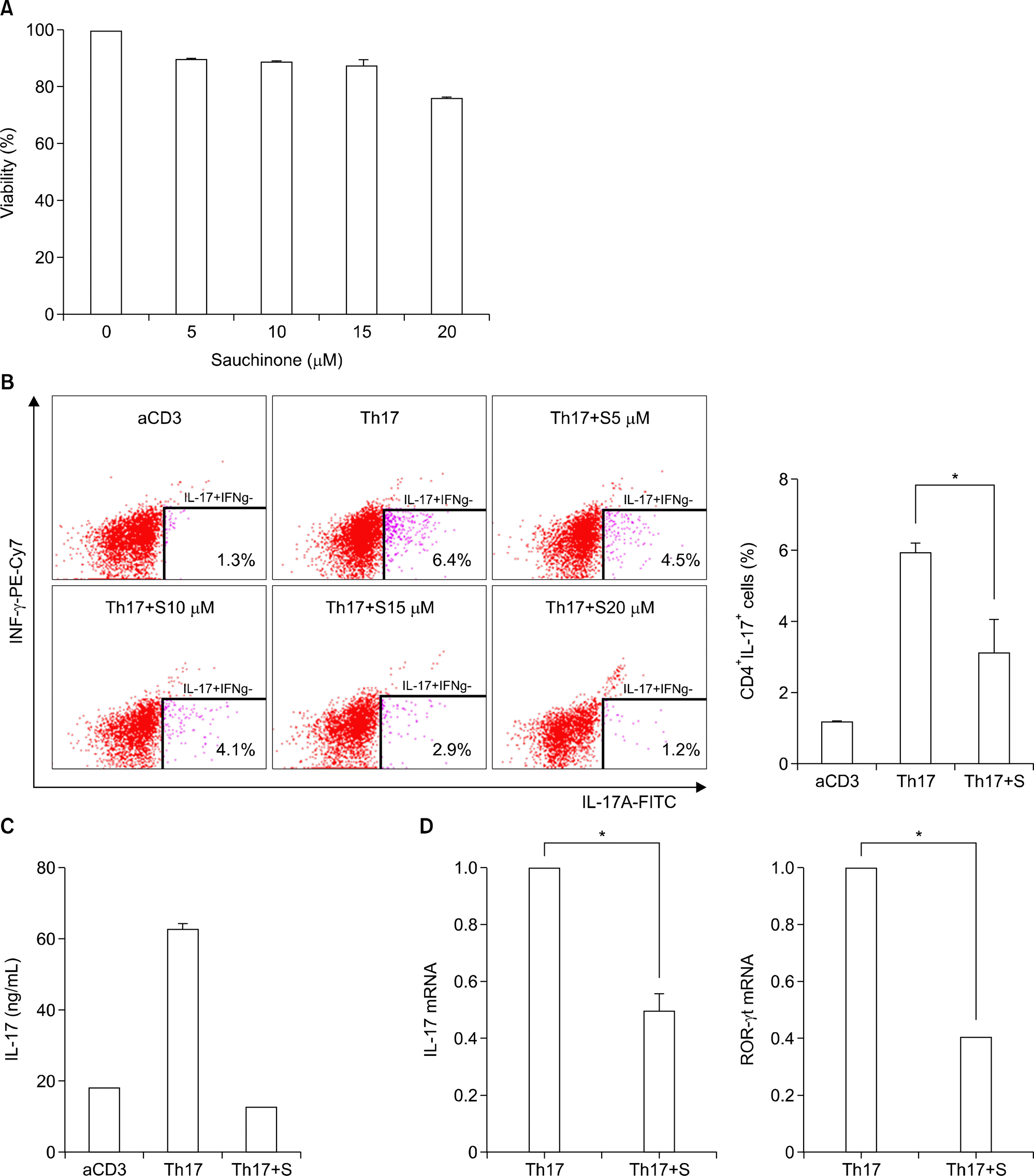 | Figure 2.Sauchinone inhibits Th17 differentiation. (A) Cytotoxicity of sauchinone was evaluated with cell viability assay using cell counting kit-8 after treatment with 0 to 20 μ M of sauchinone. The dose of sauchinone with more than 80% of cell viability was considered as a tolerable dose. (B) CD4+ T cells were differentiated into Th17 cells in the presence of sauchinone. The proportions of CD4+IL-17+ cells were determined with flowcytometry. The number of right bottom indicates the proportion of CD4+ IL-17+ cells. (C) The production of IL-17 from CD4+ T cells under Th17 skewing condition was measured with ELISA of culture supernatant after pretreatment of sauchinone. (D) The expression of IL-17 and ROR-γ t was determined with qRT-PCR of CD4+ T cells under Th17 differentiation condition after pretreatment with sauchinone. Values are presented as three independent experiments±standard error of mean. aCD3: stimulation with anti-CD3 antibodies, FITC: fluorescein isothiocyanate, IFN: interferon, IL: interleukin, ROR-γt: retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor gamma t, PE: phycoerythrin, Th17: Th17 skewing condition, Th17+ S: Th17 skewing condition in the presence of sauchinone. *p<0.05. |
