Abstract
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an emerging immunemediated fibro-inflammatory disorder which can involve any organ. The main characteristics of IgG4-RD are increased serum IgG4 concentration, abundant IgG4+ plasma cells in affected tissues, and painless swollen organs often without general symptoms. Typical pathology features of IgG4-RD are lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, dense storiform fibrosis, and obliterative pheblitis. The pathogenesis of IgG4-RD remains elu-sive, but involvement of excess production of type 2 T helper cells, regulatory T-cell cytokines, and B-cell activating factor in the development of IgG4-RD has been suggested. Diagnosis of IgG4-RD can be made on the basis of serological, imaging, particularly histopathological findings. Glucocorticoid is the first-line therapy for patients with multiple organ dysfunction and clinical symptoms. Drugs such as azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, methotrexate, and cyclophosphamide can be used as ste-roid-sparing agents. Rituximab is reported to be an effective therapy for treatment of IgG4-RD, even without concomitant glucocorticoid therapy. This review summarizes current concepts on pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and treatment of IgG4-RD.
REFERENCES
2. Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T, et al. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:732–8.

3. Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003; 38:982–4.

4. Stone JH, Khosroshahi A, Deshpande V, Chan JK, Heathcote JG, Aalberse R, et al. Recommendations for the nomenclature of IgG4-related disease and its individual organ system manifestations. Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 64:3061–7.

5. Uchida K, Masamune A, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K. Prevalence of IgG4-related disease in Japan based on nationwide survey in 2009. Int J Rheumatol. 2012; 2012; 358371.

6. Khosroshahi A, Stone JH. A clinical overview of IgG4-rela-ted systemic disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011; 23:57–66.

7. Tanaka A, Moriyama M, Nakashima H, Miyake K, Hayashida JN, Maehara T, et al. Th2 and regulatory immune reactions contribute to IgG4 production and the initiation of Mikulicz disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 64:254–63.

8. Mahajan VS, Mattoo H, Deshpande V, Pillai SS, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014; 9:315–47.

10. Akiyama M, Suzuki K, Yamaoka K, Yasuoka H, Takeshita M, Kaneko Y, et al. Number of circulating T follicular helper 2 cells correlates with IgG4 and IL-4 levels and plasmablast numbers in IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015 May 18; [Epub].DOI: DOI: 10.1002/art.39209.
11. Della-Torre E, Lanzillotta M, Doglioni C. Immunology of IgG4-related disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015; 181:191–206.

12. Lin W, Jin L, Chen H, Wu Q, Fei Y, Zheng W, et al. B cell subsets and dysfunction of regulatory B cells in IgG4-related diseases and primary Sjögren's syndrome: the similarities and differences. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014; 16:R118.

13. Sellam J, Miceli-Richard C, Gottenberg JE, Ittah M, Lavie F, Lacabaratz C, et al. Decreased B cell activating factor receptor expression on peripheral lymphocytes associated with increased disease activity in primary Sjögren's syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; 66:790–7.
14. Wallace ZS, Mattoo H, Carruthers M, Mahajan VS, Della Torre E, Lee H, et al. Plasmablasts as a biomarker for IgG4-related disease, independent of serum IgG4 concentrations. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015; 74:190–5.

16. Furukawa S, Moriyama M, Tanaka A, Maehara T, Tsuboi H, Iizuka M, et al. Preferential M2 macrophages contribute to fibrosis in IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis, so-called Mikulicz's disease. Clin Immunol. 2015; 156:9–18.

17. Watanabe T, Yamashita K, Fujikawa S, Sakurai T, Kudo M, Shiokawa M, et al. Involvement of activation of toll-like receptors and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors in enhanced IgG4 responses in autoimmune pancreatitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012; 64:914–24.

18. Khoury P, Grayson PC, Klion AD. Eosinophils in vasculitis: characteristics and roles in pathogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014; 10:474–83.

19. Padigel UM, Hess JA, Lee JJ, Lok JB, Nolan TJ, Schad GA, et al. Eosinophils act as antigen-presenting cells to induce immunity to Strongyloides stercoralis in mice. J Infect Dis. 2007; 196:1844–51.
20. Watanabe T, Yamashita K, Sakurai T, Kudo M, Shiokawa M, Uza N, et al. Toll-like receptor activation in basophils contributes to the development of IgG4-related disease. J Gastroenterol. 2013; 48:247–53.

