Abstract
Objective
Rheumatoid arthritis, the most common form of arthritis, is typically characterized by induced inflammatory pain in joints. Recent studies have reported on the expression of pain receptors such as transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) and acid sensing ion channel 3 (ASIC3), which are related to pain induction and regulation. This study was conducted to investigate the expression of TRPV1 and ASIC3 in response to the analgesic effect of an arthritis treatment in a collagen-induced arthritis (CIA).
Methods
Mice were divided into 3 groups: Control, CIA, and CIA with arthritis treatment. Mice received intraperitoneal injection with 10 mg/kg infliximab and 10 mg/kg meloxicam five times per week for 3 weeks. Mechanical hyperalgesia, histologic examination of the feet, serum levels of inflammatory cytokine such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-17 (IL-17), TRPV1 and ASIC3 expression were investigated.
Results
The serum levels of IL-6 and IL-17 were lower in the treatment group (73.77±10.11 pg/mL and 26.75±7.17 pg/mL, respectively) compared to the CIA group (p<0.001). Histological analysis showed decreased synovial cell proliferation, leukocyte infiltration, and cartilage destruction in the treatment group compared with the CIA group. The CIA group that underwent arthritis treatment showed a significantly increased withdrawal threshold of mechanical nociception on the hind paw and increased expression of TRPV1 and ASIC3 compared to the CIA group.
REFERENCES
1. Choy EH, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:907–16.

2. Watkins LR, Maier SF, Goehler LE. Immune activation: the role of proinflammatory cytokines in inflammation, illness responses and pathological pain states. Pain. 1995; 63:289–302.

3. Kojima M, Kojima T, Ishiguro N, Oguchi T, Oba M, Tsuchiya H, et al. Psychosocial factors, disease status, and quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Psychosom Res. 2009; 67:425–31.

4. Billeter AT, Hellmann JL, Bhatnagar A, Polk HC Jr. Transient receptor potential ion channels: powerful regulators of cell function. Ann Surg. 2014; 259:229–35.
5. Mamet J, Baron A, Lazdunski M, Voilley N. Proinflammatory mediators, stimulators of sensory neuron excitability via the expression of acid-sensing ion channels. J Neurosci. 2002; 22:10662–70.

6. Steen KH, Reeh PW. Sustained graded pain and hyperalgesia from harmless experimental tissue acidosis in human skin. Neurosci Lett. 1993; 154:113–6.

7. Waldmann R, Lazdunski M. H(+)-gated cation channels: neuronal acid sensors in the NaC/DEG family of ion channels. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1998; 8:418–24.

8. Han Z, Boyle DL, Manning AM, Firestein GS. AP-1 and NF-kappaB regulation in rheumatoid arthritis and murine collagen-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity. 1998; 28:197–208.
9. Chaplan SR, Pogrel JW, Yaksh TL. Role of voltage-depend-ent calcium channel subtypes in experimental tactile allodynia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994; 269:1117–23.
10. Stuart JM, Townes AS, Kang AH. Collagen autoimmune arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984; 2:199–218.

11. Kim HO, Lee SI. Experimental animal models for rheumatoid arthritis: methods and applications. J Rheum Dis. 2012; 19:189–95.

12. Sokka T. Assessment of pain in patients with rheumatic diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2003; 17:427–49.

13. Melzack R. The McGill Pain Questionnaire: major properties and scoring methods. Pain. 1975; 1:277–99.

14. Deval E, Noël J, Lay N, Alloui A, Diochot S, Friend V, et al. ASIC3, a sensor of acidic and primary inflammatory pain. EMBO J. 2008; 27:3047–55.

15. Chung MK, Jung SJ, Oh SB. Role of TRP channels in pain sensation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011; 704:615–36.

16. Zhang X, Huang J, McNaughton PA. NGF rapidly increases membrane expression of TRPV1 heat-gated ion channels. EMBO J. 2005; 24:4211–23.

17. Ikeuchi M, Kolker SJ, Burnes LA, Walder RY, Sluka KA. Role of ASIC3 in the primary and secondary hyperalgesia produced by joint inflammation in mice. Pain. 2008; 137:662–9.

18. Suzuki M, Mizuno A, Kodaira K, Imai M. Impaired pressure sensation in mice lacking TRPV4. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278:22664–8.