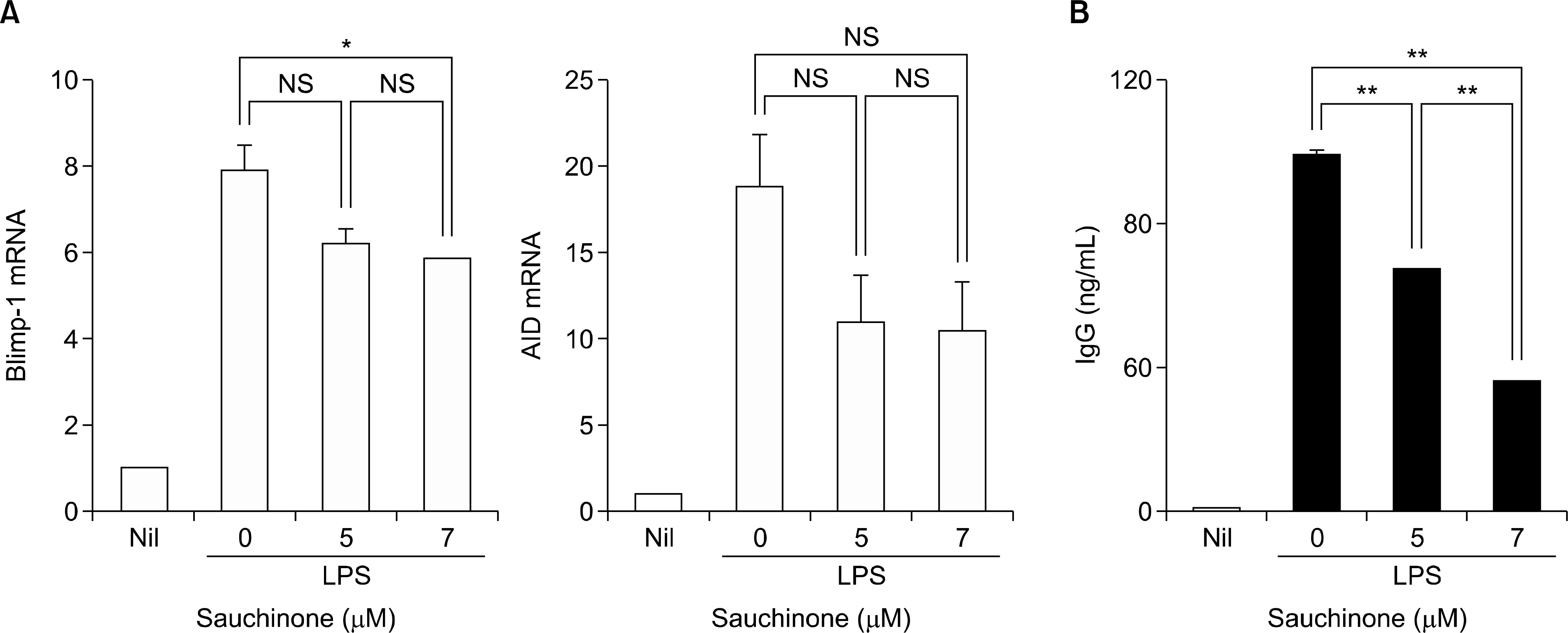 | Figure 3.Sauchinone affects B cell maturation. (A) The expression of Blimp-1 and AID was evaluated with qRT-PCR of CD19+ B cells stimulated with LPS in the presence of sauchinone. (B) The production of IgG from CD19+ B cells stimulated with LPS was measured with ELISA of culture supernatant after pretreatment with sauchinone. Values are presented as three independent experiments±standard error of mean. AID: activation-induced cytidine deaminase, Blimp-1: B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1, Ig: immunoglobulin, LPS: lipopolysaccharide, Nil: no stimulation, NS: not significant. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. |
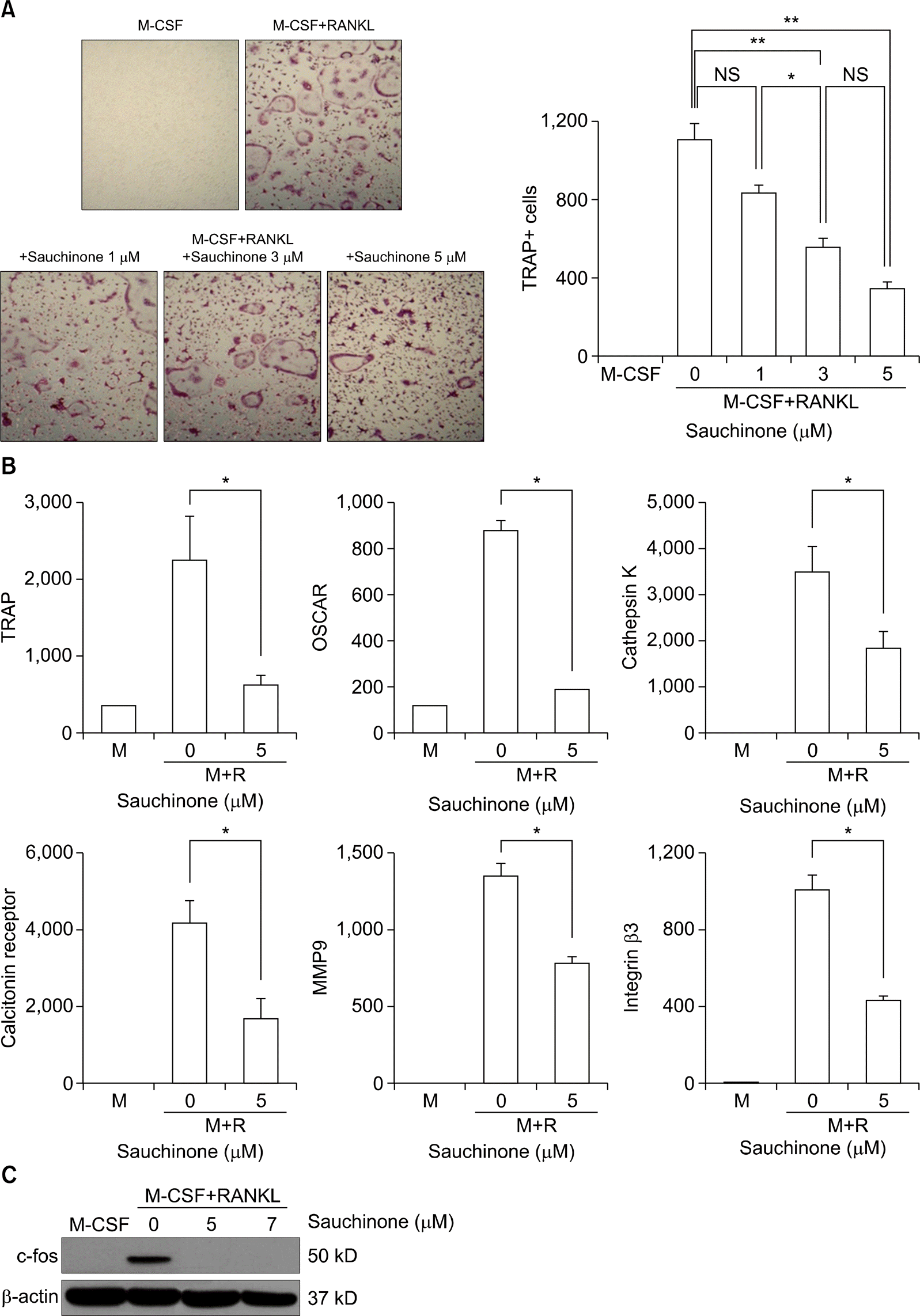 | Figure 4.Sauchinone suppresses osteoclastogenesis in a dose-dependent manner. Mice bone marrow macrophages were cultured with M-CSF and RANKL to induced osteoclastogenesis. Sauchinone was added to the culture dishes to evaluate the effect of sauchinone on osteoclastogenesis. (A) The numbers of TRAP positive cells were counted in culture dishes at various doses of sauchinone.