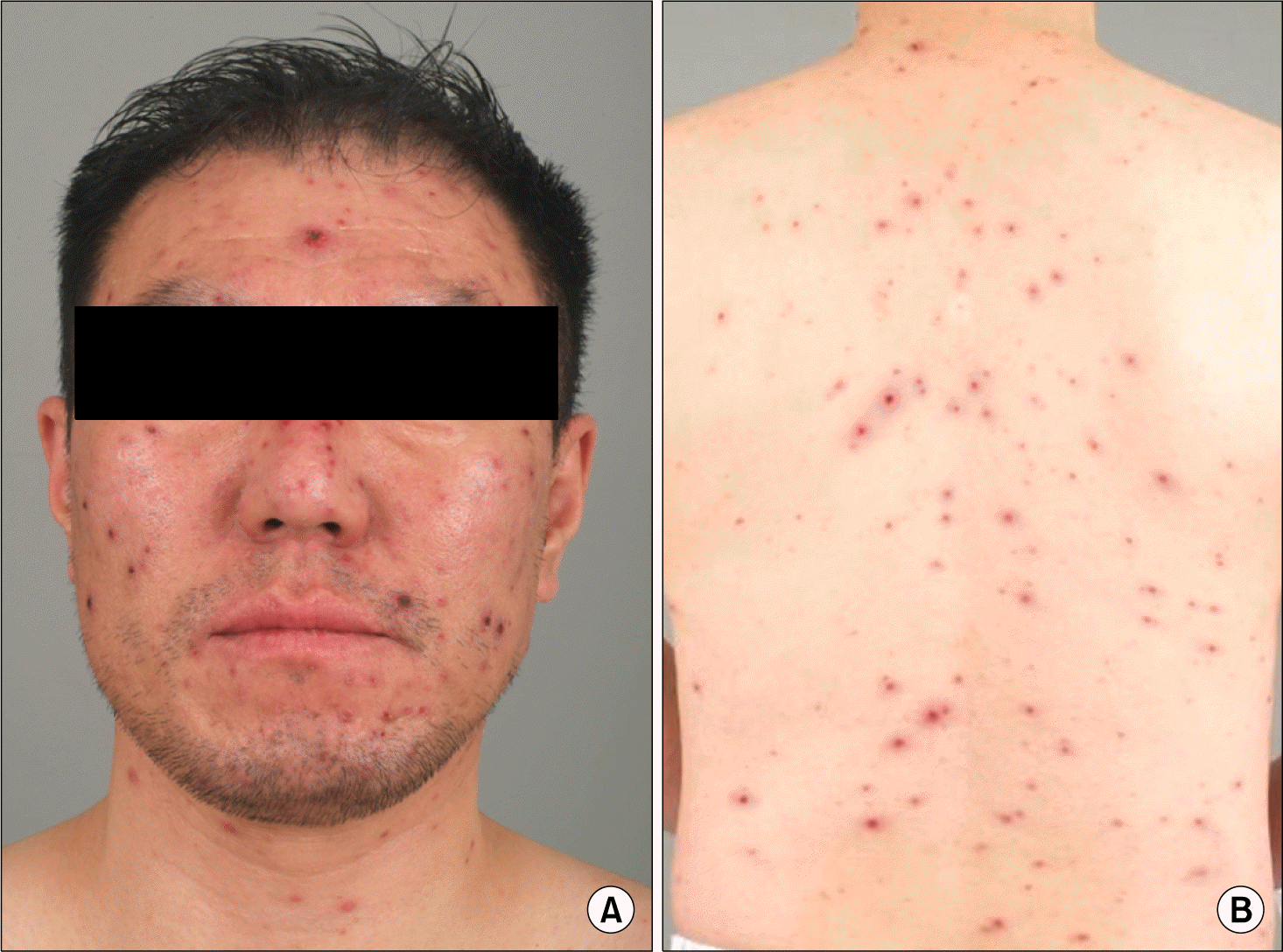
Abstract
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) inhibitors are increasingly used in treatment of inflammatory disorders because of their immunomodulatory efficacy. Increased risk of infection is an adverse effect of anti-TNF-α therapy. The incidence rate and severity of herpes zoster is significantly higher in patients on anti-TNF-α therapy than in the general population. The clinical presentation of varicella zoster virus infection is also often atypical in these patients. We experienced a patient who presented with a disseminated varicelliform rash while on etanercept therapy for ankylosing spondylitis.
REFERENCES
1. Tracey D, Klareskog L, Sasso EH, Salfeld JG, Tak PP. Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther. 2008; 117:244–79.

2. Strangfeld A, Listing J, Herzer P, Liebhaber A, Rockwitz K, Richter C, et al. Risk of herpes zoster in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF-alpha agents. JAMA. 2009; 301:737–44.
3. Salmon-Ceron D, Tubach F, Lortholary O, Chosidow O, Bretagne S, Nicolas N, et al. RATIO group. Drug-specific risk of non-tuberculosis opportunistic infections in patients receiving anti-TNF therapy reported to the 3-year prospective French RATIO registry. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011; 70:616–23.

5. Kim SY, Solomon DH. Tumor necrosis factor blockade and the risk of viral infection. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010; 6:165–74.

6. Wung PK, Holbrook JT, Hoffman GS, Tibbs AK, Specks U, Min YI, et al. WGET Research Group. Herpes zoster in immunocompromised patients: incidence, timing, and risk factors. Am J Med. 2005; 118:1416.

7. Kim HO, Kang KY, Ju JH, Kim HY, Park SH. The incidence of serious infection among rheumatoid arthritis patients exposed to tumor necrosis factor antagonists. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2010; 17:246–53.

8. Ito M, Nakano T, Kamiya T, Kitamura K, Ihara T, Kamiya H, et al. Effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha on replication of varicella-zoster virus. Antiviral Res. 1991; 15:183–92.

9. Torigo S, Ihara T, Kamiya H. IL-12, IFN-gamma, and TNF-alpha released from mononuclear cells inhibit the spread of varicella-zoster virus at an early stage of varicella. Microbiol Immunol. 2000; 44:1027–31.
10. Shale MJ. The implications of anti-tumour necrosis factor therapy for viral infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Br Med Bull. 2009; 92:61–77.

11. Ramiro S, Gaujoux-Viala C, Nam JL, Smolen JS, Buch M, Gossec L, et al. Safety of synthetic and biological DMARDs: a systematic literature review informing the 2013 update of the EULAR recommendations for management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 73:529–35.

12. Jain A, Singh JA. Harms of TNF inhibitors in rheumatic diseases: a focused review of the literature. Immunotherapy. 2013; 5:265–99.

13. Merselis JG Jr, Kaye D, Hook EW. Disseminated herpes zoster. a report of 17 cases. Arch Intern Med. 1964; 113:679–86.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download