Abstract
Behçet's disease (BD) is a multi-systemic inflammatory disease of unknown origin that affects nearly all organs including the nervous system. Although the neurological involvement is less frequent than other major presentations, it is important because it can produce severe disabilities. Peripheral nervous system manifestations are relatively rare in BD. Although few cases of peripheral neuropathy or myopathy have been reported in BD, they are cases of multiple neuropathies, sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy, or neuropathy autonomic dysfunction. Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS), also known as an acute inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, is an acute demyelinating polyradiculopathy of uncertain etiology. No case of GBS associated with BD in Korea has been reported. Herein we report on a patient of BD who suffered from weakness of extremities and was diagnosed as GBS.
REFERENCES
3. Lannuzel A, Lamaury I, Charpentier D, Caparros-Lefebvre D. Neurological manifestations of Behçet's disease in a Caribbean population: clinical and imaging findings. J Neurol. 2002; 249:410–8.

4. Al-Araji A, Kidd DP. Neuro-Behçet's disease: epidemiology, clinical characteristics, and management. Lancet Neurol. 2009; 8:192–204.

5. Altiparmak MR, Pamuk ON, Pamuk GE, Hamuryudan V, Ataman R, Serdengecti K. Colchicine neuromyopathy: a report of six cases. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2002; 20(4 Suppl 26):S13–6.
6. Shugaiv E, Kiyat-Atamer A, Tüzün E, Deymeer F, Oflazer P, Parman Y, et al. Coexistence of Guillain-Barré syndrome and Behçet's disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013; 31(3 Suppl 77):88–9.
7. Kinay D, Bebek N, Vanli E, Gurses C, Gokyigit A, Andermann F. Rasmussen's encephalitis and Behçet's disease: autoimmune disorders in first degree relatives. Epileptic Disord. 2008; 10:319–24.
8. Roh HJ, Ahn MY. Recent concept of Guillain-Barre syndrome. J Soonchunhyang Med Sci. 2009; 15:59–69.
9. Chang HK. New insights on the pathogenesis of Behçet's disease. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2004; 11:193–204.
10. Jung JY, Kim HA, Joo IS, Won JH, Koh BR, Park JJ, et al. Guillain-Barre syndrome, antiphospholipid syndrome and lupus nephritis as initial manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheum Dis. 2012; 19:274–9.

11. Kim HS, Lee SC, Hong HI, Han KH, Lee SK, Kim SS. A case of neuropsychiatric lupus presenting as guillain-barre syndrome and cerebral infarction. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2004; 11:411–6.
Figure 1.
Abnormal nerve conduction velocities and F-wave. (A) Motor nerve conduction velocity of right peroneal nerve. (B) Absent F-wave in right peroneal nerve. (C, D) Absent F-wave in both tibial nerves.
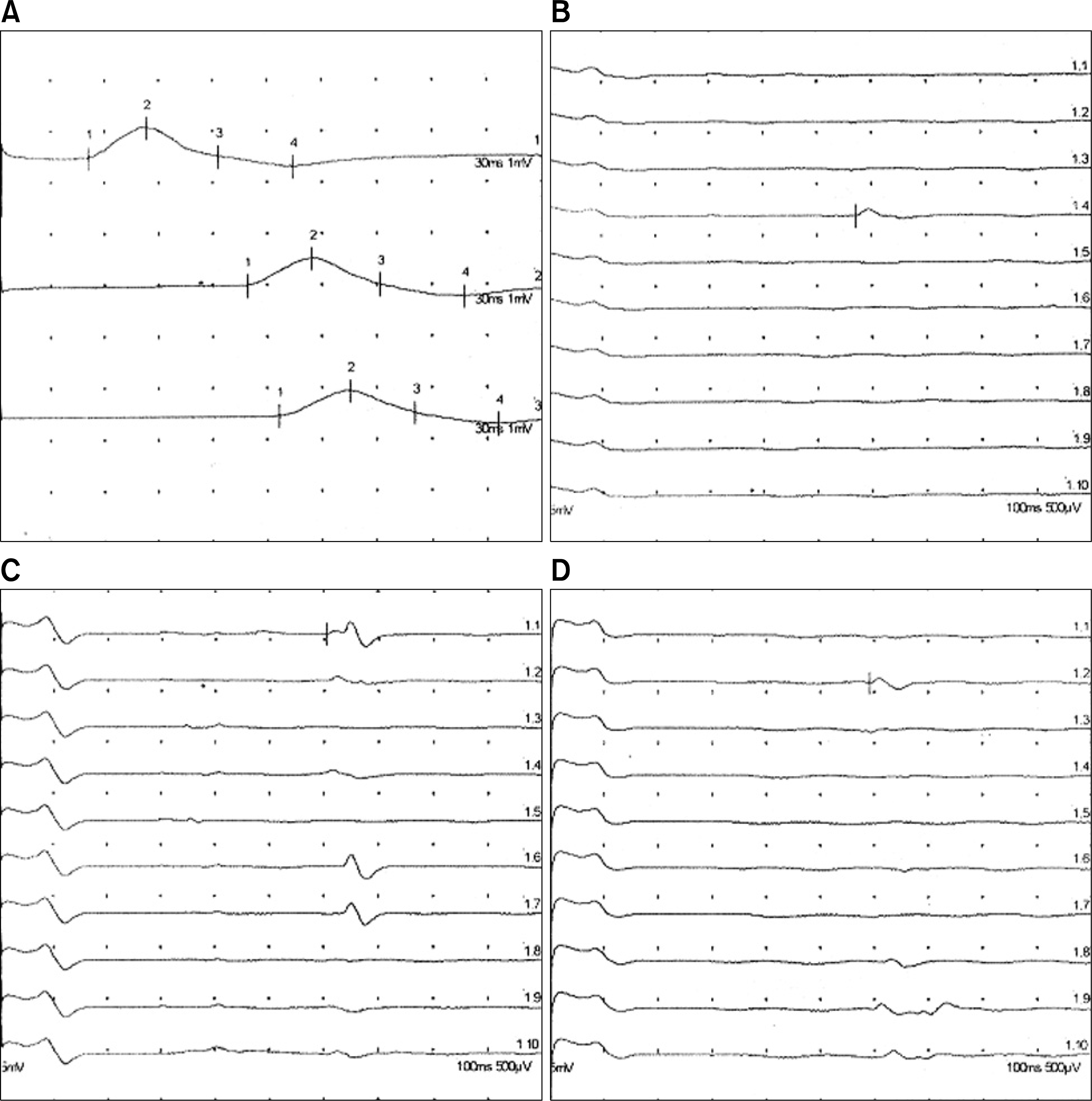
Table 1.
Electrophysiologic findings of the patient




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download