19. Staikopoulos V, Sessle BJ, Furness JB, Jennings EA. Localization of P2X2 and P2X3 receptors in rat trigeminal ganglion neurons. Neuroscience. 2007; 144:208–16.

20. Plant TD, Zöllner C, Kepura F, Mousa SS, Eichhorst J, Schaefer M, et al. Endothelin potentiates TRPV1 via ETA receptor-mediated activation of protein kinase C. Mol Pain. 2007; 3:35.

21. Sluka KA, Rasmussen LA, Edgar MM, O'Donnell JM, Walder RY, Kolker SJ, et al. Acid-sensing ion channel 3 deficiency increases inflammation but decreases pain behavior in murine arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013; 65:1194–202.

22. Anand P, Bley K. Topical capsaicin for pain management: therapeutic potential and mechanisms of action of the new high-concentration capsaicin 8% patch. Br J Anaesth. 2011; 107:490–502.

Figure 1.
Suppression of arthritis progression in CIA with treatment group. Arthritis was induced by immunization with type II collagen in complete Freund's adjuvant on day 0. On day 41, mice also received normal saline or treatment (infliximab and meloxicam) five times per week for three weeks. (A, B) Severity of arthritis was determined as described in Materials and Methods. Data are expressed as the mean±standard deviation. CIA: type II collagen induced arthritis. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 vs. control group; † p <0.05, ††p<0.01, †††p<0.001 vs. CIA group.