(B) The expression of osteoclastogenic markers were determined by qRT-PCR in the absence or presence of sauchinone. (C) The expression of c-fos, a transcription factor associated with osteoclastogenesis, was evaluated with Western blot of cells cultured with or without sauchinone. Values are presented as three independent experiments±standard error of mean. M: culture with M-CSF, M+ R: culture with M-CSF and RANKL, M-CSF: macrophage-colony stimulating factor, MMP: matrix metalloproteinase, NS: not significant, OSCAR: osteoclast-associated receptor, qRT-PCR: quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, RANKL: receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand, TRAP: tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. |
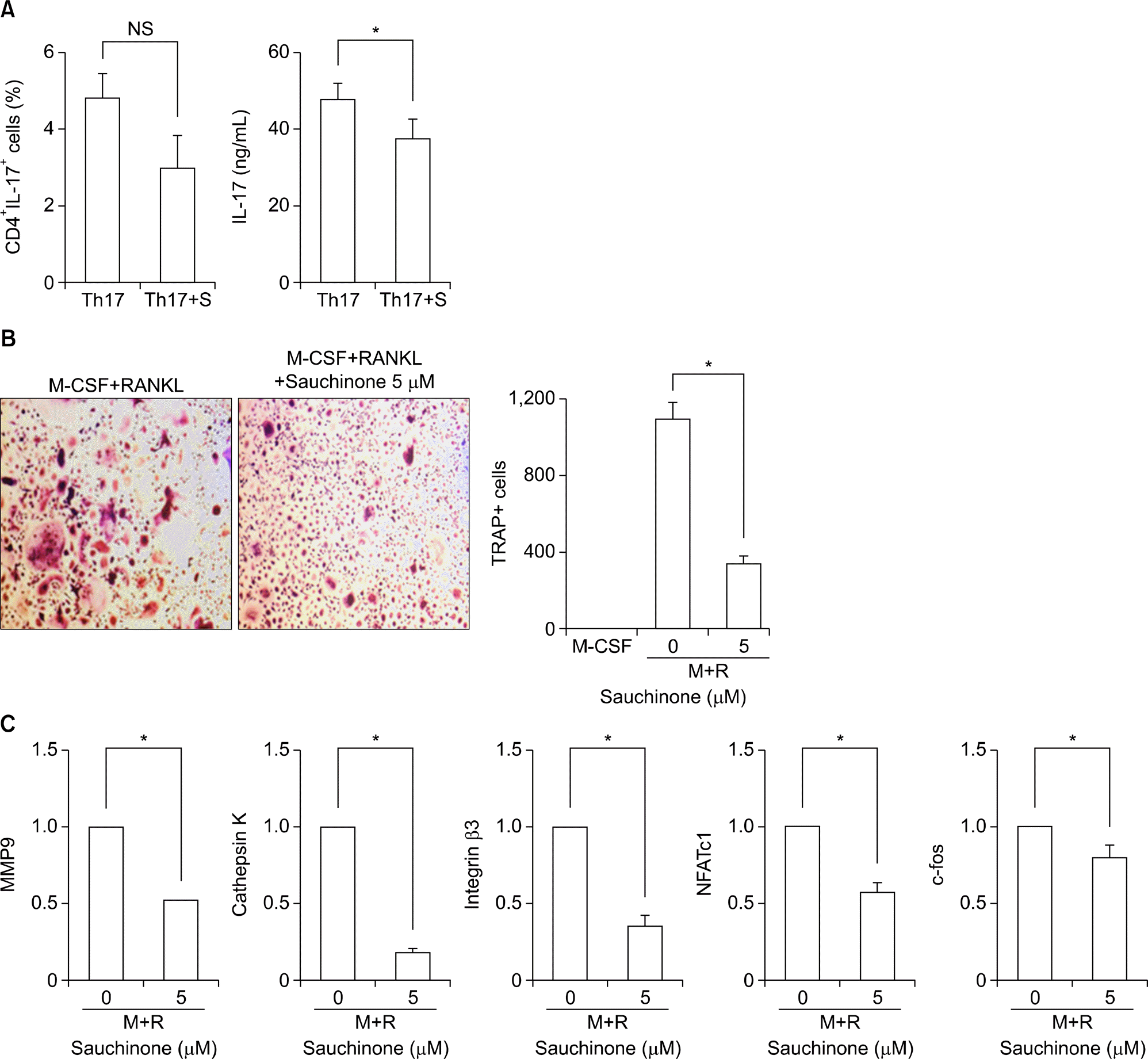 | Figure 5.Saucinone regulates Th17 differentiation and osteoclastogenesis in human mononuclear cells. To confirm the inhibitory effect of sauchinone on human cells, pripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from healthy controls were cultured in the absence or presence of sauchinone. (A) The proportion of CD4+ IL17+ T cells and the production of IL-17 under Th17 skewing condition with or without sauchinone was evaluated by flowcytometry and ELISA, respectively. (B) The number of TRAP positive cells was measured after culture with M-CSF and RANKL in the absence or presence of sauchinone. (C) The expression of osteoclastogenic markers was compared between cells differentiated to osteoclast with or without sauchinone. Values are presented as three independent experiments±standard error of mean. M: culture with M-CSF, M+ R: culture with M-CSF and RANKL, M-CSF: macro-phage-colony stimulating factor, MMP: matrix metalloproteinase, NFATc1: nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1, NS: not significant, RANKL: receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand, Th17: Th17 skewing condition, Th17+ S: Th17 skewing condition in the presence of sauchinone, TRAP: tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase. *p<0.05. |
Table 1.
Primer sequence lists for real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
AID: activation-induced cytidine deaminase, Blimp-1: B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein-1, CTR: calcitonin receptor, IL-17: interleukin-17, MMP: matrix metalloproteinase, NFATc1: nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1, OSCAR: osteoclast-associated receptor, ROR-γ t: retinoic acid receptor-related orphan receptor gamma t, TRAP: tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download