21. Bindon CI, Hale G, Brüggemann M, Waldmann H. Human monoclonal IgG isotypes differ in complement activating function at the level of C4 as well as C1q. J Exp Med. 1988; 168:127–42.

22. Fellrath JM, Kettner A, Dufour N, Frigerio C, Schneeberger D, Leimgruber A, et al. Allergen-specific T-cell tolerance induction with allergen-derived long synthetic peptides: results of a phase I trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:854–61.

23. Nouri-Aria KT, Wachholz PA, Francis JN, Jacobson MR, Walker SM, Wilcock LK, et al. Grass pollen immunotherapy induces mucosal and peripheral IL-10 responses and blocking IgG activity. J Immunol. 2004; 172:3252–9.

24. Saeki T, Nishi S, Imai N, Ito T, Yamazaki H, Kawano M, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2010; 78:1016–23.

25. Detlefsen S, Bräsen JH, Zamboni G, Capelli P, Klöppel G. Deposition of complement C3c, immunoglobulin (Ig)G4 and IgG at the basement membrane of pancreatic ducts and acini in autoimmune pancreatitis. Histopathology. 2010; 57:825–35.

26. Cornell LD, Chicano SL, Deshpande V, Collins AB, Selig MK, Lauwers GY, et al. Pseudotumors due to IgG4 immune-complex tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with autoimmune pancreatocentric disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007; 31:1586–97.

27. Holland M, Hewins P, Goodall M, Adu D, Jefferis R, Savage CO. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasm antibody IgG subclasses in Wegener's granulomatosis: a possible pathogenic role for the IgG4 subclass. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004; 138:183–92.

28. Green MG, Bystryn JC. Effect of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy on serum levels of IgG1 and IgG4 anti-desmoglein 1 and antidesmoglein 3 antibodies in pemphi-gus vulgaris. Arch Dermatol. 2008; 144:1621–4.

29. Saeki T, Ito T, Youkou A, Ishiguro H, Sato N, Yamazaki H, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura in IgG4-rela-ted disease with severe deficiency of ADAMTS-13 activity and IgG4 autoantibody against ADAMTS-13. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011; 63:1209–12.

30. Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, Yi EE, Sato Y, Yoshino T, et al. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25:1181–92.

31. Deshpande V. The pathology of IgG4-related disease: critical issues and challenges. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012; 29:191–6.

32. Deshpande V, Khosroshahi A, Nielsen GP, Hamilos DL, Stone JH. Eosinophilic angiocentric fibrosis is a form of IgG4-related systemic disease. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011; 35:701–6.

33. Deshpande V, Gupta R, Sainani N, Sahani DV, Virk R, Ferrone C, et al. Subclassification of autoimmune pancreatitis: a histologic classification with clinical significance. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011; 35:26–35.
34. Kamisawa T, Takuma K, Egawa N, Tsuruta K, Sasaki T. Autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-related sclerosing disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 7:401–9.

35. Kamisawa T, Chen PY, Tu Y, Nakajima H, Egawa N, Tsuruta K, et al. Pancreatic cancer with a high serum IgG4 concentration. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:6225–8.

36. Sah RP, Chari ST, Pannala R, Sugumar A, Clain JE, Levy MJ, et al. Differences in clinical profile and relapse rate of type 1 versus type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2010; 139:140–8.

37. Kim JH, Kim MH, Byun JH, Lee SS, Lee SJ, Park SH, et al. Diagnostic strategy for differentiating autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer: is an endoscopic retrograde pancreatography essential? Pancreas. 2012; 41:639–47.
38. Uehara T, Masumoto J, Yoshizawa A, Kobayashi Y, Hamano H, Kawa S, et al. IgG4-related disease-like fibrosis as an indicator of IgG4-related lymphadenopathy. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2013; 17:416–20.

39. Himi T, Takano K, Yamamoto M, Naishiro Y, Takahashi H. A novel concept of Mikulicz's disease as IgG4-related disease. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2012; 39:9–17.