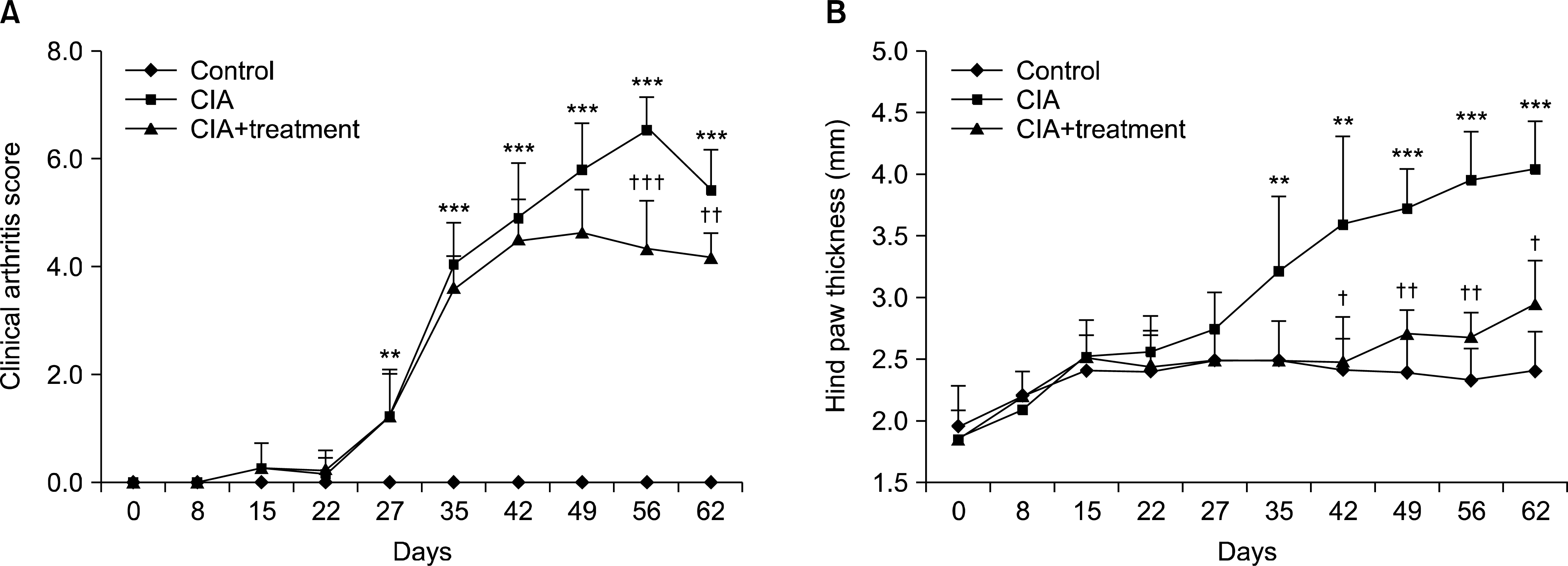
Figure 2.
Suppressive effect of arthritis treatment on levels of inflammatory cytokines. (A) The levels of immunoglobulin G an-ti-type II collagen antibody, (B) interleukin (IL)-6 and (C) IL-17 were determined in CIA mice by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. (D) Protein levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and IL-1β were measured in CIA hind paw tissue by western blot. Data are expressed as the mean±standard deviation. Values are expressed as the optical density. AU: arbitary unit, CIA: type II collagen induced arthritis, GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 vs. control group; †† p<0.01, ††† p<0.001 vs. CIA group.