40. Yao Q, Wu G, Hoschar A. IgG4-related Mikulicz's disease is a multiorgan lymphoproliferative disease distinct from Sjögren's syndrome: a Caucasian patient and literature review. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013; 31:289–94.
41. Furukawa S, Moriyama M, Kawano S, Tanaka A, Maehara T, Hayashida JN, et al. Clinical relevance of Küttner tumour and IgG4-related dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis. Oral Dis. 2015; 21:257–62.
44. Sato Y, Inoue D, Asano N, Takata K, Asaoku H, Maeda Y, et al. Association between IgG4-related disease and progressively transformed germinal centers of lymph nodes. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25:956–67.

45. Ferry JA. IgG4-related lymphadenopathy and IgG4-related lymphoma: moving targets. Diagn Histopathol. 2013; 19:128–39.

46. Hicks J, Flaitz C. Progressive transformation of germinal centers: review of histopathologic and clinical features. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2002; 65:195–202.

47. Grimm KE, Barry TS, Chizhevsky V, Hii A, Weiss LM, Siddiqi IN, et al. Histopathological findings in 29 lymph node biopsies with increased IgG4 plasma cells. Mod Pathol. 2012; 25:480–91.

49. Saeki T, Kawano M, Mizushima I, Yamamoto M, Wada Y, Nakashima H, et al. The clinical course of patients with IgG4-related kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2013; 84:826–33.

50. Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H, Nishi S, Yamaguchi Y, Hisano S, et al. Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-rela-ted kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2011; 15:615–26.

51. Yamaguchi Y, Kanetsuna Y, Honda K, Yamanaka N, Kawano M, Nagata M. Japanese Study Group on IgG4-related nephropathy. Characteristic tubulointerstitial nephritis in IgG4-related disease. Hum Pathol. 2012; 43:536–49.

52. Khosroshahi A, Ayalon R, Beck LH Jr, Salant DJ, Bloch DB, Stone JH. IgG4-related disease is not associated with anti-body to the phospholipase A2 receptor. Int J Rheumatol. 2012; 2012; 139409.

53. Wallace ZS, Deshpande V, Stone JH. Ophthalmic manifestations of IgG4-related disease: single-center experience and literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014; 43:806–17.

54. Suzuki M, Nakamaru Y, Akazawa S, Mizumachi T, Maeda M, Takagi D, et al. Nasal manifestations of immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Laryngoscope. 2013; 123:829–34.

55. Takagi D, Nakamaru Y, Fukuda S. Otologic manifestations of immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2014; 123:420–4.

56. Deshpande V, Huck A, Ooi E, Stone JH, Faquin WC, Nielsen GP. Fibrosing variant of Hashimoto thyroiditis is an IgG4 related disease. J Clin Pathol. 2012; 65:725–8.

57. Watanabe T, Maruyama M, Ito T, Fujinaga Y, Ozaki Y, Maruyama M, et al. Clinical features of a new disease concept, IgG4-related thyroiditis. Scand J Rheumatol. 2013; 42:325–30.

58. Zen Y, Inoue D, Kitao A, Onodera M, Abo H, Miyayama S, et al. IgG4-related lung and pleural disease: a clinicopathologic study of 21 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009; 33:1886–93.

59. Ryu JH, Sekiguchi H, Yi ES. Pulmonary manifestations of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease. Eur Respir J. 2012; 39:180–6.

60. Kasashima S, Zen Y, Kawashima A, Endo M, Matsumoto Y, Kasashima F, et al. A clinicopathologic study of immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease of the thoracic aorta. J Vasc Surg. 2010; 52:1587–95.

61. Inokuchi G, Hayakawa M, Kishimoto T, Makino Y, Iwase H. A suspected case of coronary periarteritis due to IgG4-related disease as a cause of ischemic heart disease. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2014; 10:103–8.

63. Zen Y, Kasashima S, Inoue D. Retroperitoneal and aortic manifestations of immunoglobulin G4-related disease. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012; 29:212–8.

64. Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Stone JH, Shinagare S, Sainani N, Hasserjian RP, et al. Rethinking Ormond's disease: “idiopathic” retroperitoneal fibrosis in the era of IgG4-related disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2013; 92:82–91.
65. Stone JH. L45. Aortitis, retroperitoneal fibrosis, and IgG4-related disease. Presse Med. 2013; 42:622–5.

66. Castelein T, Coudyzer W, Blockmans D. IgG4-related periaortitis vs idiopathic periaortitis: is there a role for atherosclerotic plaque in the pathogenesis of IgG4-related periaortitis? Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015; 54:1250–6.
67. Brito-Zerón P, Ramos-Casals M, Bosch X, Stone JH. The clinical spectrum of IgG4-related disease. Autoimmun Rev. 2014; 13:1203–10.

68. Kamisawa T, Nakajima H, Egawa N, Funata N, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A. IgG4-related sclerosing disease incorporating sclerosing pancreatitis, cholangitis, sialadenitis and retroperitoneal fibrosis with lymphadenopathy. Pancreatology. 2006; 6:132–7.

69. Lu LX, Della-Torre E, Stone JH, Clark SW. IgG4-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis: clinical features, diagnostic criteria, and treatment. JAMA Neurol. 2014; 71:785–93.
70. Bando H, Iguchi G, Fukuoka H, Taniguchi M, Yamamoto M, Matsumoto R, et al. The prevalence of IgG4-related hypophysitis in 170 consecutive patients with hypopituitarism and/or central diabetes insipidus and review of the literature. Eur J Endocrinol. 2013; 170:161–72.

71. Pieringer H, Parzer I, Wöhrer A, Reis P, Oppl B, Zwerina J. IgG4-related disease: an orphan disease with many faces. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014; 9:110.

72. Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22:21–30.

73. Okazaki K, Umehara H. Are classification criteria for IgG4-RD now possible? The concept of IgG4-related disease and proposal of comprehensive diagnostic criteria in Japan. Int J Rheumatol. 2012; 2012; 357071.

74. Ryu JH, Horie R, Sekiguchi H, Peikert T, Yi ES. Spectrum of disorders associated with elevated serum IgG4 levels encountered in clinical practice. Int J Rheumatol. 2012; 2012; 232960.

75. Boonstra K, Culver EL, de Buy Wenniger LM, van Heerde MJ, van Erpecum KJ, Poen AC, et al. Serum immunoglobulin G4 and immunoglobulin G1 for distinguishing immunoglobulin G4-associated cholangitis from primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 2014; 59:1954–63.

76. Ohshima K, Sato Y, Yoshino T. A case of IgG4-related dacryoadenitis that regressed without systemic steroid administration. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2013; 53:53–6.

77. Stone JH. IgG4-related disease: nomenclature, clinical features, and treatment. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2012; 29:177–90.

78. Shimizu Y, Yamamoto M, Naishiro Y, Sudoh G, Ishigami K, Yajima H, et al. Necessity of early intervention for IgG4-related disease: delayed treatment induces fibrosis progression. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013; 52:679–83.
79. Della-Torre E, Feeney E, Deshpande V, Mattoo H, Mahajan V, Kulikova M, et al. B-cell depletion attenuates serological biomarkers of fibrosis and myofibroblast activation in IgG4-related disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Aug 20; [Epub].DOI: DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205799.