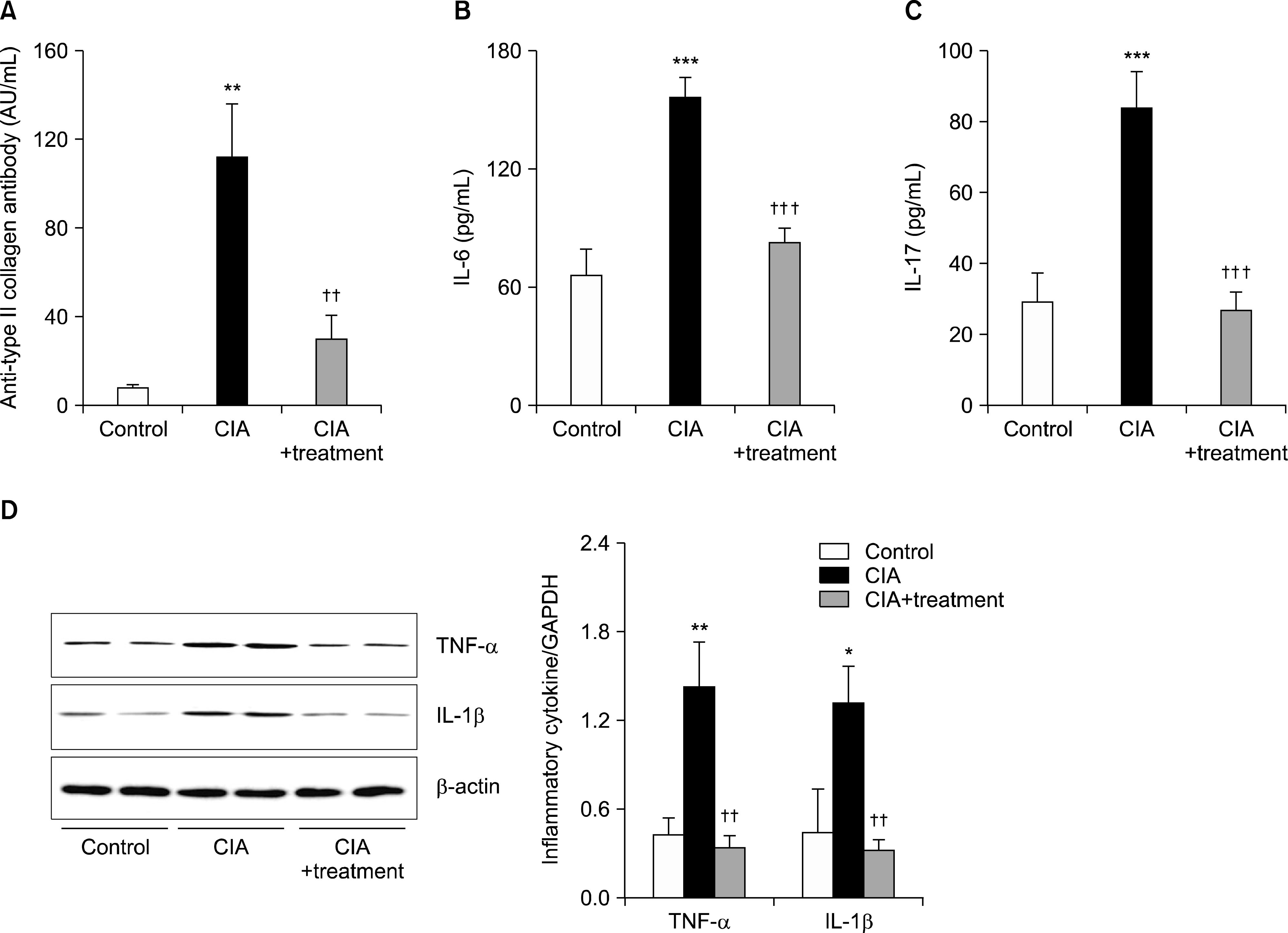
Figure 3.
Representative histological analysis of knee joints and paws was assessed by H&E (×200) and Safranin O staining (×200). CIA: type II collagen induced arthritis.
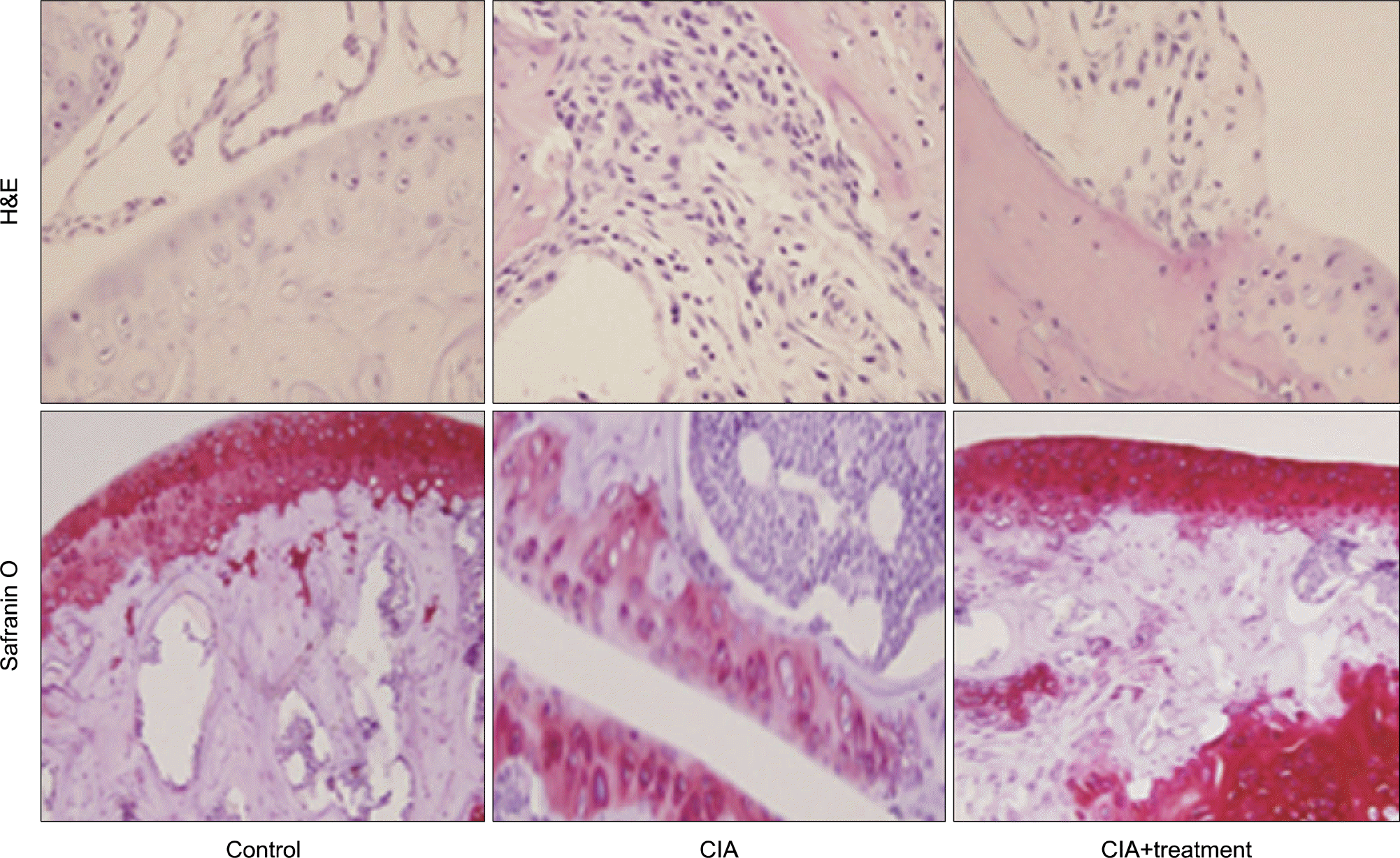
Figure 4.
Analgegic effects of arthritis treated in CIA mice. Arthritis treatment (infliximab and meloxicam) ameliorate mechanical threshold measured to von-Frey filament. Data are expressed as the mean±standard deviation. CIA: type II collagen induced arthritis. ***p<0.001 vs. control group; †† p <0.01 vs. CIA group.
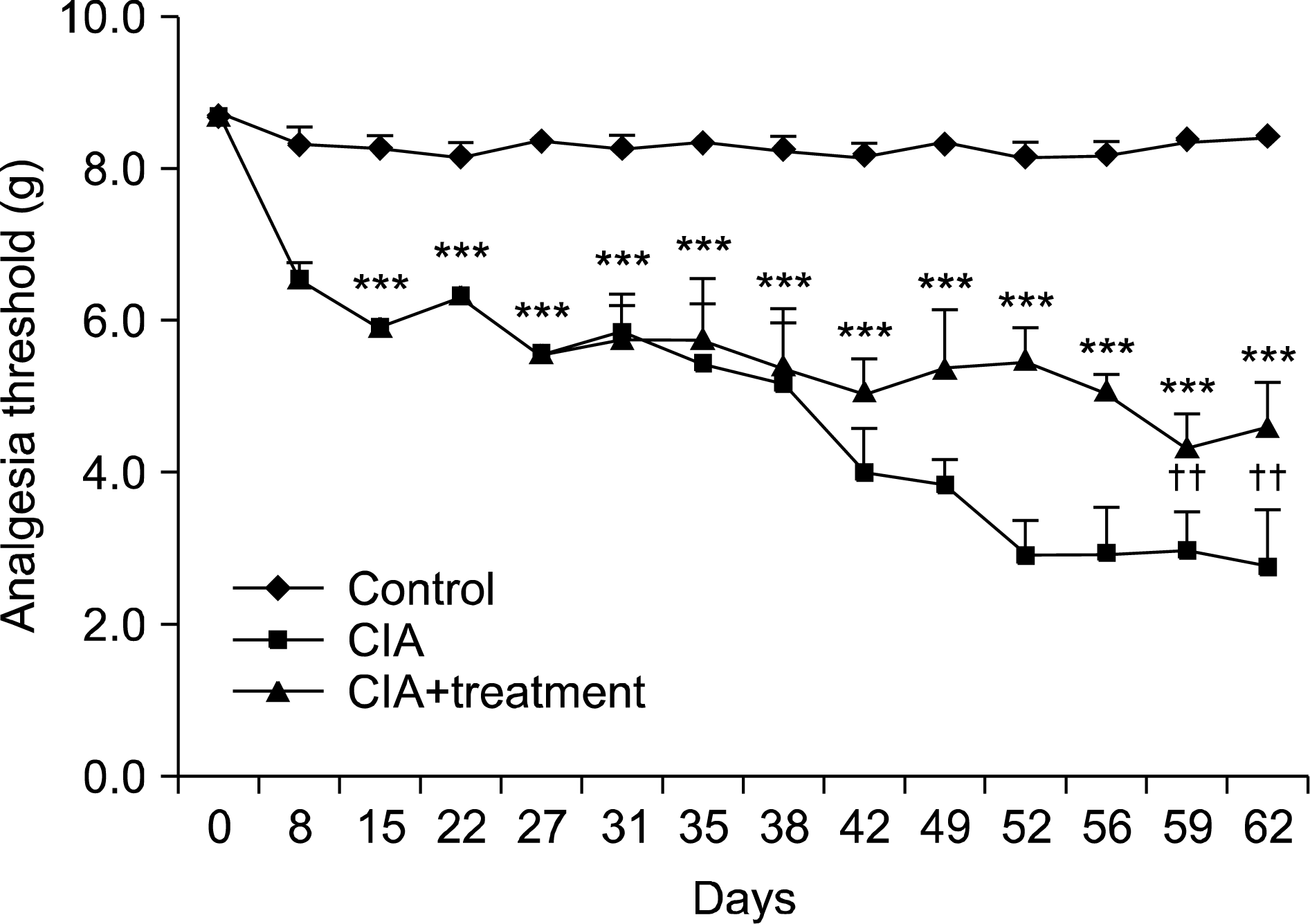
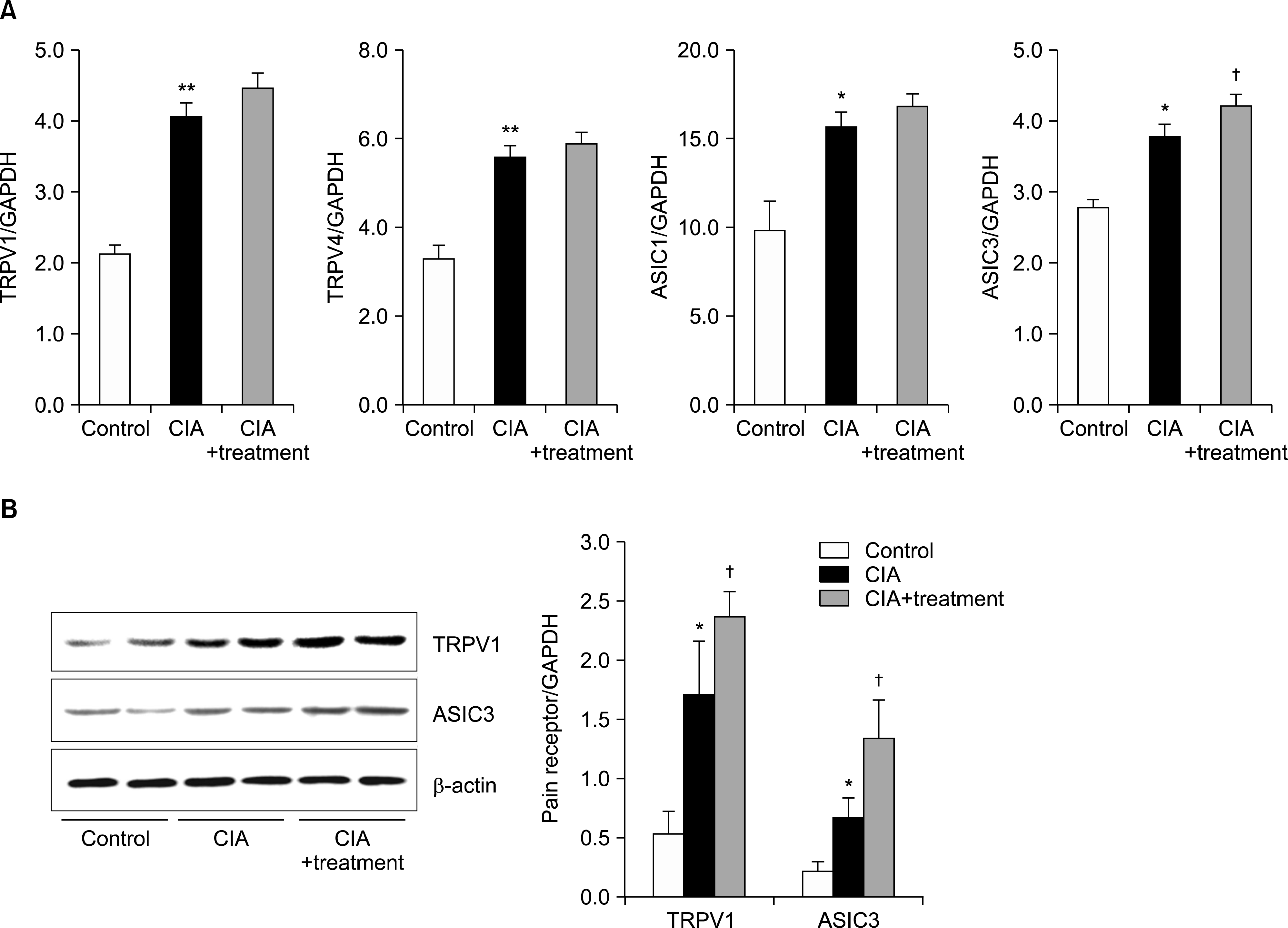
Figure 5.
Expression of pain related ion channel such as TRPV1 and ASIC3 in CIA mice. (A) Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis of TRPV1, TRPV4, ASIC1 and ASIC3 expression in CIA mice. (B) Westernblot analysis of TRPV1 and ASIC3 expression in CIA mice. β-actin was used as a loading control. Results were normalized for β-actin expression. Statistical data repeat of three independent experiments. Values are mean±standard deviation. ASIC: acid-sensing ion channel, CIA: type II collagen induced arthritis, TRPV: transient receptor potential vanilloid. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. control group; † p<0.05 vs. CIA group.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download