Figure 1.
immunoglobulin G (IgG)4 Fab-arm exchange makes bispecific antibodies. The heavy chains of IgG are bound to each other by interchain disulfide bridge. As the disulfide bonds between heavy chains of IgG4 are unstable, IgG4 easily forms intrachain disulfide bonds in the hinge region. Intrachain disulfide bond of IgG4 is linked by noncovalent interaction. When the non-con-valent bonds dissociate, half of one IgG4 molecule (a heavy chain-light chain pair) and half of another IgG4 molecule exchange randomly, forming a Fab-arm exchange. Through such processes, the IgG4 molecule becomes bispecific by acquiring two Fab-arms with different epitope specificity. This bispecific IgG4 molecule, however, loses its ability to form immune complexes as the molecules cannot crosslink antigens.
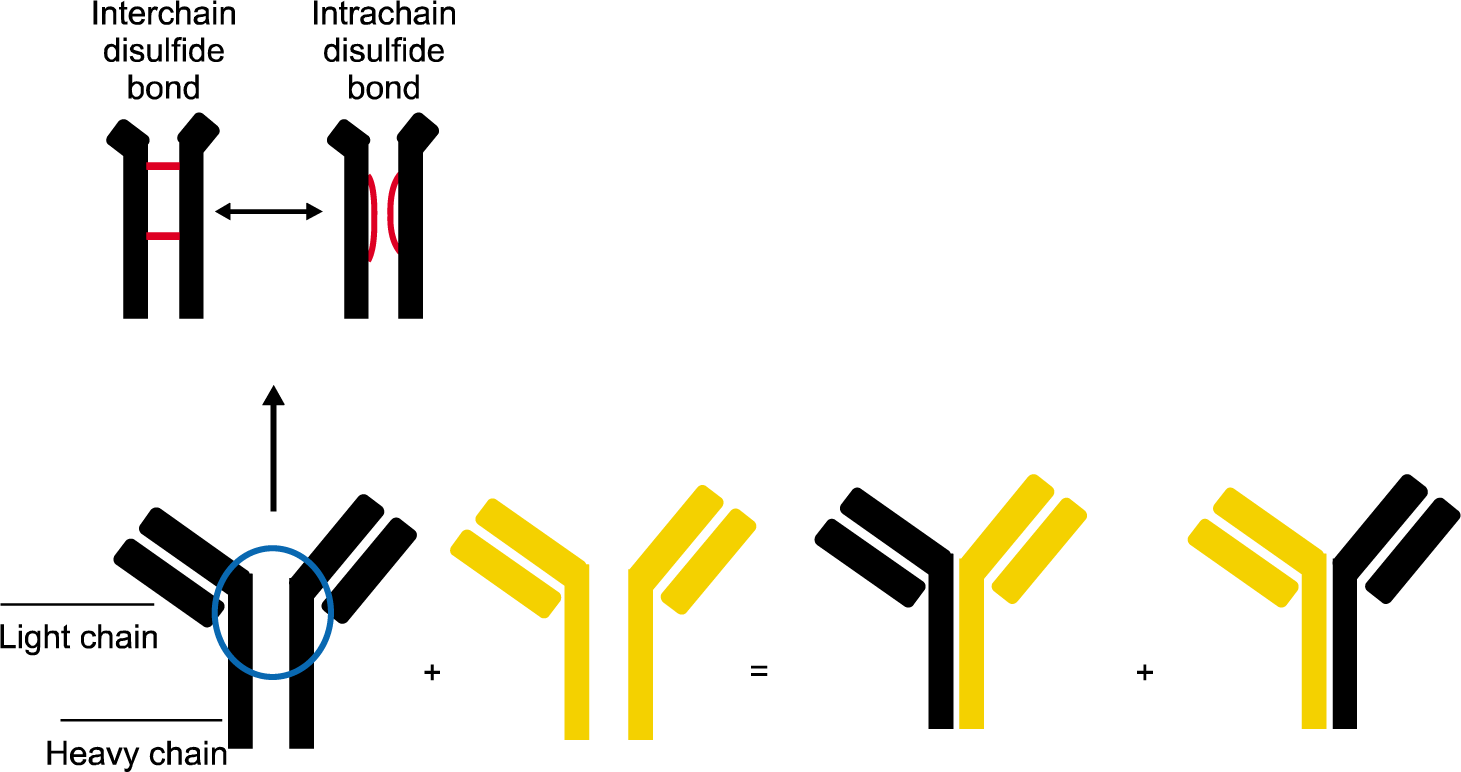
Figure 2.
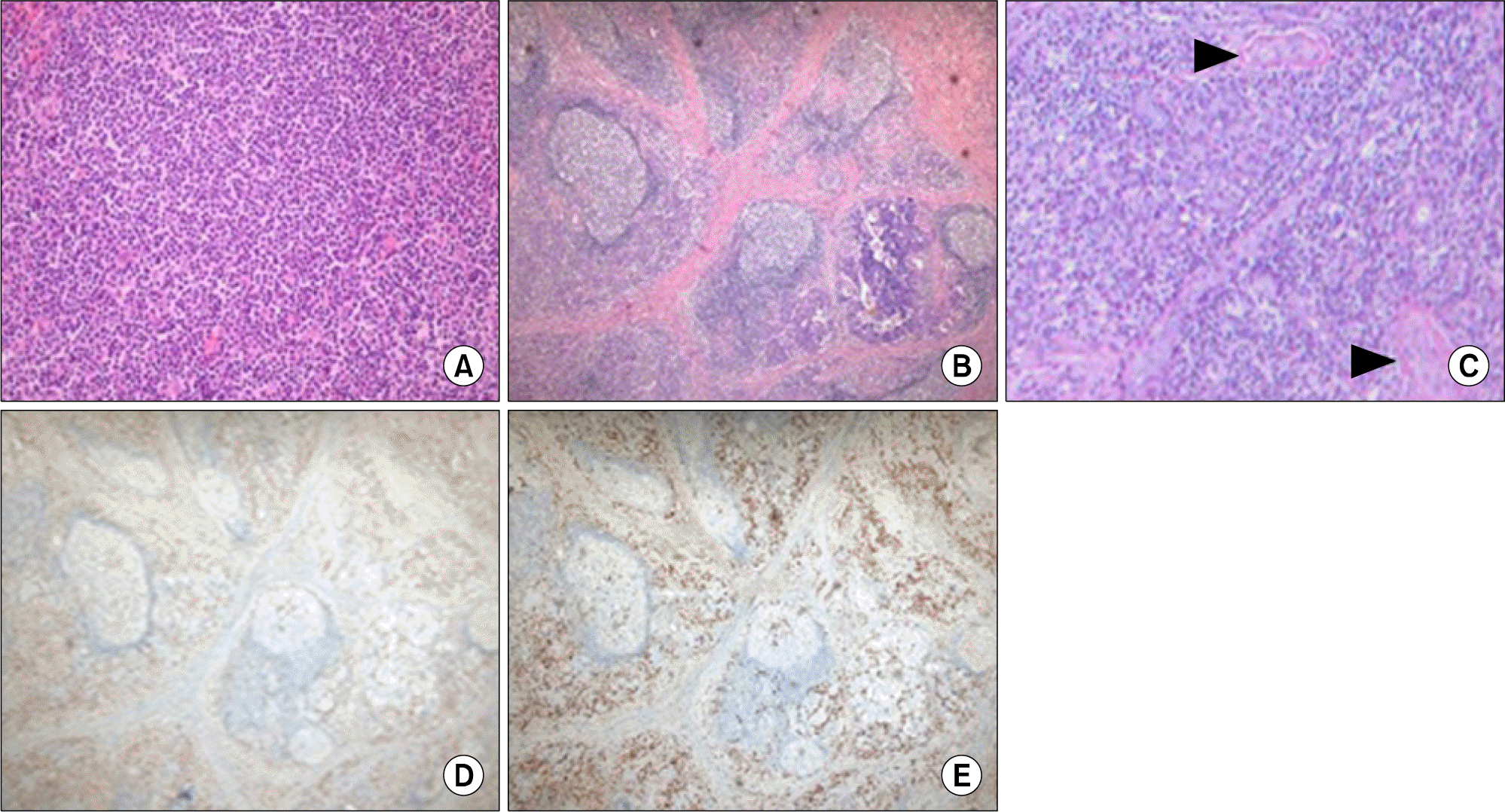
Histological and immunohistochemical findings of biopsy specimens of the lymph node (A) and submandibular gland (B∼E). (A) The germinal centersare predominantly composed of small lymphocytes, centrocytes, centroblasts, and numerous mature plasma cells (H&E, ×200). (B) The storiform pattern of fibrosis is present, indicating dense fibrosis within which lymphocytes, plasma cells, and occasional eosinophils are embedded (H&E, ×100). (C) Veins occluded by inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes and plasma cells are noted (arrowheads) (H&E, ×200). (D, E) The IgG4+/IgG+ plasma cell ratio is estimated at 90%. D: Immunoglobulin (Ig) G-immunohistochemical stain, E: IgG4-immunohistochemical stain; ×100.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download